TabLayout我们再熟悉不过了,在开发中,像这种tab切换的需求都会用到TabLayout,它是由官方提供的一个控件,在support design 包中。使用起来非常简单方便,交互效果也很不错,能满足我们开发中95%的需求。但是它有一个缺陷:不能改变Tab下划线(Indicator)的宽度。本篇文章给你带来改变Tab下划线宽度的几种方式:
1 . 通过反射设置Tab下划线的宽度
2 . 通过TabLayout setCustomView 的方式
3 . 使用第三方开源库。
一、通过反射的方式,改变TabLayout下划线的宽度
首先我们看一下原生的TabLayout的效果(没有任何修改):
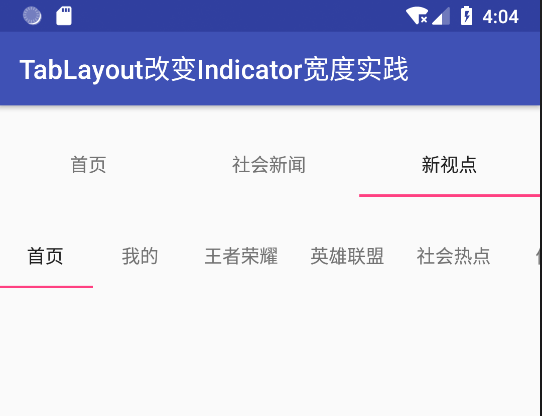
gif演示:
上图第一个固定模式(tabMode:fixed),下面是滚动模式(tabMode:scrollable),可以看到,所有Tab下方的线(即Indicator)是一样长的,不管Tab的内容是长还是短。Tab indicator的长度与最长的Tab保持一致。
TabLayout提供了tabIndicatorHeight 属性来设置indicator的高度,但是没有提供设置宽度的的api,要想改变indicator的宽度,就得去看看源码indicator是怎么实现的。简单的看一下源码:
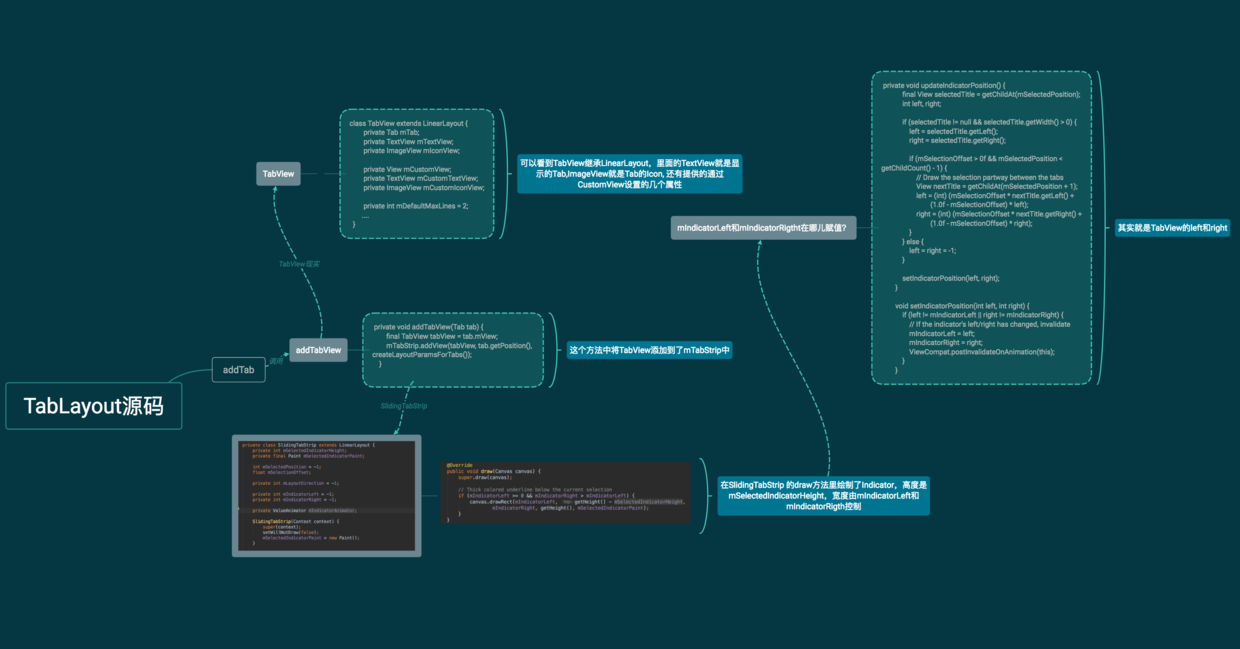
如上思维导图,其中有两个重点的东西, TabView 和 SlidingTabStrip,TabView就是我们所看到的Tab,SlidingTabStrip是TabView的父容器,继承自LinearLayout,用来处理Tab滑动相关操作,如动画,绘制Indicator等。
我们要研究indicator是怎么添加的,重点就在SlidingTabStrip 里了,这里我们看到了mSelectedIndicatorHeight,这就是我们设置Indicator的高度,在draw方法里有如下代码:
@Override
public void draw(Canvas canvas) {
super.draw(canvas);
// Thick colored underline below the current selection
if (mIndicatorLeft >= 0 && mIndicatorRight > mIndicatorLeft) {
canvas.drawRect(mIndicatorLeft, getHeight() - mSelectedIndicatorHeight,
mIndicatorRight, getHeight(), mSelectedIndicatorPaint);
}
}
这就是绘制的选中Tab的Indicator,高度是mSelectedIndicatorHeight,宽是mIndicatorRight - mIndicatorLeft 。那么者两个值是从哪儿来的呢?在updateIndicatorPosition方法中:
private void updateIndicatorPosition() {
// 选中的TabView
final View selectedTitle = getChildAt(mSelectedPosition);
int left, right;
if (selectedTitle != null && selectedTitle.getWidth() > 0) {
// left 和right 的值
left = selectedTitle.getLeft();
right = selectedTitle.getRight();
if (mSelectionOffset > 0f && mSelectedPosition < getChildCount() - 1) {
// Draw the selection partway between the tabs
View nextTitle = getChildAt(mSelectedPosition + 1);
left = (int) (mSelectionOffset * nextTitle.getLeft() +
(1.0f - mSelectionOffset) * left);
right = (int) (mSelectionOffset * nextTitle.getRight() +
