前言
说来也奇怪,高中学代码的时候,整天在刷一些noip的题目,钻研各种算法,什么递归、分治、动态规划。而真正工作后,发现很少用不到,直到这个页面才让我用到算法。其实这个页面,是我前年写的,但是一直偷懒,不想整理发布,去年的时候,在csdn上发布过一些,但是没怎么认真写,今天乘着周末认真给大家讲讲,希望能勾起大家对算法的回忆。
项目需求是一个思维导图、每个节点的个数以及数据由服务端返回,这就需要每一次点击都得计算位置以及绘制布局。
效果

这种思维导图有两种模式,一种是可以无限点击各个节点(上图),不清除之前的节点;另外一种是当点击同级节点时,其他节点的子节点清除(下图)。
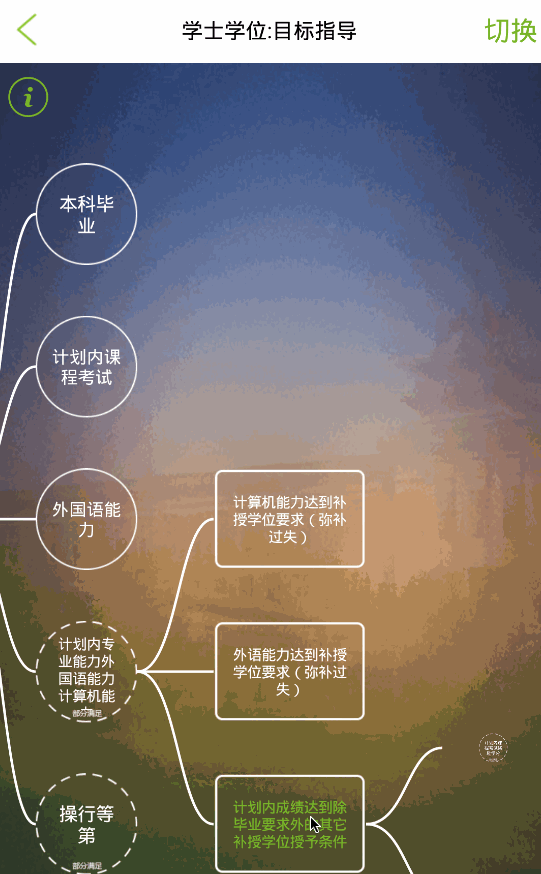
这两种模式,都可以随时随意通过右上角切换按钮进行无缝切换。
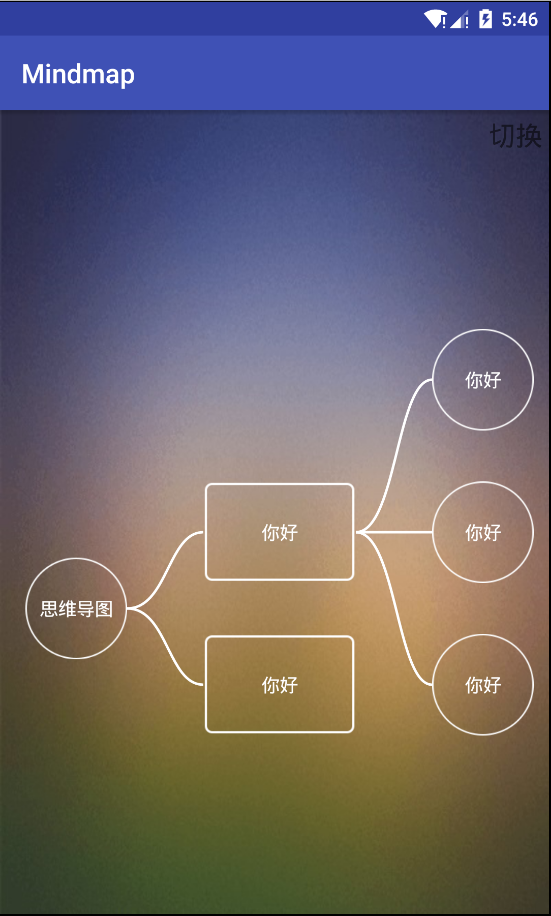
思路
1.布局:
这个布局是一张图,可能会很大,支持上下左右拖拽,这个时候,我想到了HVScrollView,只要在里面放一个RelativeLayout,随便设置一个长宽500dp,之后有新节点,像RelativeLayout中addview即可使布局增大,支持各种滚动。当节点需要清除时,调用removeview即可删除布局,减少宽高,节约内存。
2.节点:
暂时先把每个节点看作一个button,绘制的位置是根据数量来计算,其中x位置是前一个节点+某个固定值,y位置为前一个节点y-当前节点数量*每个节点高度/2
x=前一个x+a //a为节点间距。
y=前一个y-n*b/2 //n为当前节点数量 b为每个节点占位高度。3.线条
线条是4阶贝塞尔曲线,四个节点分别为下图。
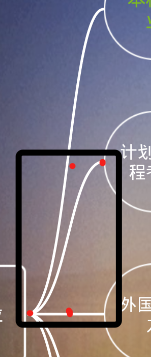
其实第一个版本没有采用贝塞尔曲线,采用的是直线图,导致下级节点可能会重复,所以在程序中不得不加入offset偏移量,便宜量则通过各级节点高度来计算。
4.位置优化
有些节点在绘制的时候,可能高于每个值,或者占了别的节点位置,这个时候就得优化位置,我暂采用,一个数据去计算每级的最高位置,然后只和这个位置进行比较。这种做法有个缺点就是只能向下绘制,即使节点中间有位置,也没办法把下一节点方进去。
5.递归
不难发现代码中每个节点都是由上一个节点绘制出来,所以代码中只要处理一个节点,然后递归调用即可。
6.节点擦除
因为可能会擦除节点,所以要尽可能记录每个节点,这样才方便擦除。这里暂时使用堆栈去记录,你可以理解成它是一个数组。
实现
几个要点讲完了,下面就一步一步实现,主要还是多扯思路。
1.节点开场有个动画,动画代码如下:
ScaleAnimation animation = new ScaleAnimation(0.0f,1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, Animation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF, 0.5f,
Animation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF, 0.5f);
animation.setInterpolator(new BounceInterpolator());
animation.setStartOffset(tree_current == 1 ? 1050 : 50);// 动画秒数。
animation.setFillAfter(true);
animation.setDuration(700);2.定义节点实体类,根据实际需求来定义
public class nodechild {
private String id;
private String name;
private String buteid;
private String butetype;
private String nodetype;
private String ispass;
public String getNodetype() {
return nodetype;
}
public void setNodetype(String nodetype) {
this.nodetype = nodetype;
}
public nodechild(String id, String name, String buteid, String butetype, String nodetype) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.buteid = buteid;
this.butetype = butetype;
this.nodetype = nodetype;
}
public nodechild(String id, String name) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
public nodechild(String id, String name, String ispass) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.ispass = ispass;
}
public String getIspass() {
return ispass;
