本篇文章由万云团队编译
原文链接:mp.weixin.qq.com/s/5-O...
如需转载请联系万云官方微信:万云Wancloud
2018年的门刚打开,区块链的火就烧成了火焰山。徐小平放言要拥抱区块链,朋友圈刷屏不止,连上班地铁上都能听到区块链,一夜起,区块链成了茶前饭后的谈资。于是乎,那个经常听到的问题又开始抓耳挠腮:区块链到底是什么鬼?关注的订阅号不停推送“一篇文章让你搞懂区块链”,“三分钟Get区块链”等不尽相同的内容,声音从四面八方聚焦到你耳边。
万云也在思考能为想了解区块链的老铁们做点什么,鉴于已有如此多区块链概念普及文,此次我们不聊枯燥的概念,而是回归区块链“技术”,一步步认真教你获得一个属于自己区块链。放心,只要你稍微懂一点技术,你就可以实现并拥有它。
|| 以下翻译自Daniel van Flymen的《Learn Blockchains by Building One》,有所删改。
|| 原文地址:hackernoon.com/learn-...
前言
概念了解:在开始前你需要知道,区块链是一种按时间将数据区块以顺序相连的方式组合在一起的链式数据结构,并通过密码学来保证其不可篡改和不可伪造的分布式账本。这些区块可以包含交易、文件以及任何你想要的数据,重要的是它们通过哈希链接在一起。
目标读者:可以轻松地阅读和编写一些基本的Python,并且对HTTP有一些了解。
所需工具:Python 3.6+、Flask、Requests:
pip install Flask==0.12.2 requests==2.18.4
除此之外还需安装HTTP工具,如Postman、cURL。
源代码地址:github.com/dvf/blockc.…
第一步:建立区块链
①实现一个Blockchain类
打开一个你常用的文本编辑器或者IDE,新建一个blockchain.py的python文件,并创建一个Blockchain类,在构造函数中创建两个空的队列,一个用于存储区块链,另一个用于存储交易。下面是Blockchain类的模板代码:
class Blockchain(object):
def __init__(self):
self.chain = []
self.current_transactions = []
def new_block(self):
# Creates a new Block and adds it to the chain
pass
def new_transaction(self):
# Adds a new transaction to the list of transactions
pass
@staticmethod
def hash(block):
# Hashes a Block
pass
@property
def last_block(self):
# Returns the last Block in the chain
pass
我们所创建的Blockchain类将用来管理链,它会存储交易,并且提供一些方法来帮助添加新的区块到链。下面是详细的实现方法。
每个区块所包含5个基本属性:index,timestamp (in Unix time),交易列表,工作量证明和前一个区块的哈希值。我们来看一个例子:
block = {
'index': 1,
'timestamp': 1506057125.900785,
'transactions': [
{
'sender': "8527147fe1f5426f9dd545de4b27ee00",
'recipient': "a77f5cdfa2934df3954a5c7c7da5df1f",
'amount': 5,
}
],
'proof': 324984774000,
'previous_hash': "2cf24dba5fb0a30e26e83b2ac5b9e29e1b161e5c1fa7425e73043362938b9824"
}
到这里,我们对于链的概念应该比较清楚了,每个新的区块都会包含上一个区块的哈希值,从而让区块链具有不可篡改的特性。如果攻击者攻击了链中比较靠前的区块,则所有后面的区块将包含不正确的哈希值。如果不能理解,慢慢消化——这是理解区块链技术的核心思想。
②将交易添加到区块
接下来我们实现一个将交易添加到区块的方法,继续看代码:
class Blockchain(object):
...
