关于作者
郭孝星,程序员,吉他手,主要从事Android平台基础架构方面的工作,欢迎交流技术方面的问题,可以去我的Github提issue或者发邮件至guoxiaoxingse@163.com与我交流。
文章目录
- 一 VirtualAPK的初始化流程
- 二 VirtualAPK的的加载流程
- 三 VirtualAPK启动组件的流程
- 3.1 Activity
- 3.2 Service
- 3.3 Broadcast Receiver
- 3.4 Content Provider
更多Android开源框架源码分析文章请参见Android open framwork analysis。
从2012年开始,插件化技术得到了很大的发展,究其原因,主要是因为随着业务的增长,主工程变得越来越难以维护,而且随着公司业务的扩展,原来的主应用也逐渐分化了多个子应用,研发团队也由 一个变成多个,但是子应用仍然需要主应用的流量入口优势,种种业务场景的需求,极大地促进了插件化技术的发展。
就目前而言,主流的插件化框架有以下几种:
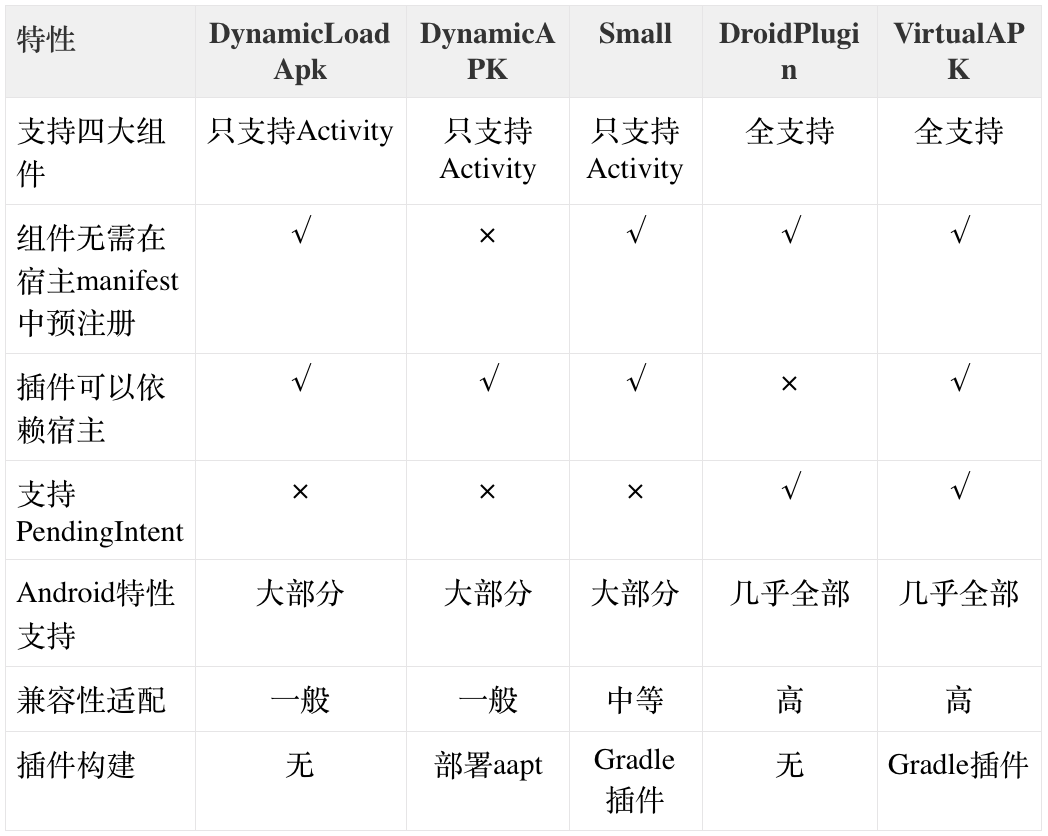
从上图对比可以看出,有着不错的表现的重点是360的DroidPlugin框架和滴滴的VirtualAPK框架,这两家公司的业务类型不同,导致了这两套框架的侧重点也有所不同,具体说来:
- DroidPlugin:DroidPlugin侧重于加载第三方独立插件,例如微信,并且插件不能访问宿主的代码和资源。这也比较符合260应用市场的业务特点。
- VirtualAPK:VirtualAPK侧重于加载业务模块,业务模块通常和宿主都有一定的耦合关系,例如需要访问宿主提供的订单、账号等数据信息等,这也比较符合滴滴业务型的业务特点。
也就是说如果我们需要去加载一个内部业务模块,并且这个业务模块很难从主工程中完全解耦,那么我们会优先选择VirtualAPK这种方案。
A powerful and lightweight plugin framework for Android
官方网站:https://github.com/didi/VirtualAPK
源码版本:0.9.1
按照国际惯例,在分析VirtualAPK的源码实现之前,先吹一波它的优点😎。如下所示:
完善的功能
- Activity:支持显示和隐式调用,支持Activity的theme和LaunchMode,支持透明主题;
- Service:支持显示和隐式调用,支持Service的start、stop、bind和unbind,并支持跨进程bind插件中的Service;
- Receiver:支持静态注册和动态注册的Receiver;
- ContentProvider:支持provider的所有操作,包括CRUD和call方法等,支持跨进程访问插件中的Provider。
- 自定义View:支持自定义View,支持自定义属性和style,支持动画;
- PendingIntent:支持PendingIntent以及和其相关的Alarm、Notification和AppWidget;
- 支持插件Application以及插件manifest中的meta-data;
- 支持插件中的so。
优秀的兼容性
- 兼容市面上几乎所有的Android手机,这一点已经在滴滴出行客户端中得到验证;
- 资源方面适配小米、Vivo、Nubia等,对未知机型采用自适应适配方案;
- 极少的Binder Hook,目前仅仅hook了两个Binder:AMS和IContentProvider,hook过程做了充分的兼容性适配;
- 插件运行逻辑和宿主隔离,确保框架的任何问题都不会影响宿主的正常运行。
极低的入侵性
- 插件开发等同于原生开发,四大组件无需继承特定的基类;
- 精简的插件包,插件可以依赖宿主中的代码和资源,也可以不依赖;
- 插件的构建过程简单,通过Gradle插件来完成插件的构建,整个过程对开发者透明。
👉 注:吹了这么多,其实这套框架还是有瑕疵的,具体的问题,在分析源码的时候我们会讲。
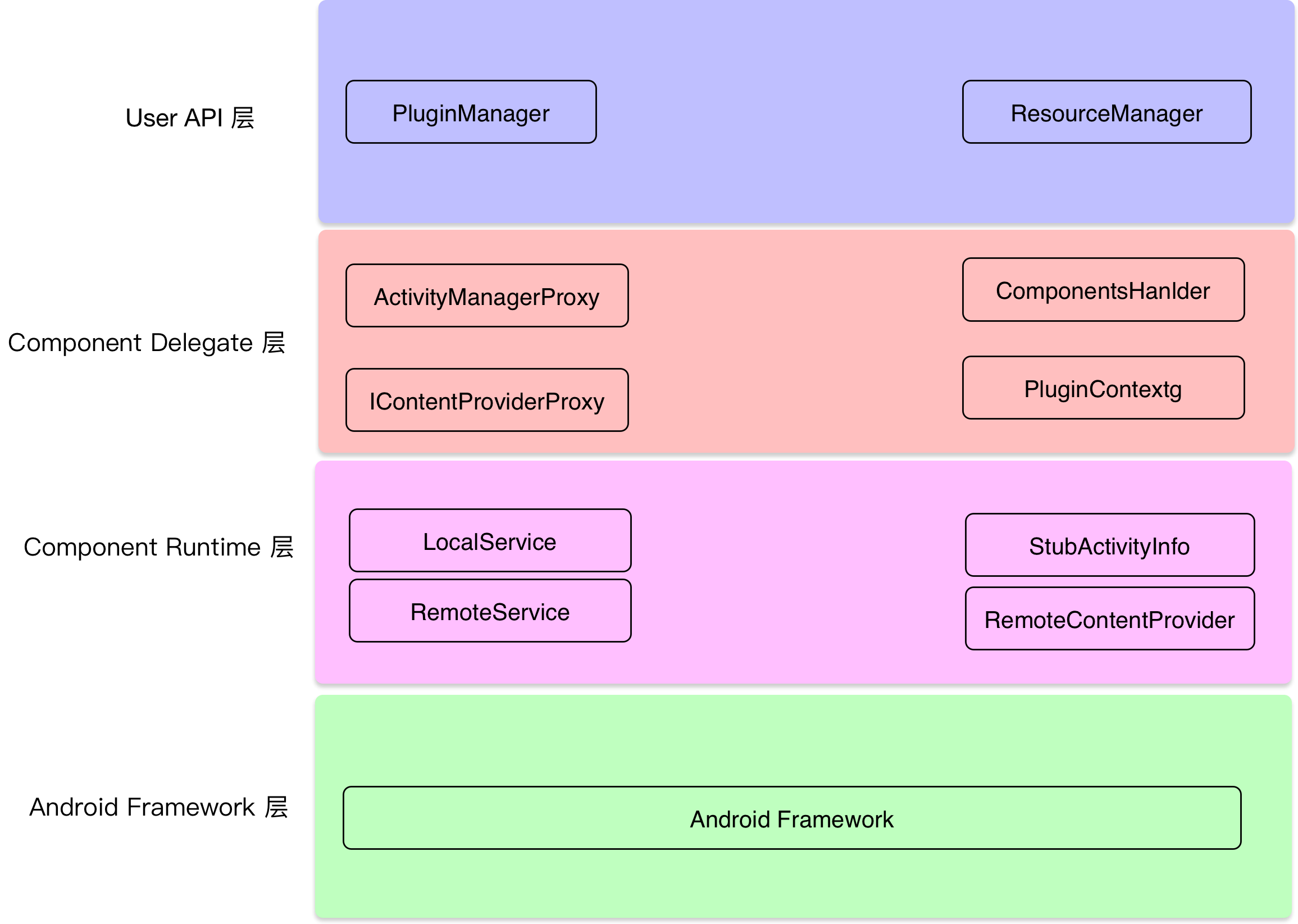
要理解一套框架,首先需要从整体去把握它,理解它的构造和层次划分,然后逐个去分析,VirtualAPK的整体架构图如下图所示:
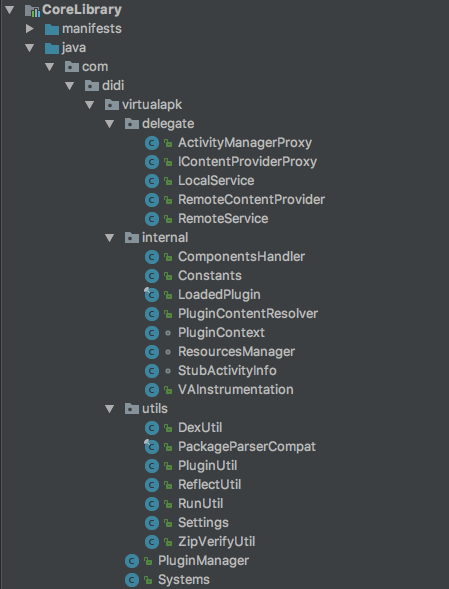
整体的源码结构也并不复杂,如下图所示:
一 VirtualAPK的初始化流程
在使用VirtualAPK之前,我们需要多VirtualAPK进行初始化,如下所示:
@Override
protected void attachBaseContext(Context base) {
super.attachBaseContext(base);
PluginManager.getInstance(base).init();
}
我们来分析了一下VirtualAPK初始化的过程中做了哪些事情,如下所示:
public class PluginManager {
private PluginManager(Context context) {
Context app = context.getApplicationContext();
// 获取Context
if (app == null) {
this.mContext = context;
} else {
this.mContext = ((Application)app).getBaseContext();
}
//初始化
prepare();
}
private void prepare() {
Systems.sHostContext = getHostContext();
//1. hook对象Instrumentation。
this.hookInstrumentationAndHandler();
//2. 根据不同的Android版本分别从ActivityManagerNative中Hook对象IActivityManager。