}
public void setIspass(String ispass) {
this.ispass = ispass;
}
public String getButeid() {
return buteid;
}
public void setButeid(String buteid) {
this.buteid = buteid;
}
public String getButetype() {
return butetype;
}
public void setButetype(String butetype) {
this.butetype = butetype;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}3.设计drawbutton绘制一个button的方法
public void drawbutton(int button_y, int button_x, int line_x, final int tree_h, final nodechild[] nc,String nodeid) {}button_x为当前节点x坐标
button_y为当前节点的y坐标
line_x为线条x坐标
tree_h为树高,即层级
nc为下层节点
nodeid业务中遇到的,代码中可以忽略。
详细代码如下:
public void drawbutton(int button_y, int button_x, int line_x, final int tree_current, final nodechild[] nc, String nodeid) {
// 存储线的起点y坐标
int line_y = button_y;
// 这个只是为了区分业务中偶数层button宽度为300,齐数层为200
button_x = tree_current % 2 == 1 ? button_x : button_x - 100;
// 得到下一层级需要绘制的数量
int num = 1;
if (tree_current != 1) num = nc.length;// 下一层个数
// 得到下一级第一个按钮的y坐标
button_y = button_y - (num - 1) * bt_width / 2;
if (button_y < tree_xnum[tree_current]) {
button_y = tree_xnum[tree_current] + 100;
}
// 移动当前布局到页面中心
if (tree_current > 2) hv.scrollTo(button_x - 400, button_y - 100);
if (tree_xnum[tree_current] < button_y + 200 + (num - 1) * bt_width)
tree_xnum[tree_current] = button_y + 200 + (num - 1) * bt_width;
// 存储下一级首个button坐标
final int button_y_f = button_y;
final int button_x_f = button_x;
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
final int bt_paly_y = bt_width;
int bt_w = tree_current % 2 == 0 ? bt_width : 200;
int bt_h = 200;
// 定义及设置button属性
bt[i] = new Button(NodeActivity.this);
if (tree_current % 2 != 0) {
bt[i].setBackgroundResource(R.drawable.allokbutton);
} else {
bt[i].setBackgroundResource(R.drawable.button33);
}
bt[i].setTextColor(Color.WHITE);
bt[i].setTextSize(15 - (int) Math.sqrt(nc[i].getName().length() - 1));
bt[i].setText(nc[i].getName());
// 定义及设置出场动画
final String nc_id = nc[i].getId();
ScaleAnimation animation = new ScaleAnimation(0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, Animation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF, 0.5f,
Animation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF, 0.5f);
animation.setInterpolator(new BounceInterpolator());
animation.setStartOffset(tree_current == 1 ? 1050 : 50);// 动画秒数。
animation.setFillAfter(true);
animation.setDuration(700);