def new_transaction(self, sender, recipient, amount):
"""
Creates a new transaction to go into the next mined Block
:param sender: <str> Address of the Sender
:param recipient: <str> Address of the Recipient
:param amount: <int> Amount
:return: <int> The index of the Block that will hold this transaction
"""
self.current_transactions.append({
'sender': sender,
'recipient': recipient,
'amount': amount,
})
return self.last_block['index'] + 1
在new_transaction()方法中向列表中添加一笔交易之后,它返回值是本次交易的index,该index会被添加到下一个待挖掘区块,后面在用户提交交易时也会用到。
③建一个新的区块
当Blockchain被实例化后,我们需要创建一个创世区块,同时为我们的创世区块添加一个工作量证明,这是挖矿的结果,我们稍后会详细讨论挖矿。
除了创建创世区块的代码,我们还需要补充new_block(),new_transaction()和hash()的方法:
import hashlib
import json
from time import time
class Blockchain(object):
def __init__(self):
self.current_transactions = []
self.chain = []
# Create the genesis block
self.new_block(previous_hash=1, proof=100)
def new_block(self, proof, previous_hash=None):
"""
Create a new Block in the Blockchain
:param proof: <int> The proof given by the Proof of Work algorithm
:param previous_hash: (Optional) <str> Hash of previous Block
:return: <dict> New Block
"""
block = {
'index': len(self.chain) + 1,
'timestamp': time(),
'transactions': self.current_transactions,
'proof': proof,
'previous_hash': previous_hash or self.hash(self.chain[-1]),
}
# Reset the current list of transactions
self.current_transactions = []
self.chain.append(block)
return block
def new_transaction(self, sender, recipient, amount):
"""
Creates a new transaction to go into the next mined Block
:param sender: <str> Address of the Sender
:param recipient: <str> Address of the Recipient
:param amount: <int> Amount
:return: <int> The index of the Block that will hold this transaction
"""
self.current_transactions.append({
'sender': sender,
'recipient': recipient,
'amount': amount,
})
return self.last_block['index'] + 1
@property
def last_block(self):
return self.chain[-1]
@staticmethod
def hash(block):
"""
Creates a SHA-256 hash of a Block
:param block: <dict> Block
:return: <str>
"""
# We must make sure that the Dictionary is Ordered, or we'll have inconsistent hashes
block_string = json.dumps(block, sort_keys=True).encode()
return hashlib.sha256(block_string).hexdigest()
到此,我们的区块链已经基本上实现了雏形。这时候,你肯定想知道新区块是怎么被挖出来的,也就是我们通常所说的“挖矿”。
④什么是工作量证明?
想了解什么是“挖矿”,就必须理解工作量证明(POW)是什么。区块链上每一个新的区块都来自于工作量证明(POW),POW的目标是计算出一串解决问题的数字,这个结果众所周知是很难计算的,但却十分容易验证,因为网络上的任何人都能够验证这个结果,这是“工作量证明”背后的核心思想。
我们来看一个非常简单的例子帮助理解:
假设整数X乘以另一个整数y的哈希值必须以0结尾,hash(x * y) = ac23dc...0. 设x = 5.求y。我们用Python来实现:
from hashlib import sha256
x = 5
y = 0 # We don't know what y should be yet...
while sha256(f'{x*y}'.encode()).hexdigest()[-1] != "0":
y += 1
print(f'The solution is y = {y}')
得到的答案是当y = 21,哈希值的结尾为0:
hash(5 * 21) = 1253e9373e...5e3600155e860
在比特币中,工作证明算法被称为Hashcash,这和我们上面所举的例子差不多,结果难于发现却易于校验。Hashcash是矿工为了创建一个新区块而争相计算的问题,计算难度通常取决于字符串中搜索的字符数,通常也会花费一定的时间才能计算得到,最终计算出来的矿工们会通过交易获得一定数量的比特币作为奖励。
⑤实现一个基本的工作量证明
首先我们为Blockchain类实现一个类似的算法:
规则:找到一个数字p,使得它与前一个区块的 proof 拼接成的字符串的 Hash 值以 4 个零开头。
import hashlib
import json
from time import time
from uuid import uuid4
class Blockchain(object):
...
def proof_of_work(self, last_proof):
"""
Simple Proof of Work Algorithm:
- Find a number p' such that hash(pp') contains leading 4 zeroes, where p is the previous p'
- p is the previous proof, and p' is the new proof
:param last_proof: <int>
:return: <int>
"""
proof = 0
while self.valid_proof(last_proof, proof) is False:
proof += 1
return proof
@staticmethod
def valid_proof(last_proof, proof):
"""
Validates the Proof: Does hash(last_proof, proof) contain 4 leading zeroes?
:param last_proof: <int> Previous Proof
:param proof: <int> Current Proof
:return: <bool> True if correct, False if not.
"""
guess = f'{last_proof}{proof}'.encode()
guess_hash = hashlib.sha256(guess).hexdigest()
return guess_hash[:4] == "0000"
通过修改前导零的数量,可以调整算法的难度,但是4个零完全足够了。你会发现,每当增加一个前导零,找到一个对应的解决方案与所需的时间之间会产生巨大的差异。
进行到这里,我们的Blockchain类已经基本完成,接下来我们实现HTTP服务进行交互。
第二步:区块链API
我们将使用Python Flask框架,Flask是一个轻量级的Web应用框架,这使我们可以通过web服务来调用Blockchian类。
①创建三个API:
•/ transactions / new为区块创建一个新的交易
•/mine告诉我们的服务器开采新的区块。
•/chain返回整个区块链。
②使用Flask
我们的“服务器”将基于Flask框架来实现区块链网络中的一个节点。 我们来添加一些模板代码:
import hashlib
import json
from textwrap import dedent
from time import time
from uuid import uuid4
from flask import Flask
class Blockchain(object):
...