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= 26) {
this.hookAMSForO();
} else {
this.hookSystemServices();
}
}
}
}
可以发现VirtualAPK在初始化的时候主要hook了两个对象,如下所示:
- hook对象Instrumentation。
- 根据不同的Android版本分别从ActivityManagerNative中Hook对象IActivityManager。
首先是Instrumentation对象。为什么要hook这个对象呢?🤔这是因为Instrumentation对象在启动Activity会有一套校验过程,其中一条就是检查Activity有没有在Manifest文件中进行注册,如下所示:
public class Instrumentation {
public static void checkStartActivityResult(int res, Object intent) {
if (res >= ActivityManager.START_SUCCESS) {
return;
}
switch (res) {
case ActivityManager.START_INTENT_NOT_RESOLVED:
case ActivityManager.START_CLASS_NOT_FOUND:
if (intent instanceof Intent && ((Intent)intent).getComponent() != null)
throw new ActivityNotFoundException(
"Unable to find explicit activity class "
+ ((Intent)intent).getComponent().toShortString()
+ "; have you declared this activity in your AndroidManifest.xml?");
throw new ActivityNotFoundException(
"No Activity found to handle " + intent);
case ActivityManager.START_PERMISSION_DENIED:
throw new SecurityException("Not allowed to start activity "
+ intent);
case ActivityManager.START_FORWARD_AND_REQUEST_CONFLICT:
throw new AndroidRuntimeException(
"FORWARD_RESULT_FLAG used while also requesting a result");
case ActivityManager.START_NOT_ACTIVITY:
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"PendingIntent is not an activity");
case ActivityManager.START_NOT_VOICE_COMPATIBLE:
throw new SecurityException(
"Starting under voice control not allowed for: " + intent);
case ActivityManager.START_NOT_CURRENT_USER_ACTIVITY:
// Fail silently for this case so we don't break current apps.
// TODO(b/22929608): Instead of failing silently or throwing an exception,
// we should properly position the activity in the stack (i.e. behind all current
// user activity/task) and not change the positioning of stacks.
Log.e(TAG,
"Not allowed to start background user activity that shouldn't be displayed"
+ " for all users. Failing silently...");
break;
default:
throw new AndroidRuntimeException("Unknown error code "
+ res + " when starting " + intent);
}
}
}
这些异常信息多半我们都很熟悉,其中have you declared this activity in your AndroidManifest.xml,就是没有注册Activity所报的异常,hook对象Instrumentation,然后替换掉里面相应 的方法,来达到绕过检查的目的,我们来看看hook的流程,如下所示:
public class PluginManager {
private void hookInstrumentationAndHandler() {
try {
Instrumentation baseInstrumentation = ReflectUtil.getInstrumentation(this.mContext);
if (baseInstrumentation.getClass().getName().contains("lbe")) {
// reject executing in paralell space, for example, lbe.