(1.0f - mSelectionOffset) * right);
}
} else {
left = right = -1;
}
// 设置mIndicatorLeft和mIndicatorRight
setIndicatorPosition(left, right);
}
void setIndicatorPosition(int left, int right) {
if (left != mIndicatorLeft || right != mIndicatorRight) {
// If the indicator's left/right has changed, invalidate
mIndicatorLeft = left;
mIndicatorRight = right;
ViewCompat.postInvalidateOnAnimation(this);
}
}
从上面的代码就可以看出,Indicator(Tab选中下划线)的宽度其实就是TabView的宽度,那么TabView的宽度是多少呢?在SlidingTabStrip的onMeasure方法中,为TabView设置了宽度。 请看代码:
@Override
protected void onMeasure(final int widthMeasureSpec, final int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
...
//以上省略
if (mMode == MODE_FIXED && mTabGravity == GRAVITY_CENTER) {
final int count = getChildCount();
// First we'll find the widest tab
//google的工程师注释写的非常清楚:第一步,找出宽度最长的Tab
int largestTabWidth = 0;
for (int i = 0, z = count; i < z; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
if (child.getVisibility() == VISIBLE) {
largestTabWidth = Math.max(largestTabWidth, child.getMeasuredWidth());
}
}
if (largestTabWidth <= 0) {
// If we don't have a largest child yet, skip until the next measure pass
return;
}
final int gutter = dpToPx(FIXED_WRAP_GUTTER_MIN);
boolean remeasure = false;
if (largestTabWidth * count <= getMeasuredWidth() - gutter * 2) {
// If the tabs fit within our width minus gutters, we will set all tabs to have
// the same width
// 第二步:将所有Tab的宽度都设置为largestTabWidth
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final LinearLayout.LayoutParams lp =
(LayoutParams) getChildAt(i).getLayoutParams();
if (lp.width != largestTabWidth || lp.weight != 0) {
lp.width = largestTabWidth;
lp.weight = 0;
remeasure = true;
}
}
} else {
// If the tabs will wrap to be larger than the width minus gutters, we need
// to switch to GRAVITY_FILL
mTabGravity = GRAVITY_FILL;
updateTabViews(false);
remeasure = true;
}
...
