使用AccountManager和AbstractAccountAuthenticator建立账户系统
为什么要使用AccountManager和AccountAuthenticatr
建立账户管理系统,可以使用SharedPreference来存储、更新、删除AuthToken,也可以用来存储、更新、删除账户和密码。既然这样,为什么还要使用AccountManager和AccountAuthenticator?
原因有一下几点:
1.AccountManager是Android系统提供的账户管理框架,十分强大和方便,可以管理不同类型账户,不同类型AuthenToken
2.AccountAuthenticator把账户的验证过程、AuthToken的获取过程分离出来,降低程序的耦合性
3.使用AccountAuthenticator会在”设置”中添加一个账户入口,感觉很酷炫。
AccountManager和Authenticator之间的关系
AccountManager和Authenticator的方法相对应,比如,AccountManager的addAccount()方法会调用Authenticator的addAccount()方法,Authenticator的方法会返回一个Bundle给AccountManager处理。具体细节后面会介绍。
使用AccountManager管理账号
顾名思义,AccountManager是用来管理用户账户。使用AccountManager有两个要点:Bundle key常量的含义、如何使用账户管理方法。 AccountManager定义了许多Bundle Key常量,可以用作Intent的key用于Activity之间传递参数;也可以作为Authenticator返回Bundle的Key,这种情况,AccountManager会根据Key的情况作出相应操作,比如,跳转到验证身份页面,返回Accont Type,AuthToken,Account Name(getAuthenToken()有返回AuthToken时必须返回Account Type和Account Name,不然会提示“the type and name should not be empty”)等。
介绍一些常用Bundle key:
| Key | 含义 |
|---|---|
| AccountManager.KEY_ACCOUNT_AUTHENTICATOR_RESPONSE | 可以调用onResult()和onError()来相应用户提供的信息 |
| AccountManager.KEY_INTENT | 开启新Activity和用户进行交互 |
| AccountManager.KEY_AUTHTOKEN | 令牌 |
| AccountManager.KEY_ACCOUNT_TYPE | 账户类型 |
| AccountManager.KEY_ACCOUNT_NAME | 账户名 |
| AccountManager.KEY_ERROR_CODE | 错误码(必须大于0) |
| AccountManager.KEY_ERROR_MESSAGE | 错误信息(必须和错误码一起使用) |
介绍一些常用AccountManager管理账户方法: 获取AuthToken:
@param account 账户
@param authTokenType token类型
@param options 额外的数据
@param activity 用来开启另外的Activity
@param callback 结果回调
@param 回调的线程,null时为主线程
public AccountManagerFuture<Bundle> getAuthToken(
final Account account, final String authTokenType, final Bundle options,
final Activity activity, AccountManagerCallback<Bundle> callback, Handler handler) 获取账户列表:
@param type 账户列表类型
public Account[] getAccountsByType(String type)从AccountManager的缓存中移除AuthToken:
@param accountType 账户类型
@param authToken 令牌
public void invalidateAuthToken(final String accountType, final String authToken) 获取密码:
@param account 账户
public String getPassword(final Account account) 接下来是重点,创建自己的Authenticator,用来验证用户信息或者与从服务器获取信息。
创建Authenticator
步骤:
1.继承AbstractAcccountAuthenticator
2.重写addAccount(),getAuthenToken()方法。如果有需要还可以重写其他方法
重写addAccount()方法:
@Override
public Bundle addAccount(AccountAuthenticatorResponse response, String accountType, String authTokenType, String[] requiredFeatures, Bundle options) throws NetworkErrorException {
Intent intent=new Intent(mContext,AuthenticatorActivity.class);
intent.putExtra(AccountManager.KEY_ACCOUNT_AUTHENTICATOR_RESPONSE,response);
Bundle bundle=new Bundle();
bundle.putParcelable(AccountManager.KEY_INTENT,intent);
return bundle;
}重写getAuthenToken()方法,要注意,如果之前成功获取过AuthenToken会缓存,之后不会在调用getAuthenToken()方法,除非调用invalidateAuthenToken():
@Override
public Bundle getAuthToken(AccountAuthenticatorResponse response, Account account, String authTokenType, Bundle options) throws NetworkErrorException {
//可以请求服务器获取token,这里为了简单直接返回
Bundle bundle;
if(!authTokenType.equals(Constants.AUTH_TOKEN_TYPE)){
bundle=new Bundle();