System.exit(0);
}
//自定义的VAInstrumentation重写了newActivity()等逻辑。Instrumentation对象也被保存了下载
final VAInstrumentation instrumentation = new VAInstrumentation(this, baseInstrumentation);
//获取ctivityThread实例
Object activityThread = ReflectUtil.getActivityThread(this.mContext);
//用自定义的VAInstrumentation重对象替换掉ActivityThread里的Instrumentation对象
ReflectUtil.setInstrumentation(activityThread, instrumentation);
ReflectUtil.setHandlerCallback(this.mContext, instrumentation);
this.mInstrumentation = instrumentation;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
在文章03Android组件框架:Android视图容器Activity中,我们提到 过Instrumentation对象用来监控应用与系统的交互行为,Activity的创建也是在Instrumentation对象里完成的,之所以要hook这个对象就是为了修改Activity创建逻辑。
这里用自定义的VAInstrumentation重对象替换掉ActivityThread里的Instrumentation对象,这样当系统启动Activity调用Instrumentation的newActivity()方法的时候就会调用自定义的VAInstrumentation 里面的newActivity()方法。
public class PluginManager {
// Android API 26及其以上
private void hookAMSForO() {
try {
Singleton<IActivityManager> defaultSingleton = (Singleton<IActivityManager>) ReflectUtil.getField(ActivityManager.class, null, "IActivityManagerSingleton");
IActivityManager activityManagerProxy = ActivityManagerProxy.newInstance(this, defaultSingleton.get());
ReflectUtil.setField(defaultSingleton.getClass().getSuperclass(), defaultSingleton, "mInstance", activityManagerProxy);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// Android API 26以下
private void hookSystemServices() {
try {
Singleton<IActivityManager> defaultSingleton = (Singleton<IActivityManager>) ReflectUtil.getField(ActivityManagerNative.class, null, "gDefault");
IActivityManager activityManagerProxy = ActivityManagerProxy.newInstance(this, defaultSingleton.get());
//从ActivityManagerNative中Hook对象IActivityManager
ReflectUtil.setField(defaultSingleton.getClass().getSuperclass(), defaultSingleton, "mInstance", activityManagerProxy);
if (defaultSingleton.get() == activityManagerProxy) {
this.mActivityManager = activityManagerProxy;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
除了Instrumentation对象,它还根据不同的Android版本分别从ActivityManagerNative中Hook对象IActivityManager,那么这个IActivityManager对象是什么呢?🤔
我们之前在文章02Android组件框架:Android组件管理者ActivityManager中 曾经聊到过它是ActivityManagerService的代理对象,通过它可以和ActivityManagerService进行IPC通信,并请求它完成一些组件管理上的工作。我们平时调用的startActivity()、startService()、bindService()等组件调用的方法 最终都是调用ActivityManagerService里的方法来完成的。
以上便是VIrtualAPK的初始化流程,我们接着来看VIrtualAPK是如何去加载一个APK文件的。👇
二 VirtualAPK的的加载流程
VirtualAPK对于加载的APK文件没有额外的约束,只需要添加VirtualAPK的插件进行编译,如下所示:
apply plugin: 'com.didi.virtualapk.plugin'
virtualApk {
packageId = 0x6f // The package id of Resources.
targetHost='source/host/app' // The path of application module in host project.
applyHostMapping = true // [Optional] Default value is true.
}
然后就可以调用PluginManager直接加载编译完成的APK,被加载的APK在PluginManager里是一个LoadedPlugin对象,VirtualAPK通过这些LoadedPlugin对象来管理APK,这些APK也可以 想在手机里直接安装的App一样运行。
String pluginPath = Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory().getAbsolutePath().concat("/Test.apk");
File plugin = new File(pluginPath);
PluginManager.getInstance(base).loadPlugin(plugin);
APK的加载流程如下图所示:
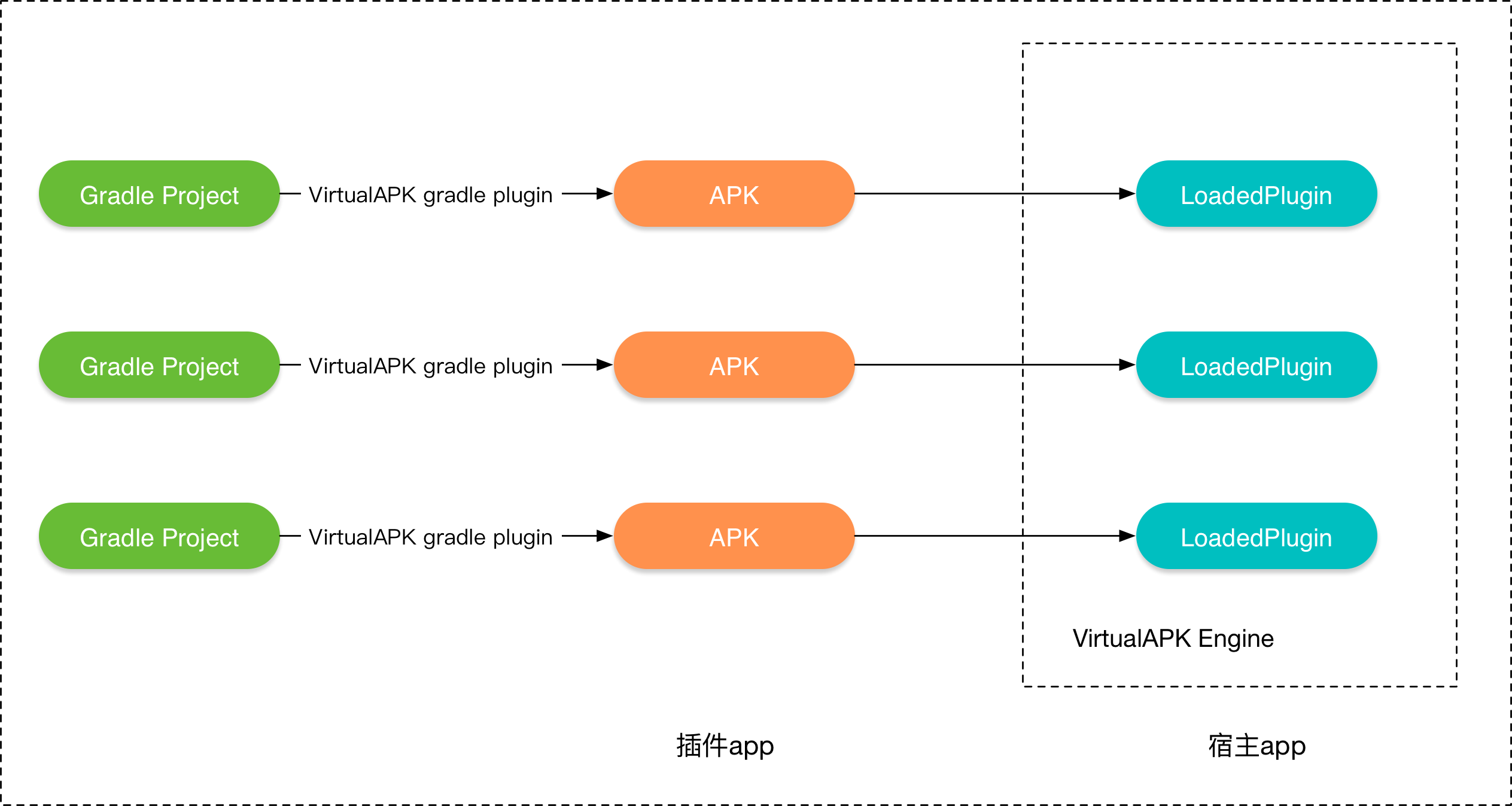
我们可以看到上面调用loadPlugin()方法去加载一个APK,我们来看一下它的实现。
public class PluginManager {
public void loadPlugin(File apk) throws Exception {
if (null == apk) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("error : apk is null.");
}
if (!apk.exists()) {
throw new FileNotFoundException(apk.getAbsolutePath());
}
// 1. 加载APK文件
LoadedPlugin plugin = LoadedPlugin.create(this, this.mContext, apk);
if (null != plugin) {
this.mPlugins.put(plugin.getPackageName(), plugin);
// try to invoke plugin's application
// 2. 尝试调用APK
plugin.invokeApplication();
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("Can't load plugin which is invalid: " + apk.getAbsolutePath());
}
}
}
这里调用了LoadedPlugin的create()方法去构建一个LoadedPlugin对象,所以的初始化操作都是在LoadedPlugin的构造方法里完成的,如下所示:
public final class LoadedPlugin {
LoadedPlugin(PluginManager pluginManager, Context context, File apk) throws PackageParser.PackageParserException {
this.mPluginManager = pluginManager;
this.mHostContext = context;
this.mLocation = apk.getAbsolutePath();
// 1. 调用PackageParser解析APK,获取PackageParser.Package对象。
this.mPackage = PackageParserCompat.parsePackage(context, apk, PackageParser.PARSE_MUST_BE_APK);
this.mPackage.applicationInfo.metaData = this.mPackage.mAppMetaData;
// 2. 构建PackageInfo对象。
this.mPackageInfo = new PackageInfo();
this.mPackageInfo.applicationInfo = this.mPackage.applicationInfo;
this.mPackageInfo.applicationInfo.sourceDir = apk.getAbsolutePath();
this.mPackageInfo.signatures = this.mPackage.mSignatures;
this.mPackageInfo.packageName = this.mPackage.packageName;
if (pluginManager.getLoadedPlugin(mPackageInfo.packageName) != null) {
throw new RuntimeException("plugin has already been loaded : " + mPackageInfo.packageName);
}
this.mPackageInfo.versionCode = this.mPackage.mVersionCode;
this.mPackageInfo.versionName = this.mPackage.mVersionName;
this.mPackageInfo.permissions = new PermissionInfo[0];
// 3. 构建PluginPackageManager对象。
this.mPackageManager = new PluginPackageManager();
this.mPluginContext = new PluginContext(this);
this.mNativeLibDir = context.getDir(Constants.NATIVE_DIR, Context.MODE_PRIVATE);
// 4. 构建Resouces对象。
this.mResources = createResources(context, apk);
// 5. 构建ClassLoader对象。
this.mClassLoader = createClassLoader(context, apk, this.mNativeLibDir, context.getClassLoader());
// 6. 拷贝so库。
tryToCopyNativeLib(apk);
// 7. 缓存Instrumentation对象。