//以下省略
}
}
这个方法很简单,一看就明白,有两个步骤:
1, 一个for循环,找出宽度最大的一个TabView
2, 再一个for 循环,设置所有TabView的宽度为最长那个TabView的宽度,即largestTabWidth
这就知道为什么前面提到的所有Tab 一样宽,不管长的还是短的。
另外一个点: 上面的
onMeasure中,执行的条件是mMode == MODE_FIXED && mTabGravity == GRAVITY_CENTER,如果是其他条件,请看updateTabViews:
void updateTabViews(final boolean requestLayout) {
for (int i = 0; i < mTabStrip.getChildCount(); i++) {
View child = mTabStrip.getChildAt(i);
child.setMinimumWidth(getTabMinWidth());
updateTabViewLayoutParams((LinearLayout.LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams());
if (requestLayout) {
child.requestLayout();
}
}
}
private void updateTabViewLayoutParams(LinearLayout.LayoutParams lp) {
if (mMode == MODE_FIXED && mTabGravity == GRAVITY_FILL) {
lp.width = 0;
lp.weight = 1;
} else {
lp.width = LinearLayout.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT;
lp.weight = 0;
}
}
如果是MODE_FIXED,并且GRAVITY_FILL,则设置weight=1,所有TabView平分屏幕宽度,MODE_SCROLLABLE ,设置的WRAP_CONTENT 。
反射改变下划线宽度
思路:知道了绘制Indicator的宽度是根据TabView的宽度来决定的,那么我们设置TabView的宽度就能改变indicator的宽,TabView的宽由其中的mTextView决定,因此,通过反射得到mTextView,设置它的宽度,就能改变Indicator的宽度,这也是网上看到的大多数的解决方法。
上代码:
public static void setTabWidth(final TabLayout tabLayout, final int padding){
tabLayout.post(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
//拿到tabLayout的mTabStrip属性
LinearLayout mTabStrip = (LinearLayout) tabLayout.getChildAt(0);
for (int i = 0; i < mTabStrip.getChildCount(); i++) {
View tabView = mTabStrip.getChildAt(i);
//拿到tabView的mTextView属性 tab的字数不固定一定用反射取mTextView
Field mTextViewField = tabView.getClass().getDeclaredField("mTextView");
mTextViewField.setAccessible(true);
TextView mTextView = (TextView) mTextViewField.get(tabView);
tabView.setPadding(0, 0, 0, 0);
//因为我想要的效果是 字多宽线就多宽,所以测量mTextView的宽度
int width = 0;
width = mTextView.getWidth();
if (width == 0) {
mTextView.measure(0, 0);
width = mTextView.getMeasuredWidth();
}
//设置tab左右间距 注意这里不能使用Padding 因为源码中线的宽度是根据 tabView的宽度来设置的
LinearLayout.LayoutParams params = (LinearLayout.LayoutParams) tabView.getLayoutParams();
params.width = width ;
params.leftMargin = padding;
params.rightMargin = padding;
tabView.setLayoutParams(params);
tabView.invalidate();
}
} catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
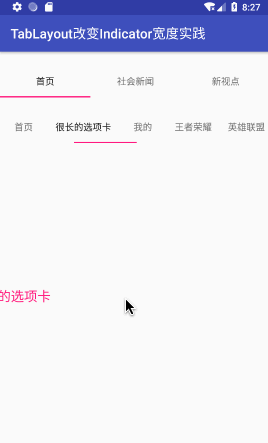
效果图如下:
提醒:这种方式改变Indicator最短也就Tab内容的宽度,如果设置很短,Tab内容就显示不下,如下图:

二、通过TabLayout setCustomView 的方式
第一种通过反射的方式设置Indicator宽度,最短只能Tab内容的宽度,如果设计师要所有选中的Tab下的Indicator都设置一个指定的宽度,这种就不行了。TabLayout可以设置自定义View,可以通过这种方法来达到目的。
1, 将TabLayout 的tabIndicatorHeight 设置为0
2,通过TabLayout 的setCustomView方式添加Tab
3, 在onTabSelected 回调种,处理Tab选中和未选中的状态;
4,为了方便使用,封装成一个通用的View
首先看布局:
enhance_tab_layout.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<android.support.design.widget.TabLayout
