#高斯模糊
高斯模糊(英语:Gaussian Blur),也叫高斯平滑,是在Adobe Photoshop、GIMP以及Paint.NET等图像处理软件中广泛使用的处理效果,通常用它来减少图像杂讯以及降低细节层次。这种模糊技术生成的图像,其视觉效果就像是经过一个半透明屏幕在观察图像,这与镜头焦外成像效果散景以及普通照明阴影中的效果都明显不同。高斯平滑也用于计算机视觉算法中的预先处理阶段,以增强图像在不同比例大小下的图像效果。 从数学的角度来看,图像的高斯模糊过程就是图像与正态分布做卷积。由于正态分布又叫作高斯分布,所以这项技术就叫作高斯模糊。图像与圆形方框模糊做卷积将会生成更加精确的焦外成像效果。由于高斯函数的傅立叶变换是另外一个高斯函数,所以高斯模糊对于图像来说就是一个低通滤波器。
高斯模糊运用了高斯的正态分布的密度函数,计算图像中每个像素的变换。
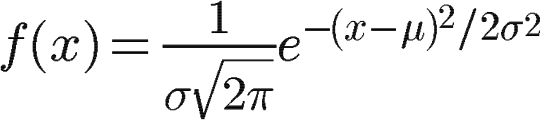
根据一维高斯函数,可以推导得到二维高斯函数:
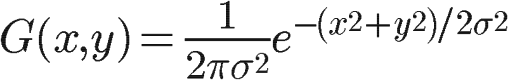
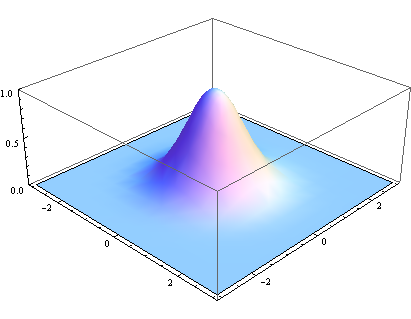
其中r是模糊半径,r^2 = x^2 + y^2,σ是正态分布的标准偏差。在二维空间中,这个公式生成的曲面的等高线是从中心开始呈正态分布的同心圆。分布不为零的像素组成的卷积矩阵与原始图像做变换。每个像素的值都是周围相邻像素值的加权平均。原始像素的值有最大的高斯分布值,所以有最大的权重,相邻像素随着距离原始像素越来越远,其权重也越来越小。这样进行模糊处理比其它的均衡模糊滤波器更高地保留了边缘效果。
其实,在iOS上实现高斯模糊是件很容易的事儿。早在iOS 5.0就有了Core Image的API,而且在CoreImage.framework库中,提供了大量的滤镜实现。
+(UIImage *)coreBlurImage:(UIImage *)image withBlurNumber:(CGFloat)blur
{
CIContext *context = [CIContext contextWithOptions:nil];
CIImage *inputImage= [CIImage imageWithCGImage:image.CGImage];
//设置filter
CIFilter *filter = [CIFilter filterWithName:@"CIGaussianBlur"];
[filter setValue:inputImage forKey:kCIInputImageKey]; [filter setValue:@(blur) forKey: @"inputRadius"];
//模糊图片
CIImage *result=[filter valueForKey:kCIOutputImageKey];
CGImageRef outImage=[context createCGImage:result fromRect:[result extent]];
UIImage *blurImage=[UIImage imageWithCGImage:outImage];
CGImageRelease(outImage);
return blurImage;
}在Android上实现高斯模糊也可以使用原生的API-----RenderScript,不过需要Android的API是17以上,也就是Android 4.2版本。
/**
* 使用RenderScript实现高斯模糊的算法
* @param bitmap
* @return
*/
public Bitmap blur(Bitmap bitmap){
//Let's create an empty bitmap with the same size of the bitmap we want to blur
Bitmap outBitmap = Bitmap.createBitmap(bitmap.getWidth(), bitmap.getHeight(), Bitmap.Config.ARGB_8888);
//Instantiate a new Renderscript
RenderScript rs = RenderScript.create(getApplicationContext());
//Create an Intrinsic Blur Script using the Renderscript
ScriptIntrinsicBlur blurScript = ScriptIntrinsicBlur.create(rs, Element.U8_4(rs));
//Create the Allocations (in/out) with the Renderscript and the in/out bitmaps
Allocation allIn = Allocation.createFromBitmap(rs, bitmap);
Allocation allOut = Allocation.createFromBitmap(rs, outBitmap);
//Set the radius of the blur: 0 < radius <= 25
blurScript.setRadius(20.0f);
//Perform the Renderscript
blurScript.setInput(allIn);
blurScript.forEach(allOut);
//Copy the final bitmap created by the out Allocation to the outBitmap
allOut.copyTo(outBitmap);
//recycle the original bitmap
bitmap.recycle();
//After finishing everything, we destroy the Renderscript.