Map<ComponentName, InstrumentationInfo> instrumentations = new HashMap<ComponentName, InstrumentationInfo>();
for (PackageParser.Instrumentation instrumentation : this.mPackage.instrumentation) {
instrumentations.put(instrumentation.getComponentName(), instrumentation.info);
}
this.mInstrumentationInfos = Collections.unmodifiableMap(instrumentations);
this.mPackageInfo.instrumentation = instrumentations.values().toArray(new InstrumentationInfo[instrumentations.size()]);
// 8. 缓存APK里的Activity信息。
Map<ComponentName, ActivityInfo> activityInfos = new HashMap<ComponentName, ActivityInfo>();
for (PackageParser.Activity activity : this.mPackage.activities) {
activityInfos.put(activity.getComponentName(), activity.info);
}
this.mActivityInfos = Collections.unmodifiableMap(activityInfos);
this.mPackageInfo.activities = activityInfos.values().toArray(new ActivityInfo[activityInfos.size()]);
// 9. 缓存APK里的Service信息。
Map<ComponentName, ServiceInfo> serviceInfos = new HashMap<ComponentName, ServiceInfo>();
for (PackageParser.Service service : this.mPackage.services) {
serviceInfos.put(service.getComponentName(), service.info);
}
this.mServiceInfos = Collections.unmodifiableMap(serviceInfos);
this.mPackageInfo.services = serviceInfos.values().toArray(new ServiceInfo[serviceInfos.size()]);
// 10. 缓存APK里的Content Provider信息。
Map<String, ProviderInfo> providers = new HashMap<String, ProviderInfo>();
Map<ComponentName, ProviderInfo> providerInfos = new HashMap<ComponentName, ProviderInfo>();
for (PackageParser.Provider provider : this.mPackage.providers) {
providers.put(provider.info.authority, provider.info);
providerInfos.put(provider.getComponentName(), provider.info);
}
this.mProviders = Collections.unmodifiableMap(providers);
this.mProviderInfos = Collections.unmodifiableMap(providerInfos);
this.mPackageInfo.providers = providerInfos.values().toArray(new ProviderInfo[providerInfos.size()]);
// 11. 将静态的广播转为动态的。
Map<ComponentName, ActivityInfo> receivers = new HashMap<ComponentName, ActivityInfo>();
for (PackageParser.Activity receiver : this.mPackage.receivers) {
receivers.put(receiver.getComponentName(), receiver.info);
try {
BroadcastReceiver br = BroadcastReceiver.class.cast(getClassLoader().loadClass(receiver.getComponentName().getClassName()).newInstance());
for (PackageParser.ActivityIntentInfo aii : receiver.intents) {
this.mHostContext.registerReceiver(br, aii);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
this.mReceiverInfos = Collections.unmodifiableMap(receivers);
this.mPackageInfo.receivers = receivers.values().toArray(new ActivityInfo[receivers.size()]);
}
}
整个LoadedPlugin对象构建的过程就是去解析APK里的组件信息,并缓存起来,具体说来:
- 调用PackageParser解析APK,获取PackageParser.Package对象。
- 构建PackageInfo对象。
- 构建PluginPackageManager对象。
- 构建Resouces对象。
- 构建ClassLoader对象。
- 拷贝so库。
- 缓存Instrumentation对象。
- 缓存APK里的Activity信息。
- 缓存APK里的Service信息。
- 缓存APK里的Content Provider信息。
- 将静态的广播转为动态的。
我们接着来看没有在宿主App的Manifest里注册的四大组件时如何被启动起来的。👇
三 VirtualAPK启动组件的流程
3.1 Activity
前面我们说过在初始化VirtualAPK的过程中使用自定义的VAInstrumentation在ActivityThread中替换掉了原生的Instrumentation对象,来达到hook到Activity启动流程的目的,绕开Instrumentation 启动Activity的校验流程。
那么VirtualAPK是如何绕过系统校验的呢?🤔
Virtual是采用占坑的方式来绕过校验的,它在库里的Manifest文件里定义了占坑的文件,如下所示:
<application>
<!-- Stub Activities -->
<activity android:name=".A$1" android:launchMode="standard"/>
<activity android:name=".A$2" android:launchMode="standard"
android:theme="@android:style/Theme.Translucent" />
<!-- Stub Activities -->
<activity android:name=".B$1" android:launchMode="singleTop"/>
<activity android:name=".B$2" android:launchMode="singleTop"/>
<activity android:name=".B$3" android:launchMode="singleTop"/>
<activity android:name=".B$4" android:launchMode="singleTop"/>
<activity android:name=".B$5" android:launchMode="singleTop"/>
<activity android:name=".B$6" android:launchMode="singleTop"/>
<activity android:name=".B$7" android:launchMode="singleTop"/>
<activity android:name=".B$8" android:launchMode="singleTop"/>
<!-- Stub Activities -->
<activity android:name=".C$1" android:launchMode="singleTask"/>
<activity android:name=".C$2" android:launchMode="singleTask"/>
<activity android:name=".C$3" android:launchMode="singleTask"/>
<activity android:name=".C$4" android:launchMode="singleTask"/>
<activity android:name=".C$5" android:launchMode="singleTask"/>
<activity android:name=".C$6" android:launchMode="singleTask"/>
<activity android:name=".C$7" android:launchMode="singleTask"/>
<activity android:name=".C$8" android:launchMode="singleTask"/>
<!-- Stub Activities -->
<activity android:name=".D$1" android:launchMode="singleInstance"/>
<activity android:name=".D$2" android:launchMode="singleInstance"/>
<activity android:name=".D$3" android:launchMode="singleInstance"/>
<activity android:name=".D$4" android:launchMode="singleInstance"/>
<activity android:name=".D$5" android:launchMode="singleInstance"/>
<activity android:name=".D$6" android:launchMode="singleInstance"/>
<activity android:name=".D$7" android:launchMode="singleInstance"/>
<activity android:name=".D$8" android:launchMode="singleInstance"/>
</application>
A、B、C、D分别代表standard、singleTop、singleTask和singleInstance四种启动模式。
VirtualAPK制造一些假的Activity替身在Manifest文件提前进行注册占坑,在启动真正的Activity时候,再将Activity填到坑里,以完成启动Activity。我们来看看具体的是实现流程:
- execStartActivity()
- realExecStartActivity()
- newActivity()
- callActivityOnCreate()
以上四个方法都是启动Activity的过程中必经的四个方法。
public class VAInstrumentation extends Instrumentation implements Handler.Callback {
public ActivityResult execStartActivity(
Context who, IBinder contextThread, IBinder token, Activity target,
