Eloquent是laravel中的orm,采取的是active record的设计模式,里面的对象不仅包括领域逻辑,还包括了数据库操作,但是大家平时使用的时候可能没有探究eloquent是怎么设计的,active record这种模式的优缺点等问题,下面我会带领大家从头开始看看Eloquent是如何设计并实现的。
本文是orm系列的第二篇,也是Eloquent演化的第一篇,Eloquent系列会尝试着讲清楚Eloquent是如何一步一步演化到目前功能强大的版本的,但是毕竟个人能力有限,不可能分析的非常完善,总会有不懂的地方,所以讲的不错误的地方,恳请大牛们能指出,或者如果你有什么地方是没看懂的,也请指出问题来,因为可能那地方就是我自己没看懂,所以没讲明白,也请提出来,然后我们一起讨论的,让我们能共同的进步的。
初始化
Eloquent首先要对数据库连接做抽象,于是有了Connection类,内部主要是对PDO的一个封装,但是如果只有Connection的话,一个问题是,我们需要直面sql,于是就有了Builder类,其功能就是屏蔽sql,让我们能用面向对象的方式来完成sql的查询功能,Builder应该是sql builder,此时Eloquent的主要的类就如下:
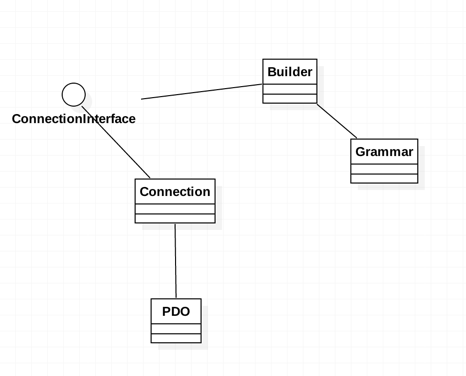
其中Builder负责sql的组装,Connection负责具体的数据库交互,其中多出来一个Grammar,其负责主要是负责将Builder里面存储的数据转化为sql。
note:此处版本是54d73c6,通过 git co 54d73c6 可以查看
model引入
接着我们继续演化,要引进Model,要实现Active Record模式,在46966ec中首次加入了Eloquent/Model类,有兴趣的同学可以git co 46966ec查看,刚提交上来的时候,Model类中大概如下:
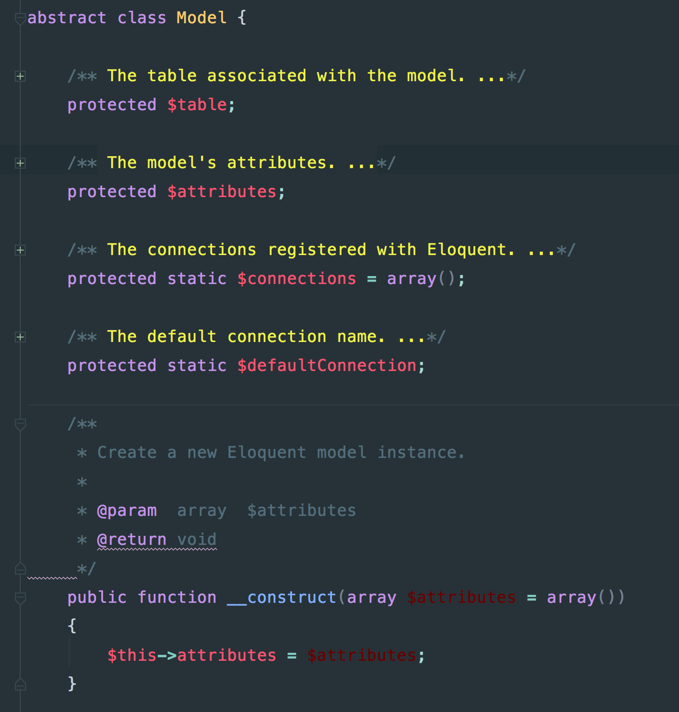
可以看到属性通过定义table,connection,将具体的数据库操作是委托给了connection类,然后Model自己是负责领域逻辑,同时会定义一些静态方法,如create,find,save,充当了Row Data Gateway角色,此时的类图如下:
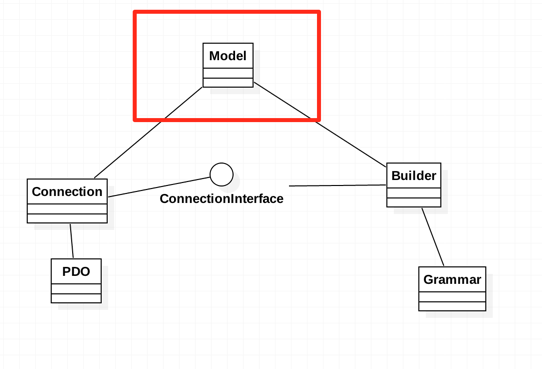
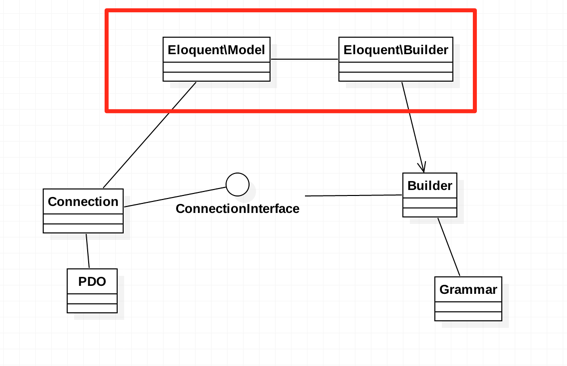
此时新增的Model类直接依赖于Connection和Builder,带来的问题是耦合,于是就有了一个改动,在Model同一层级上引入了一新的Builder,具体通过git co c420bd8查看。
use Illuminate\Database\Query\Builder as BaseBuilder;
class Builder extends BaseBuilder {
/**
* The model being queried.