# Instantiate our Node
app = Flask(__name__)
# Generate a globally unique address for this node
node_identifier = str(uuid4()).replace('-', '')
# Instantiate the Blockchain
blockchain = Blockchain()
@app.route('/mine', methods=['GET'])
def mine():
return "We'll mine a new Block"
@app.route('/transactions/new', methods=['POST'])
def new_transaction():
return "We'll add a new transaction"
@app.route('/chain', methods=['GET'])
def full_chain():
response = {
'chain': blockchain.chain,
'length': len(blockchain.chain),
}
return jsonify(response), 200
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(host='0.0.0.0', port=5000)
以下是对上面添加的内容的进行简要说明:
Line15:实例化Flask web服务节点。
Line18:为我们的服务节点创建一个随机的名称。
Line21:实例化Blockchain类。
Line24-26:创建一个路由为/mine的GET请求的,调用后端Blockchain的new block方法。
Line28-30:创建一个路由为/transactions/new的POST请求,将数据发送给后端Blockchina的new transaction方法。
Line32-38:创建一个路由为/chain的GET请求,将返回整个链。
Line40-41:在端口5000上运行服务器。
③实现交易
下面是用户发起交易时发送到服务器的请求:
{
"sender": "my address",
"recipient": "someone else's address",
"amount": 5
}
由于我们已经有了将交易添加到区块的方法,接下去就十分容易了。
下面我们来实现添加交易的函数:
import hashlib
import json
from textwrap import dedent
from time import time
from uuid import uuid4
from flask import Flask, jsonify, request
...
@app.route('/transactions/new', methods=['POST'])
def new_transaction():
values = request.get_json()
# Check that the required fields are in the POST'ed data
required = ['sender', 'recipient', 'amount']
if not all(k in values for k in required):
return 'Missing values', 400
# Create a new Transaction
index = blockchain.new_transaction(values['sender'], values['recipient'], values['amount'])
response = {'message': f'Transaction will be added to Block {index}'}
return jsonify(response), 201
④实现挖矿
我们的挖矿方法是魔法发生的地方。它十分容易,只做三件事情:计算工作量证明;通过新增一笔交易奖励矿工一定数量的比特币;创建新的区块并将其添加到链中来。
import hashlib
import json
from time import time
from uuid import uuid4
from flask import Flask, jsonify, request
...
@app.route('/mine', methods=['GET'])
def mine():
# We run the proof of work algorithm to get the next proof...
last_block = blockchain.last_block
last_proof = last_block['proof']
proof = blockchain.proof_of_work(last_proof)