Intent intent, int requestCode, Bundle options) {
//1. 将隐式Intent转换为显式Intent,Virtual是通过intent.setClassName(this, "com.guoxiaoxing.plugin.MainActivity");这种
//方式来启动Activity的,这里将包名封装成真正的ComponentName对象。
mPluginManager.getComponentsHandler().transformIntentToExplicitAsNeeded(intent);
// null component is an implicitly intent
if (intent.getComponent() != null) {
Log.i(TAG, String.format("execStartActivity[%s : %s]", intent.getComponent().getPackageName(),
intent.getComponent().getClassName()));
//2. 用注册过的StubActivity替换掉真实的Activity以便绕过校验。
this.mPluginManager.getComponentsHandler().markIntentIfNeeded(intent);
}
//3. 生成了占坑的StubActivity的Intent。调用realExecStartActivity()方法继续执行Activity的启动,借此绕过校验。
ActivityResult result = realExecStartActivity(who, contextThread, token, target,
intent, requestCode, options);
return result;
}
private ActivityResult realExecStartActivity(
Context who, IBinder contextThread, IBinder token, Activity target,
Intent intent, int requestCode, Bundle options) {
ActivityResult result = null;
try {
Class[] parameterTypes = {Context.class, IBinder.class, IBinder.class, Activity.class, Intent.class,
int.class, Bundle.class};
// 用占坑的StubActivity的Intent去启动Activity,借此绕过校验。
result = (ActivityResult)ReflectUtil.invoke(Instrumentation.class, mBase,
"execStartActivity", parameterTypes,
who, contextThread, token, target, intent, requestCode, options);
} catch (Exception e) {
if (e.getCause() instanceof ActivityNotFoundException) {
throw (ActivityNotFoundException) e.getCause();
}
e.printStackTrace();
}
return result;
}
}
该方法主要做了三件事情,如下所示:
- 将隐式Intent转换为显式Intent,Virtual是通过intent.setClassName(this, "com.guoxiaoxing.plugin.MainActivity");这种 方式来启动Activity的,这里将包名封装成真正的ComponentName对象。
- 用注册过的StubActivity替换掉真实的Activity以便绕过检测。
- 生成了占坑的StubActivity的Intent。调用realExecStartActivity()方法继续执行Activity的启动,借此绕过校验。
其中重点就在于注册过的StubActivity替换掉真实的Activity以便绕过检测,我们来看看它的实现,如下所示:
public class ComponentsHandler {
public void markIntentIfNeeded(Intent intent) {
if (intent.getComponent() == null) {
return;
}
// 包名
String targetPackageName = intent.getComponent().getPackageName();
// 类名
String targetClassName = intent.getComponent().getClassName();
// 搜索对应启动模式的占坑StubActivity
if (!targetPackageName.equals(mContext.getPackageName()) && mPluginManager.getLoadedPlugin(targetPackageName) != null) {
// 做一个插件的标记
intent.putExtra(Constants.KEY_IS_PLUGIN, true);
// 存包名
intent.putExtra(Constants.KEY_TARGET_PACKAGE, targetPackageName);
// 存类名,之所以存储这些信息是为了以后获取真正的Activity的Intent信息去启动真正的Activity。
intent.putExtra(Constants.KEY_TARGET_ACTIVITY, targetClassName);
// 查找StubActivity
dispatchStubActivity(intent);
}
}
private void dispatchStubActivity(Intent intent) {
ComponentName component = intent.getComponent();
String targetClassName = intent.getComponent().getClassName();
// 获取intent对应的LoadedPlugin对象
LoadedPlugin loadedPlugin = mPluginManager.getLoadedPlugin(intent);
// 根据ComponentName信息获取对应的ActivityInfo
ActivityInfo info = loadedPlugin.getActivityInfo(component);
if (info == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("can not find " + component);
}
//启动模式
int launchMode = info.launchMode;
Resources.Theme themeObj = loadedPlugin.getResources().newTheme();
// 替换掉对应的主题
themeObj.applyStyle(info.theme, true);
// 获取对应的StubActivity
String stubActivity = mStubActivityInfo.getStubActivity(targetClassName, launchMode, themeObj);
Log.i(TAG, String.format("dispatchStubActivity,[%s -> %s]", targetClassName, stubActivity));
// 设置StubActivity的全路径名
intent.setClassName(mContext, stubActivity);
}
}
我们来看看具体是如何查询StubActivity的,如下所示:
class StubActivityInfo {
// 标准模式Activity的最大个数
public static final int MAX_COUNT_STANDARD = 1;
// 栈顶复用模式Activity的最大个数
public static final int MAX_COUNT_SINGLETOP = 8;
// 栈内复用模式Activity的最大个数
public static final int MAX_COUNT_SINGLETASK = 8;
// 单例模式Activity的最大个数
public static final int MAX_COUNT_SINGLEINSTANCE = 8;
//那些占坑的Activity的全路径名
public static final String corePackage = "com.didi.virtualapk.core";
public static final String STUB_ACTIVITY_STANDARD = "%s.A$%d";
public static final String STUB_ACTIVITY_SINGLETOP = "%s.B$%d";
public static final String STUB_ACTIVITY_SINGLETASK = "%s.C$%d";
public static final String STUB_ACTIVITY_SINGLEINSTANCE = "%s.D$%d";
public final int usedStandardStubActivity = 1;
public int usedSingleTopStubActivity = 0;
public int usedSingleTaskStubActivity = 0;
public int usedSingleInstanceStubActivity = 0;
private HashMap<String, String> mCachedStubActivity = new HashMap<>();
public String getStubActivity(String className, int launchMode, Theme theme) {
// 1. 先从缓存中查找StuActivity。
String stubActivity= mCachedStubActivity.get(className);
if (stubActivity != null) {
return stubActivity;
}
TypedArray array = theme.obtainStyledAttributes(new int[]{
android.R.attr.windowIsTranslucent,
android.R.attr.windowBackground
});
boolean windowIsTranslucent = array.getBoolean(0, false);
array.recycle();
if (Constants.DEBUG) {
Log.d("StubActivityInfo", "getStubActivity, is transparent theme ? " + windowIsTranslucent);
}
// 标准启动模式:com.didi.virtualapk.core.A$1
stubActivity = String.format(STUB_ACTIVITY_STANDARD, corePackage, usedStandardStubActivity);
switch (launchMode) {
case ActivityInfo.LAUNCH_MULTIPLE: {
// 标准启动模式:com.didi.virtualapk.core.$1,每次自增1
stubActivity = String.format(STUB_ACTIVITY_STANDARD, corePackage, usedStandardStubActivity);
if (windowIsTranslucent) {
stubActivity = String.format(STUB_ACTIVITY_STANDARD, corePackage, 2);
}
break;
}
case ActivityInfo.LAUNCH_SINGLE_TOP: {
// 栈顶复用模式:com.didi.virtualapk.core.$,每次自增1,范围从1 - 8.