bt[i].startAnimation(animation);
final int i1 = i;
// 设置监听
bt[i].setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// 如果是擦除模式,擦除其他同级节点及线条
if (model) mstack.pop(tree_current);
// 防止多次点击,偷懒的解决办法
if (((Button)v).getHint() != null) {
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), ((Button)v).getText(), Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
return;
}
((Button)v).setHint("1");
insertLayout.setEnabled(false);
int w = button_y_f + i1 * bt_paly_y;
int h = button_x_f + bt_paly_y / 2 * 3;
getRemoteInfo(w, h, button_y_f + i1 * bt_paly_y, button_x_f, tree_current + 1, nc_id,
nc[i1].getButeid());
}
});
// 把button通过布局add到页面里
layoutParams[i] = new RelativeLayout.LayoutParams(bt_w, bt_h);
layoutParams[i].topMargin = button_y + i * bt_paly_y;
layoutParams[i].leftMargin = button_x;
insertLayout.addView(bt[i], layoutParams[i]);
// 把线绘制到页面里
if (tree_current != 1) {
if (button_y + 100 + i * 300 - (line_y + 100) >= 0) {//为了优化内存,也是醉了
view = new DrawGeometryView(this, 50, 50, button_x + 100 - (line_x + bt_paly_y) + 50 + (tree_current % 2 == 0 ? 100 : 0), button_y + 100 + i * 300
- (line_y + 100) + 50, nc[i].getButetype());
layoutParams1[i] = new RelativeLayout.LayoutParams(Math.abs(line_x - button_x) + 500, 100 + button_y + i * 300 - line_y);
view.invalidate();
layoutParams1[i].topMargin = (line_y + 100) - 50;// line_y-600;//Math.min(line_y+100,button_y+100
layoutParams1[i].leftMargin = (line_x + bt_paly_y) - 50;// line_x+300;
if (tree_current % 2 == 0) layoutParams1[i].leftMargin -= 100;
insertLayout.addView(view, layoutParams1[i]);
} else {
view = new DrawGeometryView(this, 50, -(button_y + 100 + i * 300 - (line_y + 100)) + 50, button_x - line_x - 150 + (tree_current % 2 == 0 ? 100 : 0), 50,
nc[i].getButetype());
layoutParams1[i] = new RelativeLayout.LayoutParams(Math.abs(line_x - button_x) + 500, 100 + Math.abs(button_y + i * 300
- line_y));
view.invalidate();
layoutParams1[i].topMargin = (button_y + 100 + i * 300) - 50;// line_y-600;//Math.min(line_y+100,button_y+100
layoutParams1[i].leftMargin = (line_x + bt_paly_y) - 50;// line_x+300;
if (tree_current % 2 == 0) layoutParams1[i].leftMargin -= 100;
insertLayout.addView(view, layoutParams1[i]);
}
// line入栈
mstack.push(view, tree_current);
}
// button入栈
mstack.push(bt[i], tree_current);
}
}注释写的很全,有一些数值没抽取出来,有点乱,但不影响阅读。
4.划线方法
public class DrawGeometryView extends View {
