前言
通常来说一个dubbo服务都是对内给内部调用的,但也有可能一个服务就是需要提供给外部使用,并且还不能有使用语言的局限性。
比较标准的做法是对外的服务我们统一提供一个openAPI,这样的调用方需要按照标准提供相应的appID以及密钥来进行验签才能使用。这样固然是比较规范和安全,但复杂度也不亚于开发一个单独的系统了。
这里所讲到的没有那么复杂,就只是把一个不需要各种权限检验的dubbo服务对外提供为HTTP服务。
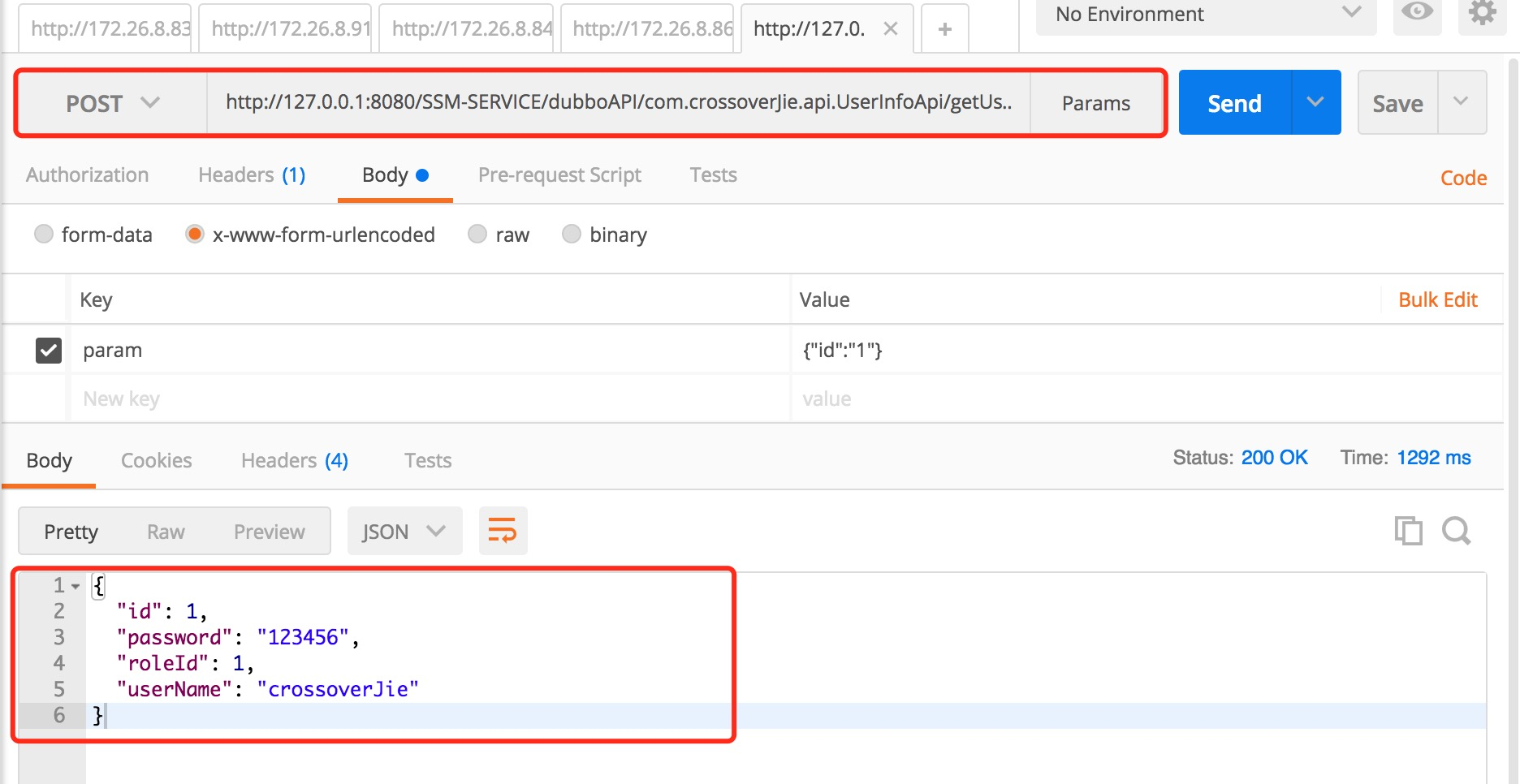
调用示例:
准备工作
以下是本文所涉及到的一些知识点:
- Spring相关知识。
- Java反射相关知识。
- SpringMVC相关知识。
其实思路很简单,就是利用
SpringMVC提供一个HTTP接口。
在该接口中通过入参进行反射找到具体的dubbo服务实现进行调用。
HttpProviderConf配置类
首先需要定义一个HttpProviderConf类用于保存声明需要对外提供服务的包名,毕竟我们反射时需要用到一个类的全限定名:
public class HttpProviderConf {
/**
* 提供http访问的包
*/
private List<String> usePackage ;
//省略getter setter方法
}就只有一个usePackage成员变量,用于存放需要包名。
至于用List的原因是允许有多个。
请求响应入参、出参
HttpRequest入参
public class HttpRequest {
private String param ;//入参
private String service ;//请求service
private String method ;//请求方法
//省略getter setter方法
}其中param是用于存放真正调用dubbo服务时的入参,传入json在调用的时候解析成具体的参数对象。
service存放dubbo服务声明的interface API的包名。
method则是真正调用的方法名称。
HttpResponse 响应
public class HttpResponse implements Serializable{
private static final long serialVersionUID = -552828440320737814L;
private boolean success;//成功标志
private String code;//信息码
private String description;//描述
//省略getter setter方法
}这里只是封装了常用的HTTP服务的响应数据。
暴露服务controller
最重要的则是controller里的实现代码了。
先贴代码:
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/dubboAPI")
public class DubboController implements ApplicationContextAware{
private final static Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(DubboController.class);
@Autowired
private HttpProviderConf httpProviderConf;
//缓存作用的map
private final Map<String, Class<?>> cacheMap = new HashMap<String, Class<?>>();
protected ApplicationContext applicationContext;
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping(value = "/{service}/{method}",method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String api(HttpRequest httpRequest, HttpServletRequest request,
@PathVariable String service,
@PathVariable String method) {
logger.debug("ip:{}-httpRequest:{}",getIP(request), JSON.toJSONString(httpRequest));
String invoke = invoke(httpRequest, service, method);
logger.debug("callback :"+invoke) ;
return invoke ;
}
private String invoke(HttpRequest httpRequest,String service,String method){
httpRequest.setService(service);
httpRequest.setMethod(method);
HttpResponse response = new HttpResponse() ;
logger.debug("input param:"+JSON.toJSONString(httpRequest));
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(httpProviderConf.getUsePackage())){