rs.destroy();
return outBitmap;
}我们开发的图像框架cv4j也提供了一个滤镜来实现高斯模糊。
GaussianBlurFilter filter = new GaussianBlurFilter();
filter.setSigma(10);
RxImageData.bitmap(bitmap).addFilter(filter).into(image2);

可以看出,cv4j实现的高斯模糊跟RenderScript实现的效果一致。
其中,GaussianBlurFilter的代码如下:
public class GaussianBlurFilter implements CommonFilter {
private float[] kernel;
private double sigma = 2;
ExecutorService mExecutor;
CompletionService<Void> service;
public GaussianBlurFilter() {
kernel = new float[0];
}
public void setSigma(double a) {
this.sigma = a;
}
@Override
public ImageProcessor filter(final ImageProcessor src){
final int width = src.getWidth();
final int height = src.getHeight();
final int size = width*height;
int dims = src.getChannels();
makeGaussianKernel(sigma, 0.002, (int)Math.min(width, height));
mExecutor = TaskUtils.newFixedThreadPool("cv4j",dims);
service = new ExecutorCompletionService<>(mExecutor);
// save result
for(int i=0; i<dims; i++) {
final int temp = i;
service.submit(new Callable<Void>() {
public Void call() throws Exception {
byte[] inPixels = src.toByte(temp);
byte[] temp = new byte[size];
blur(inPixels, temp, width, height); // H Gaussian
blur(temp, inPixels, height, width); // V Gaussain
return null;
}
});
}
for (int i = 0; i < dims; i++) {
try {
service.take();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
mExecutor.shutdown();
return src;
}
/**
* <p> here is 1D Gaussian , </p>
*
* @param inPixels
* @param outPixels
* @param width
* @param height
*/
private void blur(byte[] inPixels, byte[] outPixels, int width, int height)
{
int subCol = 0;
int index = 0, index2 = 0;
float sum = 0;
int k = kernel.length-1;
for(int row=0; row<height; row++) {
int c = 0;
index = row;
for(int col=0; col<width; col++) {
sum = 0;
for(int m = -k; m< kernel.length; m++) {
subCol = col + m;
if(subCol < 0 || subCol >= width) {
subCol = 0;
}
index2 = row * width + subCol;
c = inPixels[index2] & 0xff;
sum += c * kernel[Math.abs(m)];
}
outPixels[index] = (byte)Tools.clamp(sum);
index += height;
}
}
}
public void makeGaussianKernel(final double sigma, final double accuracy, int maxRadius) {
int kRadius = (int)Math.ceil(sigma*Math.sqrt(-2*Math.log(accuracy)))+1;
if (maxRadius < 50) maxRadius = 50; // too small maxRadius would result in inaccurate sum.