private int beginx=0;
private int beginy=0;
private int stopx=100;
private int stopy=100;
private int offset=0;
private String word="dd";
/**
*
* @param context
* @param attrs
*/
public DrawGeometryView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
/**
*
* @param context
*/
public DrawGeometryView(Context context,int beginx,int beginy,int stopx,int stopy,String word) {
super(context);
this.beginx=beginx;
this.beginy=beginy;
this.stopx=stopx;
this.stopy=stopy;
if (word==null) word="";
this.word=word;
}
public int Dp2Px(Context context, float dp) {
final float scale = context.getResources().getDisplayMetrics().density;
return (int) (dp * scale + 0.5f);
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
Paint redPaint = new Paint(); // 红色画笔
redPaint.setAntiAlias(true); // 抗锯齿效果,显得绘图平滑
redPaint.setColor(Color.WHITE); // 设置画笔颜色
redPaint.setStrokeWidth(5.0f);// 设置笔触宽度
redPaint.setStyle(Style.STROKE);// 设置画笔的填充类型(完全填充)
redPaint.setTextSize(50);//字体
Path mPath=new Path();
mPath.reset();
//起点
mPath.moveTo(beginx, beginy);
//贝塞尔曲线
mPath.cubicTo(beginx+80, beginy, beginx+80, stopy,stopx-100, stopy);
//画path
canvas.drawPath(mPath, redPaint);
}
}这个方法里还有一些项目里的文字绘制,我删掉了部分代码。
5.堆栈
public class Mystack {
View[] v = new View[1500];
int[] treehigh = new int[1500];
int size = 0;
public void push(View view, int treecurrent) {
size++;
v[size] = view;
treehigh[size] = treecurrent;
}
public void pop(int treecurrent) {
while (treehigh[size] > treecurrent && size > 0) {
if (size > 0) insertLayout.removeView(v[size]);
size--;
}
for (int j = 49; j > treecurrent; j--) {//树高清0
tree_xnum[j] = 0;
}
for (int x = size; x > 0; x--) {
if (treehigh[x] > treecurrent) {
insertLayout.removeView(v[x]);
}//修复栈顶元素被前一层树元素占用bug,但是会浪费少量内存,考虑到内存很小,暂时不优化吧。
if (treehigh[x] == treecurrent) {
try {
((Button) v[x]).setHint(null);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}这段代码主要是用一个数组去存view,其实我应该用SparseArray的,当时随手写了普通数组,后来也懒得改。push把view存入数组,pop遍历后把层级高的view清除并移除元素。
5.至于切换模式的代码,那就简单了,就是一个取非操作
murp_nodemodel_title.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), !model ? "已切换到擦除模式,点击节点会擦除后面节点,赶快试试吧。" : "已切换到正常模式,所有节点在一张图上,赶快试试吧。", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
model = !model;
}
});总结
总体上实现了思维导图的绘制,但是,还有很多地方值得优化,比如节点宽高没有抽取出来;堆栈也需要优化;计算节点占位高度不够严谨;如果大家有时间,可以折腾下哦。
源码地址github.com/qq273681448…
觉得好的话,记得关注我哦!