//没有error_code的情况,不会抛出异常
//bundle.putInt(AccountManager.KEY_ERROR_CODE,1);
bundle.putString(AccountManager.KEY_ERROR_MESSAGE,"invalid authToken");
return bundle;
}
AccountManager am=AccountManager.get(mContext);
String psw=am.getPassword(account);
if(!TextUtils.isEmpty(psw)){
//链接服务器获取token
Random random=new Random();
bundle=new Bundle();
bundle.putString(AccountManager.KEY_AUTHTOKEN,random.nextLong()+"");
//不返回name和type会报错“the type and name should not be empty”
bundle.putString(AccountManager.KEY_ACCOUNT_TYPE,account.type);
bundle.putString(AccountManager.KEY_ACCOUNT_NAME,account.name);
return bundle;
}
bundle=new Bundle();
Intent intent=new Intent(mContext,AuthenticatorActivity.class);
bundle.putParcelable(AccountManager.KEY_INTENT,intent);
intent.putExtra(AccountManager.KEY_ACCOUNT_TYPE,account.type);
intent.putExtra(AccountManager.KEY_ACCOUNT_NAME,account.name);
intent.putExtra(AccountManager.KEY_ACCOUNT_AUTHENTICATOR_RESPONSE,response);
return bundle;
}3.为Authenticator创建Service
public class AuthenticatorService extends Service{
private MyAuthenticator mAuthenticator=new MyAuthenticator(this);
@Nullable
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return mAuthenticator.getIBinder();
}
}4.为了把Authenticator组件添加到账户管理框架,需要添加Metadata文件描述组件,在res/xml/目录下声明组件
<account-authenticator xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:accountType="com.lm.example.accountmanagersample"
android:icon="@drawable/ic_delete"
android:smallIcon="@drawable/ic_delete"
android:label="@string/app_name"
/>accountType很重要,用来唯一标识Authenticator,AccountManager的方法中有accountType的参数需要和此处保持一致。
5.在Manifest文件声明之前创建的Service
<service android:name=".AuthenticatorService">
<intent-filter>
<action
android:name="android.accounts.AccountAuthenticator" />
</intent-filter>
<meta-data
android:name="android.accounts.AccountAuthenticator"
android:resource="@xml/authenticator"/>
</service>源码分析
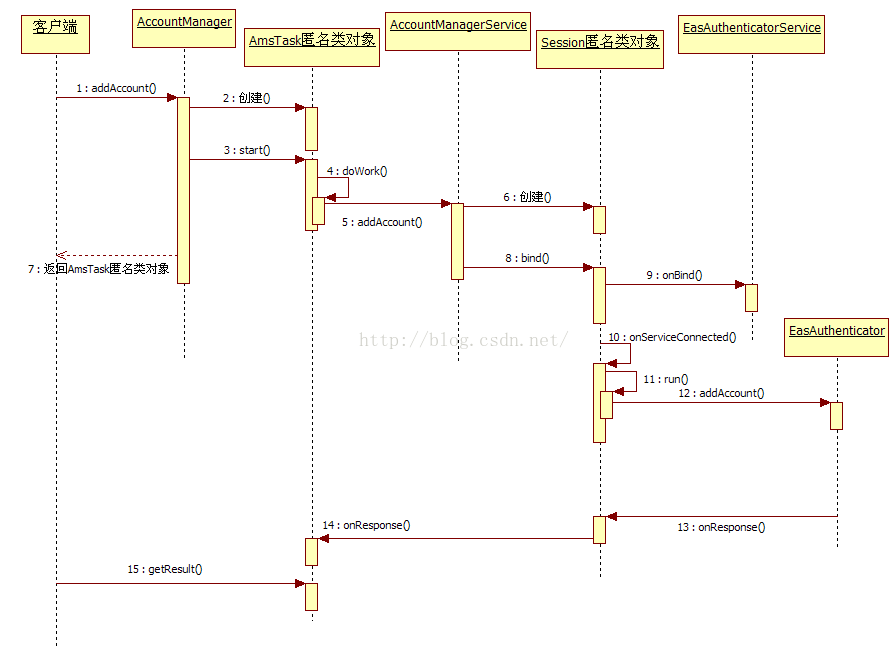
从源码角度分析AccountManager和Authenticator之间的关系,主要介绍AccountManager的addAccount()和getAuthToken()方法。 首先分析addAccount(),addAccount()源码如下。
/* @param accountType The type of account to add; must not be null
* @param authTokenType The type of auth token (see {@link #getAuthToken})
* this account will need to be able to generate, null for none
* @param requiredFeatures The features (see {@link #hasFeatures}) this
* account must have, null for none
* @param addAccountOptions Authenticator-specific options for the request,
* may be null or empty
* @param activity The {@link Activity} context to use for launching a new
* authenticator-defined sub-Activity to prompt the user to create an
* account; used only to call startActivity(); if null, the prompt
* will not be launched directly, but the necessary {@link Intent}
* will be returned to the caller instead
* @param callback Callback to invoke when the request completes,
* null for no callback
* @param handler {@link Handler} identifying the callback thread,
* null for the main thread
* @return An {@link AccountManagerFuture} which resolves to a Bundle with