boolean isPac = false ;
for (String pac : httpProviderConf.getUsePackage()) {
if (service.startsWith(pac)){
isPac = true ;
break ;
}
}
if (!isPac){
//调用的是未经配置的包
logger.error("service is not correct,service="+service);
response.setCode("2");
response.setSuccess(false);
response.setDescription("service is not correct,service="+service);
}
}
try {
Class<?> serviceCla = cacheMap.get(service);
if (serviceCla == null){
serviceCla = Class.forName(service) ;
logger.debug("serviceCla:"+JSON.toJSONString(serviceCla));
//设置缓存
cacheMap.put(service,serviceCla) ;
}
Method[] methods = serviceCla.getMethods();
Method targetMethod = null ;
for (Method m : methods) {
if (m.getName().equals(method)){
targetMethod = m ;
break ;
}
}
if (method == null){
logger.error("method is not correct,method="+method);
response.setCode("2");
response.setSuccess(false);
response.setDescription("method is not correct,method="+method);
}
Object bean = this.applicationContext.getBean(serviceCla);
Object result = null ;
Class<?>[] parameterTypes = targetMethod.getParameterTypes();
if (parameterTypes.length == 0){
//没有参数
result = targetMethod.invoke(bean);
}else if (parameterTypes.length == 1){
Object json = JSON.parseObject(httpRequest.getParam(), parameterTypes[0]);
result = targetMethod.invoke(bean,json) ;
}else {
logger.error("Can only have one parameter");
response.setSuccess(false);
response.setCode("2");
response.setDescription("Can only have one parameter");
}
return JSON.toJSONString(result) ;
}catch (ClassNotFoundException e){
logger.error("class not found",e);
response.setSuccess(false);
response.setCode("2");
response.setDescription("class not found");
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
logger.error("InvocationTargetException",e);
response.setSuccess(false);
response.setCode("2");
response.setDescription("InvocationTargetException");
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
logger.error("IllegalAccessException",e);
response.setSuccess(false);
response.setCode("2");
response.setDescription("IllegalAccessException");
}
return JSON.toJSONString(response) ;
}
/**
* 获取IP
* @param request
* @return
*/
private String getIP(HttpServletRequest request) {
if (request == null)
return null;
String s = request.getHeader("X-Forwarded-For");
if (s == null || s.length() == 0 || "unknown".equalsIgnoreCase(s)) {
s = request.getHeader("Proxy-Client-IP");
}
if (s == null || s.length() == 0 || "unknown".equalsIgnoreCase(s)) {