usedSingleTopStubActivity = usedSingleTopStubActivity % MAX_COUNT_SINGLETOP + 1;
stubActivity = String.format(STUB_ACTIVITY_SINGLETOP, corePackage, usedSingleTopStubActivity);
break;
}
case ActivityInfo.LAUNCH_SINGLE_TASK: {
// 栈内模式:com.didi.virtualapk.core.C$,每次自增1,范围从1 - 8.
usedSingleTaskStubActivity = usedSingleTaskStubActivity % MAX_COUNT_SINGLETASK + 1;
stubActivity = String.format(STUB_ACTIVITY_SINGLETASK, corePackage, usedSingleTaskStubActivity);
break;
}
case ActivityInfo.LAUNCH_SINGLE_INSTANCE: {
// 单例模式模式:com.didi.virtualapk.core.D$,每次自增1,范围从1 - 8.
usedSingleInstanceStubActivity = usedSingleInstanceStubActivity % MAX_COUNT_SINGLEINSTANCE + 1;
stubActivity = String.format(STUB_ACTIVITY_SINGLEINSTANCE, corePackage, usedSingleInstanceStubActivity);
break;
}
default:break;
}
// 将查找到的Activity放到缓存中
mCachedStubActivity.put(className, stubActivity);
return stubActivity;
}
}
可以看着这里边完成了占坑StubActivity的查找,如下所示:
- 标准启动模式:com.didi.virtualapk.core.$1,每次自增1。
- 栈顶复用模式:com.didi.virtualapk.core.$,每次自增1,范围从1 - 8.
- 栈内复用模式:com.didi.virtualapk.core.C$,每次自增1,范围从1 - 8.
- 单例模式模式:com.didi.virtualapk.core.D$,每次自增1,范围从1 - 8.
既然这里为了染过检验把要启动的Activity变成了占坑的StubActivity。那么真正启动Activity的时候就要再次变回来,我们接着分析。
public class VAInstrumentation extends Instrumentation implements Handler.Callback {
@Override
public Activity newActivity(ClassLoader cl, String className, Intent intent) throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, ClassNotFoundException {
try {
cl.loadClass(className);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// 1. 根据Intent查找对应的LoadedPlugin。
LoadedPlugin plugin = this.mPluginManager.getLoadedPlugin(intent);
// 2. 从Intent中提取真正的targetClassName。
String targetClassName = PluginUtil.getTargetActivity(intent);
Log.i(TAG, String.format("newActivity[%s : %s]", className, targetClassName));
if (targetClassName != null) {
// 3. 这个mBase是我们上面保存的原生的Instrumentation对象,调用它的newActivity()方法去完成Activity的构建,这
// 相当于是一个动态代理模式。getClassLoader()是自己构建的一个DexClassLoader类,专门用来加载APK里面的类。
Activity activity = mBase.newActivity(plugin.getClassLoader(), targetClassName, intent);
activity.setIntent(intent);
try {
// for 4.1+
ReflectUtil.setField(ContextThemeWrapper.class, activity, "mResources", plugin.getResources());
} catch (Exception ignored) {
// ignored.
}
return activity;
}
}
return mBase.newActivity(cl, className, intent);
}
}
VAInstrumentation覆写了Instrumentation的newActivity方法,这个方法主要做了三件事情:
- 根据Intent查找对应的LoadedPlugin。
- 从Intent中提取真正的targetClassName。
- 这个mBase是我们上面保存的原生的Instrumentation对象,调用它的newActivity()方法去完成Activity的构建,这 相当于是一个动态代理模式。getClassLoader()是自己构建的一个DexClassLoader类,专门用来加载APK里面的类。
通过上面的分析,整体的思路就非常清晰了,如下所示:
提前在Manifest文件里注册多个占坑的StubActivity,校验阶段,将Intent里的className替换成StubActivity,并保存原有的Activity信息,借此通过校验。启动阶段,再 从Intent中取出真正的Activity信息,调用Instrumentation的newActivity()方法继续执行Activity的启动。
整体的思路还是挺机制的👍,当然占坑思想很早就有Android的同学提出来了,这也是实现插件化的思路的一种。介绍完了Activity的启动流程,我们接着来看Service的启动流程。👇
3.2 Service
Service的启动采用动态代理AMS,拦截Service的相关操作请求,然后转给ActivityManagerProxy处理,我们来看一看。
public class ActivityManagerProxy implements InvocationHandler {
private Object startService(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
// 获取IApplicationThread对象。
IApplicationThread appThread = (IApplicationThread) args[0];
// 获取跳转Intent。
Intent target = (Intent) args[1];
// 检查Service的信息
ResolveInfo resolveInfo = this.mPluginManager.resolveService(target, 0);
if (null == resolveInfo || null == resolveInfo.serviceInfo) {
// is host service
return method.invoke(this.mActivityManager, args);
}
return startDelegateServiceForTarget(target, resolveInfo.serviceInfo, null, RemoteService.EXTRA_COMMAND_START_SERVICE);
}
private ComponentName startDelegateServiceForTarget(Intent target, ServiceInfo serviceInfo, Bundle extras, int command) {
Intent wrapperIntent = wrapperTargetIntent(target, serviceInfo, extras, command);
return mPluginManager.getHostContext().startService(wrapperIntent);
}
private Intent wrapperTargetIntent(Intent target, ServiceInfo serviceInfo, Bundle extras, int command) {
// fill in service with ComponentName
target.setComponent(new ComponentName(serviceInfo.packageName, serviceInfo.name));
String pluginLocation = mPluginManager.getLoadedPlugin(target.getComponent()).getLocation();
// 判断交给LocalService处理还是交给RemoteService处理,LocalService和RemoteService分别对应是否
// 在新进程中启动Service。
boolean local = PluginUtil.isLocalService(serviceInfo);
Class<? extends Service> delegate = local ? LocalService.class : RemoteService.class;
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setClass(mPluginManager.getHostContext(), delegate);
intent.putExtra(RemoteService.EXTRA_TARGET, target);
// 保存一下这个command,分别对应不同的操作。
intent.putExtra(RemoteService.EXTRA_COMMAND, command);
intent.putExtra(RemoteService.EXTRA_PLUGIN_LOCATION, pluginLocation);
if (extras != null) {
intent.putExtras(extras);
}
return intent;
}
}
所以本质上讲,不管是启动、绑定还是关闭Intent,最终都是调用LocalService或者RemoteService里的onStartCommand()方法进行操作请求的分发。
LocalService和RemoteService都已经在VirtualAPK的Manifest文件里进行了注册,如下所示:
<application>
<!-- Local Service running in main process -->
<service android:name="com.didi.virtualapk.delegate.LocalService" />
<!-- Daemon Service running in child process -->
<service android:name="com.didi.virtualapk.delegate.RemoteService" android:process=":daemon">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="${applicationId}.intent.ACTION_DAEMON_SERVICE" />
</intent-filter>
</service>
</application>
我们接着来看看它们俩的具体实现。
3.2.1 LocalService
public class LocalService extends Service {
private static final String TAG = "LocalService";
// 插件APK里的目标Service
public static final String EXTRA_TARGET = "target";
public static final String EXTRA_COMMAND = "command";
public static final String EXTRA_PLUGIN_LOCATION = "plugin_location";
public static final int EXTRA_COMMAND_START_SERVICE = 1;
public static final int EXTRA_COMMAND_STOP_SERVICE = 2;
public static final int EXTRA_COMMAND_BIND_SERVICE = 3;
public static final int EXTRA_COMMAND_UNBIND_SERVICE = 4;
private PluginManager mPluginManager;
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return new Binder();
}