*
* @var Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model
*/
protected $model;
....
}里面具体就是在基础BaseBuilder上通过Model来获取一些信息设置,譬如$this->from($model->getTable())这种操作,还有一个好处是保持了BaseBuilder的纯净,没有形成Model和BaseBuilder之间的双向依赖,通过Model同层的Builder来去耦合,如下图所示:
relation进入
下一步是要引入1-1,1-N,N-N的关系了,可以通过git co 912de03查看,此时一个新增的类的情况如下:
├── Builder.php
├── Model.php
└── Relations
├── BelongsTo.php
├── BelongsToMany.php
├── HasMany.php
├── HasOne.php
├── HasOneOrMany.php
└── Relation.php其中Relation是基类,然后其他的几个都继承它。
此时关系处理上主要的逻辑是调用Model的HasOne等表关系的方法,返回Relation的子类,然后通过Relation来处理进而返回数据,这么说可能有点绕,我们下面具体介绍下每个关系的实现,大家可能就理解了。
先看HasOne,即OneToOne的关系,看代码
public function hasOne($related, $foreignKey = null)
{
$foreignKey = $foreignKey ?: $this->getForeignKey();
$instance = new $related;
return new HasOne($instance->newQuery(), $this, $foreignKey);
}我们看到当调用Model的hasOne方法后,返回是一个HasOne,即Relation,当我们调用Relation的方法时,是怎么处理的呢?通过魔术方法__call,将其委托给了Eloquent\Builder,
public function __call($method, $parameters)
{
if (method_exists($this->query, $method))
{
return call_user_func_array(array($this->query, $method), $parameters);
}
throw new \BadMethodCallException("Method [$method] does not exist.");
}即其实Relation是对Eloquent\Builder的一个封装,支持面向对象式的sql操作,我们下面来看下当我们使用HasOne的时候发生了什么。
假设我们有个User,Phone,然后User和Phone的关系是HasOne,在User声明上就会有
class User extends Model
{
/**
* Get the phone record associated with the user.
*/
public function phone()
{
return $this->hasOne('App\Phone');
}
}此时HasOne的构造函数如下:
// builder是Eloquent\Builder, parent是Uer,$foreign_key是user_id
$relation = new HasOne($builder, $parent, $foreign_key);当使用User::with('phone')->get()的时候,就会去eager load进phone了,具体的过程中,在调用Eloquent\Builder的get的时候,里面有个逻辑是:
if (count($models) > 0)
{
$models = $this->eagerLoadRelations($models);
}获取has one关系,我们跟着看到代码,会调用到函数eagerLoadRelation,具体看代码:
protected function eagerLoadRelation(array $models, $relation, Closure $constraints)
{
$instance = $this->getRelation($relation);
...
$instance->addEagerConstraints($models);
$models = $instance->initializeRelation($models, $relation);
$results = $instance->get();
return $instance->match($models, $results, $relation);
}其中getRelation会调用到User()->phone(),即此处$instance是HasOne,接着调用HasOne->addEagerConstraints()和HasOne->initializeRelation(),具体的代码是:
// class HasOne
public function addEagerConstraints(array $models)
{
// 新增foreignKey的条件
$this->query->whereIn($this->foreignKey, $this->getKeys($models));
}
public function initRelation(array $models, $relation)
{
foreach ($models as $model)
{
$model->setRelation($relation, null);
}
return $models;
}
// class Model
public function setRelation($relation, $value)
{
$this->relations[$relation] = $value;
}最后调用match方法,就是正确的给每个model设置好relation关系。
以上就是我们分析的HasOne的实现,其他的关系都类似,此处不再重复,然后eager load的含义是指,当我们要加载多个数据的时候,我们尽可能用一条sql解决,而不是多条sql,具体来说如果我们有多个Users,需要加载Phones的,如果不采用eager,在每个sql就是where user_id=?,而eager模式则是where user_id in (?,?,?),这样差异就很明显了.
note:以上分析的代码是:git co f6e2170
讲到这,我们列举下对象之间的关系
One-To-One
User 和 Phone的1对1的关系,
class User extends Model
{
/**
* Get the phone record associated with the user.