s = request.getHeader("WL-Proxy-Client-IP");
}
if (s == null || s.length() == 0 || "unknown".equalsIgnoreCase(s)) {
s = request.getHeader("HTTP_CLIENT_IP");
}
if (s == null || s.length() == 0 || "unknown".equalsIgnoreCase(s)) {
s = request.getHeader("HTTP_X_FORWARDED_FOR");
}
if (s == null || s.length() == 0 || "unknown".equalsIgnoreCase(s)) {
s = request.getRemoteAddr();
}
if ("127.0.0.1".equals(s) || "0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1".equals(s))
try {
s = InetAddress.getLocalHost().getHostAddress();
} catch (UnknownHostException unknownhostexception) {
return "";
}
return s;
}
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
}先一步一步的看:
首先是定义了一个
DubboController,并使用了SpringMVC的注解对外暴露HTTP服务。实现了
org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware类,
实现了setApplicationContext()方法用于初始化Spring上下文对象,在之后可以获取到容器里的相应对象。核心的
invoke()方法。- 调用时:
http://127.0.0.1:8080/SSM-SERVICE/dubboAPI/com.crossoverJie.api.UserInfoApi/getUserInfo。 - 具体如上文的调用实例。先将
com.crossoverJie.api.UserInfoApi、getUserInfo赋值到httpRequest入参中。 判断传入的包是否是对外提供的。如下配置:
<!--dubbo服务暴露为http服务--> <bean class="com.crossoverJie.dubbo.http.conf.HttpProviderConf"> <property name="usePackage"> <list> <!--需要暴露服务的接口包名,可多个--> <value>com.crossoverJie.api</value> </list> </property> </bean> <!--扫描暴露包--> <context:component-scan base-package="com.crossoverJie.dubbo.http"/>其中的
com.crossoverJie.api就是自己需要暴露的包名,可以多个。接着在缓存
map中取出反射获取到的接口类类型,如果获取不到则通过反射获取,并将值设置到缓存map中,这样不用每次都反射获取,可以节省系统开销(反射很耗系统资源)。- 接着也是判断该接口中是否有传入的
getUserInfo方法。 - 取出该方法的参数列表,如果没有参数则直接调用。
- 如果有参数,判断个数。这里最多只运行一个参数。也就是说在真正的
dubbo调用的时候只能传递一个BO类型,具体的参数列表可以写到BO中。因为如果有多个在进行json解析的时候是无法赋值到两个参数对象中去的。 - 之后进行调用,将调用返回的数据进行返回即可。
总结
通常来说这样提供的HTTP接口再实际中用的不多,但是很方便调试。
比如写了一个dubbo的查询接口,在测试环境或者是预发布环境中就可以直接通过HTTP请求的方式进行简单的测试,或者就是查询数据。比在Java中写单测来测试或查询快的很多。
安装
git clone https://github.com/crossoverJie/SSM-DUBBO-HTTP.gitcd SSM-DUBBO-HTTPmvn cleanmvn install使用
<dependency>
<groupId>com.crossoverJie</groupId>
<artifactId>SSM-HTTP-PROVIDER</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0</version>
</dependency>spring配置
<!--dubbo服务暴露为http服务-->
<bean class="com.crossoverJie.dubbo.http.conf.HttpProviderConf">
<property name="usePackage">
<list>
<!--需要暴露服务的接口包名,可多个-->
<value>com.crossoverJie.api</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
<!--扫描暴露包-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.crossoverJie.dubbo.http"/>个人博客地址:crossoverjie.top。
GitHub地址:github.com/crossoverJi…。