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
// 获取PluginManager单例
mPluginManager = PluginManager.getInstance(this);
}
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
if (null == intent || !intent.hasExtra(EXTRA_TARGET) || !intent.hasExtra(EXTRA_COMMAND)) {
return START_STICKY;
}
Intent target = intent.getParcelableExtra(EXTRA_TARGET);
// 获取command信息
int command = intent.getIntExtra(EXTRA_COMMAND, 0);
if (null == target || command <= 0) {
return START_STICKY;
}
// 获取组件信息
ComponentName component = target.getComponent();
// 根据组件信息获取对应的LoadedPlugin
LoadedPlugin plugin = mPluginManager.getLoadedPlugin(component);
// ClassNotFoundException when unmarshalling in Android 5.1
target.setExtrasClassLoader(plugin.getClassLoader());
switch (command) {
// 启动Service
case EXTRA_COMMAND_START_SERVICE: {
// 获取ActivityThread对象。
ActivityThread mainThread = (ActivityThread)ReflectUtil.getActivityThread(getBaseContext());
// 获取IApplicationThread对象。
IApplicationThread appThread = mainThread.getApplicationThread();
Service service;
if (this.mPluginManager.getComponentsHandler().isServiceAvailable(component)) {
// 尝试从ComponentsHandler里获取Service、
service = this.mPluginManager.getComponentsHandler().getService(component);
} else {
try {
// 调用DexClassLoader加载Service类。
service = (Service) plugin.getClassLoader().loadClass(component.getClassName()).newInstance();
Application app = plugin.getApplication();
IBinder token = appThread.asBinder();
Method attach = service.getClass().getMethod("attach", Context.class, ActivityThread.class, String.class, IBinder.class, Application.class, Object.class);
IActivityManager am = mPluginManager.getActivityManager();
// 调用attch()方法,绑定应用上下文。
attach.invoke(service, plugin.getPluginContext(), mainThread, component.getClassName(), token, app, am);
// 回调Service的onCreate()方法。
service.onCreate();
// 插入Service
this.mPluginManager.getComponentsHandler().rememberService(component, service);
} catch (Throwable t) {
return START_STICKY;
}
}
// 回调Service的onStartCommand()方法。
service.onStartCommand(target, 0, this.mPluginManager.getComponentsHandler().getServiceCounter(service).getAndIncrement());
break;
}
// 绑定服务
case EXTRA_COMMAND_BIND_SERVICE: {
ActivityThread mainThread = (ActivityThread)ReflectUtil.getActivityThread(getBaseContext());
IApplicationThread appThread = mainThread.getApplicationThread();
Service service = null;
if (this.mPluginManager.getComponentsHandler().isServiceAvailable(component)) {
// 尝试从ComponentsHandler里获取Service、
service = this.mPluginManager.getComponentsHandler().getService(component);
} else {
try {
// 调用DexClassLoader加载Service类。
service = (Service) plugin.getClassLoader().loadClass(component.getClassName()).newInstance();
Application app = plugin.getApplication();
IBinder token = appThread.asBinder();
Method attach = service.getClass().getMethod("attach", Context.class, ActivityThread.class, String.class, IBinder.class, Application.class, Object.class);
IActivityManager am = mPluginManager.getActivityManager();
// 调用attch()方法,绑定应用上下文。
attach.invoke(service, plugin.getPluginContext(), mainThread, component.getClassName(), token, app, am);
// 回调Service的onCreate()方法。
service.onCreate();
// 插入Service
this.mPluginManager.getComponentsHandler().rememberService(component, service);
} catch (Throwable t) {
t.printStackTrace();
}
}
try {
// 回调Service的onBind()方法。
IBinder binder = service.onBind(target);
IBinder serviceConnection = PluginUtil.getBinder(intent.getExtras(), "sc");
IServiceConnection iServiceConnection = IServiceConnection.Stub.asInterface(serviceConnection);
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= 26) {
ReflectUtil.invokeNoException(IServiceConnection.class, iServiceConnection, "connected",
new Class[]{ComponentName.class, IBinder.class, boolean.class},
new Object[]{component, binder, false});
} else {
iServiceConnection.connected(component, binder);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
break;
}
// 停止服务
case EXTRA_COMMAND_STOP_SERVICE: {
// 从ComponentsHandler移除Service的记录
Service service = this.mPluginManager.getComponentsHandler().forgetService(component);
if (null != service) {
try {
// 回调Service的onDestroy()方法
service.onDestroy();
} catch (Exception e) {
Log.e(TAG, "Unable to stop service " + service + ": " + e.toString());
}
} else {
Log.i(TAG, component + " not found");
}
break;
}
case EXTRA_COMMAND_UNBIND_SERVICE: {
// 从ComponentsHandler移除Service的记录
Service service = this.mPluginManager.getComponentsHandler().forgetService(component);
if (null != service) {
try {
// 回调Service的onUnbind()方法
service.onUnbind(target);
// 回调Service的onDestroy()方法
service.onDestroy();
} catch (Exception e) {
Log.e(TAG, "Unable to unbind service " + service + ": " + e.toString());
}
} else {
Log.i(TAG, component + " not found");
}
break;
}
}
return START_STICKY;
}
}
你可以发现整个类的实现,就相当于重写了Service启动的一部分流程,主要包括上下文绑定和一些生命周期方法的回调,这一块的具体内容可以参照我们之前写的文章05Android组件框架:Android后台服务Service 除此之外,它还使用了ComponentsHandler来管理Service,毕竟我们只在Manifest中注册了一个LocalService,ComponentsHandler主要用来插入和删除Service以及管理ServiceConnection。这样 就即便只注册了一个LocalService,也可以启动插件APK里的多个Service了。
我们接着来看看RemoteService,👇
3.2.2 RemoteService
public class RemoteService extends LocalService {
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
// onBind()方法返回空,说明不能被绑定。
return null;
}
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
if (intent == null) {
return super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId);
}
Intent target = intent.getParcelableExtra(EXTRA_TARGET);
if (target != null) {
String pluginLocation = intent.getStringExtra(EXTRA_PLUGIN_LOCATION);
ComponentName component = target.getComponent();
LoadedPlugin plugin = PluginManager.getInstance(this).getLoadedPlugin(component);
if (plugin == null && pluginLocation != null) {
try {
// 比LocalService多了一个从文件加载APK插件的操作
PluginManager.getInstance(this).loadPlugin(new File(pluginLocation));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
return super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId);
}
}
RemoteService继承与于LocalService,它们俩的区别就在于onBind()和onStartCommand()方法的实现上,如下所示:
- RemoteService的onBind()方法返回空,说明不能被绑定。
