事件分发的案例
案例说明:
- LinearLayout 下面有3个recyclerView
- 当手指在屏幕的中间上半屏滑动的时候,3个recyclerView会一起滑动
- 当手指在屏幕的下半屏滑动的饿时候,各自区域的recyclerView单独滑动
先看下 效果图:
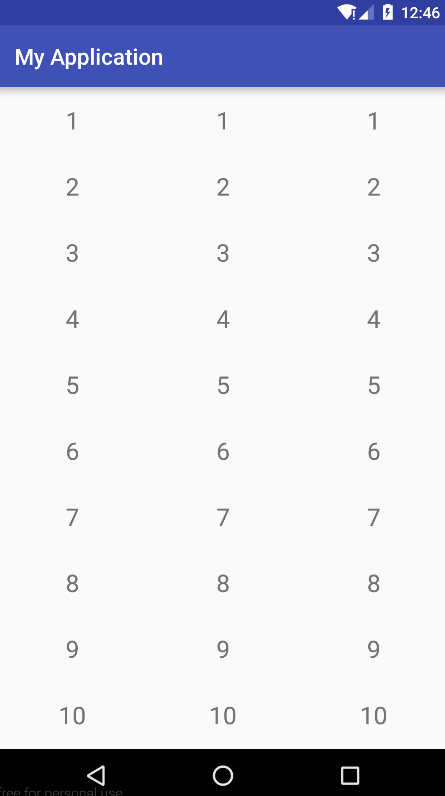
代码说明:
需要重写LinearLayout:
public class MyLinearlayout extends LinearLayout {
public MyLinearlayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
@Override
public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
return super.dispatchTouchEvent(ev);
}
@Override
public boolean onInterceptTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
//屏幕的三分之一宽度
int width=getWidth()/3;
int height=getHeight();
int count=getChildCount();
if(event.getX()<width){
this.getChildAt(0).dispatchTouchEvent(event);
return true;
}else if(event.getX()<2*width){
//判断手指滑动的高度
if(event.getY()<height/2){
//将事件分发给3个子view
for(int i=0;i<count;i++){
this.getChildAt(i).dispatchTouchEvent(event);
}
return true;
}else {
this.getChildAt(1).dispatchTouchEvent(event);
return true;
}
}else {
this.getChildAt(2).dispatchTouchEvent(event);
return true;
}
}
}至于为什么要重写LinearLayout ,需要理解事件分发的原理:
分发的原理是从上到下,响应的顺序是从下向上的,也就是说,当我们手指滑动屏幕的时候,Linearlayout 会比他根节点下的Recyclerview先获得到这个事件,so,我们需要在父类控件(LinearLayout)中去拦截这个事件,然后在onTouchEvent方法中去决定让哪个控件去消费这个事件
如果对事件分发原理还不是很了解的,这里推荐一篇博客跟你,说的很详细事件分发原理详解
注意事项:
- 事件分发有3个重要的方法,分别是 dispatchTouchEvent()、 onInterceptTouchEvent()、onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event)
- 只有有子类的控件的ViewGroup才去重写onInterceptTouchEvent(),这里的LinearLayout就可以重写,一旦重写onInterceptTouchEvent(),将返回值设置为true,那么接下来就会执行onTouchEvent().
- 在onTouchEvent() 方法中 就可以根据手指的在屏幕的位置,来将事件分发给哪一个子view,具体写法参考上面的onTouchEvent(),需要注意的是,dispatchTouchEvent()一般是直接拿来使用的,而不去重写。比如说,想将事件分发给第一个子view,就可以这么写this.getChildAt(0).dispatchTouchEvent(event);
之后在布局xml中引用就可以了:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<com.gcg.dispatchexm.ui.view.MyLinearlayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="horizontal"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<android.support.v7.widget.RecyclerView
android:id="@+id/rl"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1">
</android.support.v7.widget.RecyclerView>
<android.support.v7.widget.RecyclerView
android:id="@+id/rl2"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1">
</android.support.v7.widget.RecyclerView>
<android.support.v7.widget.RecyclerView
android:id="@+id/rl3"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1">
</android.support.v7.widget.RecyclerView>
</com.gcg.dispatchexm.ui.view.MyLinearlayout>如果还不是很了解,请参考demo