# We must receive a reward for finding the proof.
# The sender is "0" to signify that this node has mined a new coin.
blockchain.new_transaction(
sender="0",
recipient=node_identifier,
amount=1,
)
# Forge the new Block by adding it to the chain
previous_hash = blockchain.hash(last_block)
block = blockchain.new_block(proof, previous_hash)
response = {
'message': "New Block Forged",
'index': block['index'],
'transactions': block['transactions'],
'proof': block['proof'],
'previous_hash': block['previous_hash'],
}
return jsonify(response), 200
需要注意的是,开采块的交易接收者是我们自己服务器节点的地址,我们在这里所做的大部分工作只是与Blockchain类进行交互,基于以上我们区块链已经完成了,接下来开始交互演示。
第三步:交互演示
您可以使用cURL或Postman与API进行交互。
启动服务器:
$ python blockchain.py
* Running on http://127.0.0.1:5000/ (Press CTRL+C to quit)
尝试通过向http:// localhost:5000 / mine发出GET请求来挖掘区块:
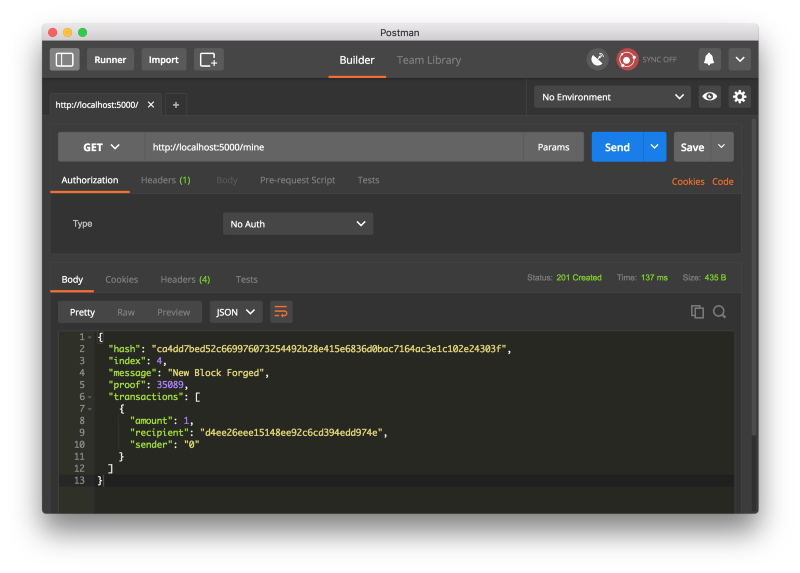
创建一个新的交易,向http://localhost:5000/transactions/new发出一个POST请求:
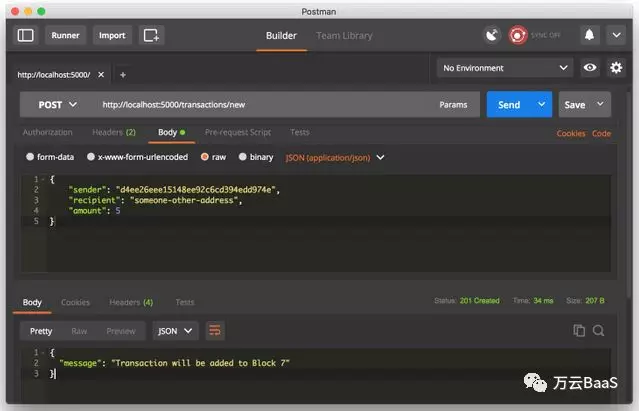
也可以使用cURL发送请求:
$ curl -X POST -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{
"sender": "d4ee26eee15148ee92c6cd394edd974e",
"recipient": "someone-other-address",
"amount": 5
}' "http://localhost:5000/transactions/new"
以上仅为交互演示的示例,你可以在你自己所完成的区块链上进行更多尝试。
第四步:共识机制
我们有一个基本的区块链可以进行交易和挖矿,但其实区块链更重要的意义在于它们是分布式的。那么我们需要确保所有的节点都运行在同一条链上,这就是回归到了共识问题,如果要满足在网络上有多个节点并且不断增加,我们必须要实现共识算法。
①注册新的节点
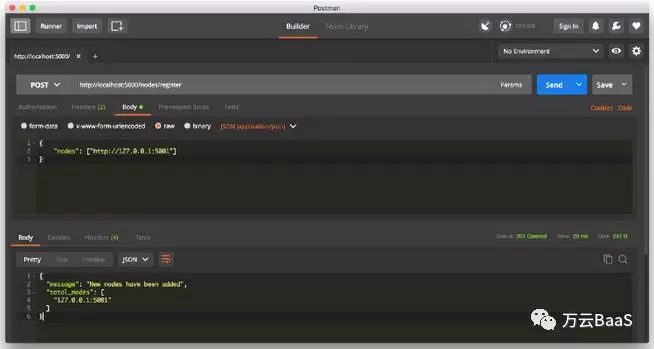
在实现共识算法之前,需要找到一种方式让网络上的节点知道其相邻的节点,每个节点都需要存储网络上其他节点的记录。因此,我们需要新增几个方法来帮助实现:
1./nodes/register接受URL形式的新节点列表。
- / nodes / resolve来执行我们的共识算法,它可以解决任何冲突,确保节点具有正确的链。
下面我们将修改Blockchain的构造函数以提供注册节点的方法:
...
from urllib.parse import urlparse
...
class Blockchain(object):
def __init__(self):
...
self.nodes = set()
...
def register_node(self, address):
"""
Add a new node to the list of nodes
:param address: <str> Address of node. Eg. 'http://192.168.0.5:5000'
:return: None
"""
parsed_url = urlparse(address)
self.nodes.add(parsed_url.netloc)
注意,我们使用set()集合来保存节点列表,这是确保新节点的添加是幂等的简便方法,这意味着无论我们添加特定节点多少次,它都只会出现一次。
②实现共识算法
如前所述,当一个节点与另一个节点有不同时会发生冲突,为了解决这个问题,我们遵循取最长链原则,通过使用此算法,让网络中的节点间达成共识。
...