- RemoteService的onStartCommand()方法比LocalService多了一个从文件加载APK插件的操作,也就是说它可以加载别的APK(别的进程)的Service。
3.3 Broadcast Receiver
Broadcast Receiver就比较简单了,直接将静态广播转为动态广播,免去注册的过程。
// 将静态的广播转为动态的。
Map<ComponentName, ActivityInfo> receivers = new HashMap<ComponentName, ActivityInfo>();
for (PackageParser.Activity receiver : this.mPackage.receivers) {
receivers.put(receiver.getComponentName(), receiver.info);
try {
BroadcastReceiver br = BroadcastReceiver.class.cast(getClassLoader().loadClass(receiver.getComponentName().getClassName()).newInstance());
for (PackageParser.ActivityIntentInfo aii : receiver.intents) {
this.mHostContext.registerReceiver(br, aii);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
3.4 Content Provider
VirtualAPK通过动态代理IContentProvider,拦截ContentProvider的相关操作请求,然后转给PluginContentResolver来处理。IContentProvider对象的hook实际上是在PluginManager里 完成的,如下所示:
public class PluginManager {
private void hookIContentProviderAsNeeded() {
// 拿到占坑的Content Provider,然后主动去调用它的call()方法,call()方法
// 会调用RemoteContentProvider的getContentProvider构建一个RemoteContentProvider。
Uri uri = Uri.parse(PluginContentResolver.getUri(mContext));
mContext.getContentResolver().call(uri, "wakeup", null, null);
try {
Field authority = null;
Field mProvider = null;
// 获取ActivityThread对象
ActivityThread activityThread = (ActivityThread) ReflectUtil.getActivityThread(mContext);
// 获取ContentProvider Map
Map mProviderMap = (Map) ReflectUtil.getField(activityThread.getClass(), activityThread, "mProviderMap");
Iterator iter = mProviderMap.entrySet().iterator();
// 变量查询相应的ContentProvider
while (iter.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry) iter.next();
Object key = entry.getKey();
Object val = entry.getValue();
String auth;
if (key instanceof String) {
auth = (String) key;
} else {
if (authority == null) {
authority = key.getClass().getDeclaredField("authority");
authority.setAccessible(true);
}
auth = (String) authority.get(key);
}
if (auth.equals(PluginContentResolver.getAuthority(mContext))) {
if (mProvider == null) {
mProvider = val.getClass().getDeclaredField("mProvider");
mProvider.setAccessible(true);
}
IContentProvider rawProvider = (IContentProvider) mProvider.get(val);
// 获取对应的IContentProvider
IContentProvider proxy = IContentProviderProxy.newInstance(mContext, rawProvider);
mIContentProvider = proxy;
Log.d(TAG, "hookIContentProvider succeed : " + mIContentProvider);
break;
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
ContentProvider也在Manifest文件里进行了占坑注册,如下所示:
<application>
<provider
android:name="com.didi.virtualapk.delegate.RemoteContentProvider"
android:authorities="${applicationId}.VirtualAPK.Provider"
android:process=":daemon" />
</application>
获取到IContentProvider对象后,就可以对它进行动态代理,拦截它里面的操作,例如:query、insert、update、delete等操,在这些操作里吧用户调用的URI缓存占坑Provider的URI,再 把原来的URI作为参数拼接在占坑Provider后面即可。这个替换和拼接的过程是由PluginContentResolver的wrapperUri()方法来完成的,如下所示:
public class PluginContentResolver extends ContentResolver {
@Keep
public static Uri wrapperUri(LoadedPlugin loadedPlugin, Uri pluginUri) {
String pkg = loadedPlugin.getPackageName();
String pluginUriString = Uri.encode(pluginUri.toString());
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder(PluginContentResolver.getUri(loadedPlugin.getHostContext()));
//先加入占坑Provider的URI
builder.append("/?plugin=" + loadedPlugin.getLocation());
// 再将目标URI和packageName拼接上去
builder.append("&pkg=" + pkg);
builder.append("&uri=" + pluginUriString);
Uri wrapperUri = Uri.parse(builder.toString());
return wrapperUri;
}
}
可以发现上面占坑的Provider是RemoteContentProvider,它继承ContentProvider,相当于是它的代理类,如下所示:
public class RemoteContentProvider extends ContentProvider {
private ContentProvider getContentProvider(final Uri uri) {
final PluginManager pluginManager = PluginManager.getInstance(getContext());
Uri pluginUri = Uri.parse(uri.getQueryParameter(KEY_URI));
final String auth = pluginUri.getAuthority();
// 1. 尝试从缓存中获取ContentProvider。
ContentProvider cachedProvider = sCachedProviders.get(auth);
if (cachedProvider != null) {
return cachedProvider;
}
synchronized (sCachedProviders) {
// 2. 获取LoadedPlugin对象。
LoadedPlugin plugin = pluginManager.getLoadedPlugin(uri.getQueryParameter(KEY_PKG));
if (plugin == null) {
try {
pluginManager.loadPlugin(new File(uri.getQueryParameter(KEY_PLUGIN)));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 3. 从LoadedPlugin对象里获取Provider相关信息ProviderInfo。
final ProviderInfo providerInfo = pluginManager.resolveContentProvider(auth, 0);
if (providerInfo != null) {
RunUtil.runOnUiThread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
LoadedPlugin loadedPlugin = pluginManager.getLoadedPlugin(uri.getQueryParameter(KEY_PKG));
// 4. 利用反射创建ContentProvider对象。
ContentProvider contentProvider = (ContentProvider) Class.forName(providerInfo.name).newInstance();
contentProvider.attachInfo(loadedPlugin.getPluginContext(), providerInfo);
// 5. 将ContentProvider对象存入缓存中。
sCachedProviders.put(auth, contentProvider);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, true);
return sCachedProviders.get(auth);
}
}
return null;
}
}
整个构建ContentProvider对象的流程如下所示:
- 尝试从缓存中获取ContentProvider。
- 获取LoadedPlugin对象。
- 从LoadedPlugin对象里获取Provider相关信息ProviderInfo。
- 利用反射创建ContentProvider对象。
- 将ContentProvider对象存入缓存中。
我们再接着来看看RemoteContentProvider里面的增删改查操作,如下所示:
public class RemoteContentProvider extends ContentProvider {
@Override
public Cursor query(Uri uri, String[] projection, String selection, String[] selectionArgs, String sortOrder) {
// 1. 通过传入的URI生成一个新的Provider。
ContentProvider provider = getContentProvider(uri);
// 2. 拿到目标URI。
Uri pluginUri = Uri.parse(uri.getQueryParameter(KEY_URI));
if (provider != null) {
// 3. 执行最终的查询操作。
return provider.query(pluginUri, projection, selection, selectionArgs, sortOrder);
}
return null;
}
}
query()方法的逻辑也十分简单,如下所示:
- 通过传入的URI生成一个新的Provider。
- 拿到目标URI。
- 执行最终的查询操作。
好了,四大组件的启动流程都分析完了,我们再来总结一下:
- Activity:在宿主apk中提前占坑,然后通过“欺上瞒下”的方式绕过校验,启动插件APK里的Activity;
- Service:通过代理Service的方式去分发,VirtualAPK使用了两个代理Service,即LocalService和RemoteService。
- BroadcastReceiver:将静态广播转为动态广播。
- ContentProvider:通过一个代理Provider进行操作的分发。
以上便是整个VrtualAPK框架的原理分析。