if (kRadius > maxRadius) kRadius = maxRadius;
kernel = new float[kRadius];
for (int i=0; i<kRadius; i++) // Gaussian function
kernel[i] = (float)(Math.exp(-0.5*i*i/sigma/sigma));
double sum; // sum over all kernel elements for normalization
if (kRadius < maxRadius) {
sum = kernel[0];
for (int i=1; i<kRadius; i++)
sum += 2*kernel[i];
} else
sum = sigma * Math.sqrt(2*Math.PI);
for (int i=0; i<kRadius; i++) {
double v = (kernel[i]/sum);
kernel[i] = (float)v;
}
return;
}
}#空间卷积
二维卷积在图像处理中会经常遇到,图像处理中用到的大多是二维卷积的离散形式。
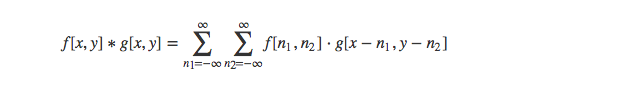
以下是cv4j实现的各种卷积效果。

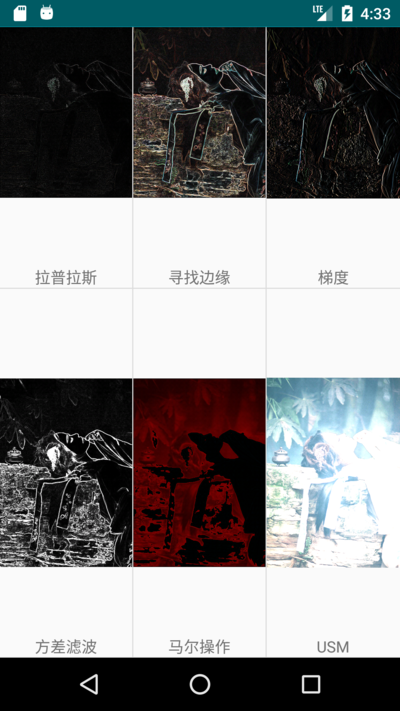
cv4j 目前支持如下的空间卷积滤镜
| filter | 名称 | 作用 |
|---|---|---|
| ConvolutionHVFilter | 卷积 | 模糊或者降噪 |
| MinMaxFilter | 最大最小值滤波 | 去噪声 |
| SAPNoiseFilter | 椒盐噪声 | 增加噪声 |
| SharpFilter | 锐化 | 增强 |
| MedimaFilter | 中值滤波 | 去噪声 |
| LaplasFilter | 拉普拉斯 | 提取边缘 |
| FindEdgeFilter | 寻找边缘 | 梯度提取 |
| SobelFilter | 梯度 | 获取x、y方向的梯度提取 |
| VarianceFilter | 方差滤波 | 高通滤波 |
| MaerOperatorFilter | 马尔操作 | 高通滤波 |
| USMFilter | USM | 增强 |
#总结
cv4j 是gloomyfish和我一起开发的图像处理库,目前还处于早期的版本。
目前已经实现的功能:
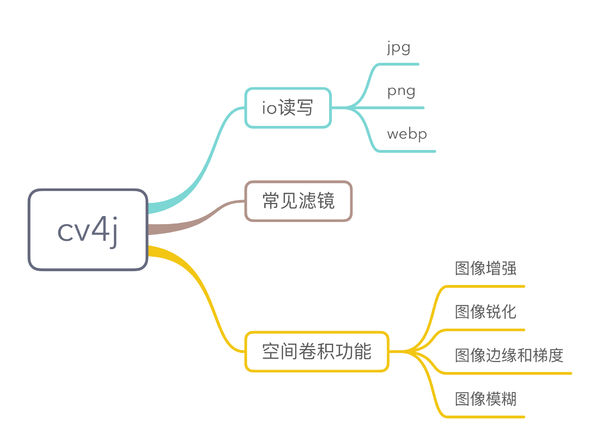
这周,我们对 cv4j 做了较大的调整,对整体架构进行了优化。还加上了空间卷积功能(图片增强、锐化、模糊等等)。接下来,我们会做二值图像的分析(腐蚀、膨胀、开闭操作、轮廓提取等等)