* these fields if activity was specified and an account was created:
* <ul>
* <li> {@link #KEY_ACCOUNT_NAME} - the name of the account created
* <li> {@link #KEY_ACCOUNT_TYPE} - the type of the account
* </ul>
*/
public AccountManagerFuture<Bundle> addAccount(final String accountType,
final String authTokenType, final String[] requiredFeatures,
final Bundle addAccountOptions,
final Activity activity, AccountManagerCallback<Bundle> callback, Handler handler) {
if (accountType == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("accountType is null");
final Bundle optionsIn = new Bundle();
if (addAccountOptions != null) {
optionsIn.putAll(addAccountOptions);
}
optionsIn.putString(KEY_ANDROID_PACKAGE_NAME, mContext.getPackageName());
return new AmsTask(activity, handler, callback) {
public void doWork() throws RemoteException {
mService.addAccount(mResponse, accountType, authTokenType,
requiredFeatures, activity != null, optionsIn);
}
}.start();
}新建了个AmsTask实例,重写了dowork()方法, doWrok()中AccountManagerService实例调用了addAccount()方法,有个参数mResponse是AmTask实例的成员变量。先看下AmsTask主要实现。
private abstract class AmsTask extends FutureTask<Bundle> implements AccountManagerFuture<Bundle> {
final IAccountManagerResponse mResponse;
final Handler mHandler;
final AccountManagerCallback<Bundle> mCallback;
final Activity mActivity;
public AmsTask(Activity activity, Handler handler, AccountManagerCallback<Bundle> callback) {
super(new Callable<Bundle>() {
public Bundle call() throws Exception {
throw new IllegalStateException("this should never be called");
}
});
mHandler = handler;
mCallback = callback;
mActivity = activity;
mResponse = new Response();
}
} AmsTask继承FutureTask,当setException(Throwable t)被调用后,调用get()方法会抛出该异常。
AccountManagerService的addAccount()方法的主要实现如下。
@Override
public void addAccount(final IAccountManagerResponse response, final String accountType,final String authTokenType, final String[] requiredFeatures,final boolean expectActivityLaunch, final Bundle optionsIn) {
......
new Session(accounts, response, accountType, expectActivityLaunch,
true /* stripAuthTokenFromResult */, null /* accountName */,
false /* authDetailsRequired */,true /*updateLastAuthenticationTime */) {
@Override
public void run() throws RemoteException {
mAuthenticator.addAccount(this, mAccountType, authTokenType, requiredFeatures,options);
}
@Override
protected String toDebugString(long now) {
return super.toDebugString(now) + ", addAccount"
+ ", accountType " + accountType
+ ", requiredFeatures "
+ (requiredFeatures != null
? TextUtils.join(",", requiredFeatures)
: null);
}
}.bind();
......
}看到重点了,Session实例重写run()方法中调用了Authenticator的addAccount()方法,并且绑定Authenticator的Service。接下来看看Authenticator的addAccount()方法(并不是我们重写的addAccount()方法)。
public void addAccount(IAccountAuthenticatorResponse response, String accountType,String authTokenType, String[] features, Bundle options)
throws RemoteException {
......
try {
final Bundle result=
AbstractAccountAuthenticator.this.addAccount(
new AccountAuthenticatorResponse(response),
accountType, authTokenType, features, options);
......