import requests
class Blockchain(object)
...
def valid_chain(self, chain):
"""
Determine if a given blockchain is valid
:param chain: <list> A blockchain
:return: <bool> True if valid, False if not
"""
last_block = chain[0]
current_index = 1
while current_index < len(chain):
block = chain[current_index]
print(f'{last_block}')
print(f'{block}')
print("\n-----------\n")
# Check that the hash of the block is correct
if block['previous_hash'] != self.hash(last_block):
return False
# Check that the Proof of Work is correct
if not self.valid_proof(last_block['proof'], block['proof']):
return False
last_block = block
current_index += 1
return True
def resolve_conflicts(self):
"""
This is our Consensus Algorithm, it resolves conflicts
by replacing our chain with the longest one in the network.
:return: <bool> True if our chain was replaced, False if not
"""
neighbours = self.nodes
new_chain = None
# We're only looking for chains longer than ours
max_length = len(self.chain)
# Grab and verify the chains from all the nodes in our network
for node in neighbours:
response = requests.get(f'http://{node}/chain')
if response.status_code == 200:
length = response.json()['length']
chain = response.json()['chain']
# Check if the length is longer and the chain is valid
if length > max_length and self.valid_chain(chain):
max_length = length
new_chain = chain
# Replace our chain if we discovered a new, valid chain longer than ours
if new_chain:
self.chain = new_chain
return True
return False
valid_chain()负责检查一个链是否有效,具体方法是循环读取每个区块并验证哈希和证明。
resolve_conflicts()负责循环读取所有相邻节点,获取它们的链并使用上面的方法验证它们的有效性。如果找到了一个更长的有效链,则取代我们当前的链。
我们将两个方法注册到我们的API中,一个用于添加相邻节点,另一个用于解决冲突:
@app.route('/nodes/register', methods=['POST'])
def register_nodes():
values = request.get_json()
nodes = values.get('nodes')
if nodes is None:
return "Error: Please supply a valid list of nodes", 400
for node in nodes:
blockchain.register_node(node)
response = {
'message': 'New nodes have been added',
'total_nodes': list(blockchain.nodes),
}
return jsonify(response), 201
@app.route('/nodes/resolve', methods=['GET'])
def consensus():
replaced = blockchain.resolve_conflicts()
if replaced:
response = {
'message': 'Our chain was replaced',
'new_chain': blockchain.chain
}
else:
response = {
'message': 'Our chain is authoritative',
'chain': blockchain.chain
}
return jsonify(response), 200
最后,如果你愿意的话可以开启另一台机器,并在你的网络上运转不同的节点。或者使用同一台机器上的不同端口启动进程。我在我的机器的不同端口创建另外一个节点,并将其注册到当前区块链网络中。 因此,我有两个节点:http:// localhost:5000和http:// localhost:5001。
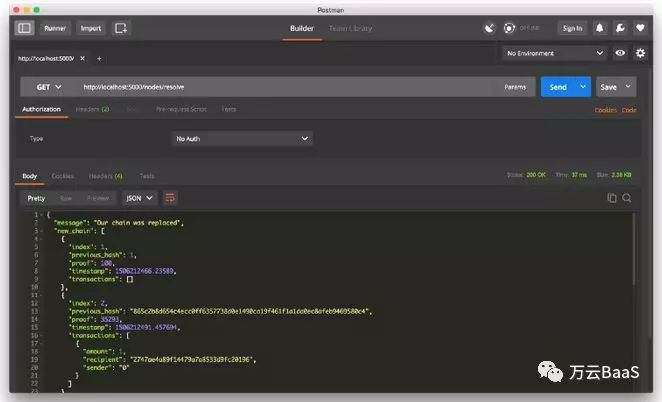
为了确保链更长,我在节点2上挖掘了一些新的区块。 之后,我在节点1上调用GET / nodes / resolve,此处的链已经被共识算法计算后的得到的新链所替代。
现在,你可以邀请一些朋友来一起测试你的区块链了。
本文教程到此结束,那么,属于你自己的区块链撸好了吗?别忘了分享给身边同为程序员的朋友,一起来撸区块链!
本篇文章由万云团队编译,如需转载请联系万云官方微信:万云Wancloud