*/
public function phone()
{
return $this->hasOne('App\Phone');
}
}
// 逆向定义
class Phone extends Model
{
/**
* Get the user that owns the phone.
*/
public function user()
{
return $this->belongsTo('App\User');
}
}sql的查询类似于下面
select id from phone where user_id in (1)
select id from user where id in (phone.user_id)One-To-Many
以Post和Comment为例,一个Post会有多个Comment
class Post extends Model
{
/**
* Get the comments for the blog post.
*/
public function comments()
{
return $this->hasMany('App\Comment');
}
}
// reverse
class Comment extends Model
{
/**
* Get the post that owns the comment.
*/
public function post()
{
return $this->belongsTo('App\Post');
}
}此处的sql和HasOne一致
select id from comment where post_id in (1)
select id from post where id in (comment.post_id)Many To Many
以user和role为例,一个用户会有不同的角色,一个角色也会有不同的人,这个时候就需要一张中间表role_user,代码声明上如下:
class User extends Model
{
/**
* The roles that belong to the user.
*/
public function roles()
{
return $this->belongsToMany('App\Role');
}
}
class Role extends Model
{
/**
* The users that belong to the role.
*/
public function users()
{
return $this->belongsToMany('App\User');
}
}这个关系我们稍微具体讲下,我们在使用上可能会是下面这样子的
return $this->belongsToMany('App\Role', 'user_roles', 'user_id', 'role_id');在构造函数中,会调用addConstraints方法,如下
// class belongsToMany
public function addConstraints()
{
$this->setSelect()->setJoin()->setWhere();
}此处会预先设置setSelect()->setJoin()->setWhere(),作用分别是:
setSelect() : 在select的字段中新增 role.*,user_role.id as pivot_id
setJoin():新增join, join user_role on role.id = user_role.role_id,联合查询
setWhere():新增 user_id = ?
查询的表是role,join表user_role
在get的时候,其逻辑和HasOne等关系也所有不同,代码如下:
// class belongsToMany
public function get($columns = array('*'))
{
$models = $this->query->getModels($columns);
$this->hydratePivotRelation($models);
if (count($models) > 0)
{
$models = $this->query->eagerLoadRelations($models);
}
return new Collection($models);
}此处有个方法叫hydratePivotRelation,我们进入看下到底是怎么回事
// class belongsToMany
protected function hydratePivotRelation(array $models)
{
// 将中间记录取出来,设置属性pivot为Model pivot
foreach ($models as $model)
{
$values = $this->cleanPivotAttributes($model);
$pivot = $this->newExistingPivot($values);
$model->setRelation('pivot', $pivot);
}
}其实做的事情就是设置了Role的pivot属性。
到这,我们就分析完了eloquent在f6e2170版本上具有的功能了,到目前为止,eloquent的类图如下:
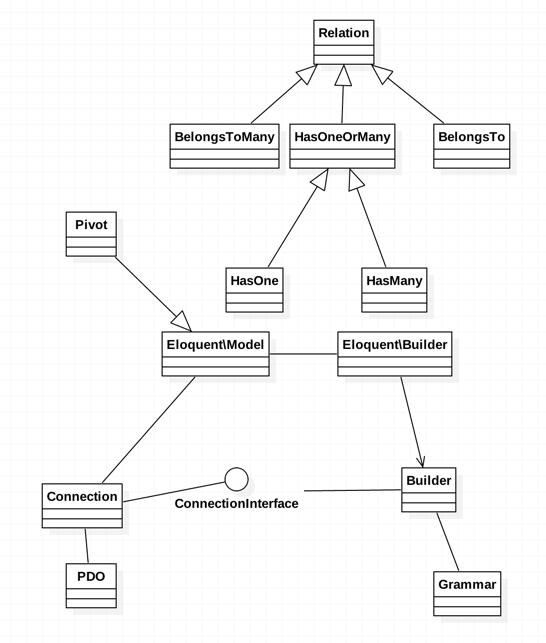
总结
目前,我们分析到的版本是f6e2170,已经具备了一个orm该需要的功能了,Connection负责数据库操作,Builder负责面向对象的sql操作,Grammar负责sql的拼装,Eloquent/Model是Active Record模式的核心Model,同时具备领域逻辑和数据库操作功能,其中数据库操作功能是委托给了Eloquent/Builder,同时我们也定义了对象的3种关系,1-1,1-N,N-N,下一阶段,Eloquent将会实现migrations or database modification logic的功能,尽情期待。
这是orm的第二篇,你的鼓励是我继续写下去的动力,期待我们共同进步。