if (result != null) {
response.onResult(result);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
handleException(response, "addAccount", accountType, e);
}
}这里才正真调用了我们重写的addAccount()方法,会返回Bundle,Session的onResult()方法会先处理Bundle,满足条件(mExpectActivityLaunch && result != null&& result.containsKey(AccountManager.KEY_INTENT))还可能调用response的onError()或onResult方法,这里的onError()方法和onResult()方法是IAccountManagerResponse.Stub实现的方法。先看看Session的onResult()方法。
@Override
public void onResult(Bundle result) {
Bundle.setDefusable(result, true);
mNumResults++;
Intent intent = null;
if (result != null&& (intent = result.getParcelable(AccountManager.KEY_INTENT)) != null) {
checkKeyIntent(Binder.getCallingUid(),intent);
// Omit passwords if the caller isn't permitted to see them.
if (!mIsPasswordForwardingAllowed) {
result.remove(AccountManager.KEY_PASSWORD);
}
}
IAccountManagerResponse response;
if (mExpectActivityLaunch && result != null
&& result.containsKey(AccountManager.KEY_INTENT)) {
response = mResponse;
} else {
response = getResponseAndClose();
}
if (response == null) {
return;
}
if (result == null) {
if (Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.VERBOSE)) {
Log.v(TAG, getClass().getSimpleName() + " calling onError() on response "+ response);
}
sendErrorResponse(response,AccountManager.ERROR_CODE_INVALID_RESPONSE,"null bundle returned");
return;
}
if ((result.getInt(AccountManager.KEY_ERROR_CODE, -1) > 0) && (intent == null)) {
// All AccountManager error codes are greater
// than 0
sendErrorResponse(response,result.getInt(AccountManager.KEY_ERROR_CODE),result.getString(AccountManager.KEY_ERROR_MESSAGE));
return;
}
// Strip auth token from result.
result.remove(AccountManager.KEY_AUTHTOKEN);
if (Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.VERBOSE)) {
Log.v(TAG,getClass().getSimpleName() + " calling onResult() on response " + response);
}
// Get the session bundle created by authenticator. The
// bundle contains data necessary for finishing the session
// later. The session bundle will be encrypted here and
// decrypted later when trying to finish the session.
Bundle sessionBundle = result.getBundle(AccountManager.KEY_ACCOUNT_SESSION_BUNDLE);
if (sessionBundle != null) {
String accountType = sessionBundle.getString(AccountManager.KEY_ACCOUNT_TYPE);
if (TextUtils.isEmpty(accountType)
|| !mAccountType.equalsIgnoreCase(accountType)) {
Log.w(TAG, "Account type in session bundle doesn't match request.");
}
// Add accountType info to session bundle. This will
// override any value set by authenticator.
sessionBundle.putString(AccountManager.KEY_ACCOUNT_TYPE, mAccountType);
// Encrypt session bundle before returning to caller.
try {
CryptoHelper cryptoHelper = CryptoHelper.getInstance();
Bundle encryptedBundle = cryptoHelper.encryptBundle(sessionBundle);
result.putBundle(AccountManager.KEY_ACCOUNT_SESSION_BUNDLE, encryptedBundle);
} catch (GeneralSecurityException e) {
if (Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.DEBUG)) {
Log.v(TAG, "Failed to encrypt session bundle!", e);
}
sendErrorResponse(response, AccountManager.ERROR_CODE_INVALID_RESPONSE,
"failed to encrypt session bundle");
return;
}
}
sendResponse(response, result);
}
}Session的onResult()方法看到KEY_ERROR_CODE大于0才会setException()。
IAccountManagerResponse.Stub的具体实现。
/** Handles the responses from the AccountManager */
private class Response extends IAccountManagerResponse.Stub {
public void onResult(Bundle bundle) {
Intent intent = bundle.getParcelable(KEY_INTENT);
if (intent != null && mActivity != null) {
// since the user provided an Activity we will silently start intents
// that we see mActivity.startActivity(intent);
// leave the Future running to wait for the real response to this request
} else if (bundle.getBoolean("retry")) {
try {
doWork();
} catch (RemoteException e) {
// this will only happen if the system process is dead, which means
// we will be dying ourselves
}
} else {
set(bundle);
}
}
public void onError(int code, String message) {
if (code == ERROR_CODE_CANCELED ||
code == ERROR_CODE_USER_RESTRICTED
|| code == ERROR_CODE_MANAGEMENT_DISABLED_FOR_ACCOUNT_TYPE) {
// the authenticator indicated that this request was canceled or we were
// forbidden to fulfill; cancel now
cancel(true /* mayInterruptIfRunning */);
return;
}
setException(convertErrorToException(code, message));
}
}getAhthToken的流程和addAccount流程差不多,可自行分析。
demo地址:
github.com/wslaimin/Ac…