android:id="@+id/enhance_tab_view"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
app:tabIndicatorHeight="0dp"
>
</android.support.design.widget.TabLayout>
</FrameLayout>
Tab item 布局:tab_item_layout.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:gravity="center"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tab_item_text"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textSize="13sp"
android:text="首页"
android:textColor="#333333"
/>
<View
android:id="@+id/tab_item_indicator"
android:layout_width="30dp"
android:layout_height="2dp"
android:layout_marginTop="5dp"
android:background="@color/colorAccent"
android:visibility="invisible"
/>
</LinearLayout>
如上,TextView显示Tab内容,下面的View就是Tab下面的Indicator(下划线)。 自己定义的View,宽度随便你改。
添加Tab的时候使用setCustomView 方法:
/**
* 添加tab
* @param tab
*/
public void addTab(String tab){
mTabList.add(tab);
View customView = getTabView(getContext(),tab,mIndicatorWidth,mIndicatorHeight,mTabTextSize);
mCustomViewList.add(customView);
mTabLayout.addTab(mTabLayout.newTab().setCustomView(customView));
}
/**
* 获取Tab 显示的内容
*
* @param context
* @param
* @return
*/
public static View getTabView(Context context,String text,int indicatorWidth,int indicatorHeight,int textSize) {
View view = LayoutInflater.from(context).inflate(R.layout.tab_item_layout, null);
TextView tabText = (TextView) view.findViewById(R.id.tab_item_text);
if(indicatorWidth>0){
View indicator = view.findViewById(R.id.tab_item_indicator);
ViewGroup.LayoutParams layoutParams = indicator.getLayoutParams();
layoutParams.width = indicatorWidth;
layoutParams.height = indicatorHeight;
indicator.setLayoutParams(layoutParams);
}
tabText.setTextSize(textSize);
tabText.setText(text);
return view;
}
然后在onTabSelected中处理状态:
@Override
public void onTabSelected(TabLayout.Tab tab) {
mViewPager.setCurrentItem(tab.getPosition());
EnhanceTabLayout mTabLayout = mTabLayoutRef.get();
if(mTabLayoutRef!=null){
List<View> customViewList = mTabLayout.getCustomViewList();
if(customViewList == null || customViewList.size() ==0){
return;
}
for (int i=0;i<customViewList.size();i++){
View view = customViewList.get(i);
if(view == null){
return;
}
TextView text = (TextView) view.findViewById(R.id.tab_item_text);
View indicator = view.findViewById(R.id.tab_item_indicator);
if(i == tab.getPosition()){ // 选中状态
text.setTextColor(mTabLayout.mSelectTextColor);
indicator.setBackgroundColor(mTabLayout.mSelectIndicatorColor);
indicator.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
}else{// 未选中状态
text.setTextColor(mTabLayout.mUnSelectTextColor);
indicator.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE);
}
}
}
}
代码其实挺简单的,但是如果项目中多处使用到,都这样来处理的话,就显得麻烦,因此,我们通过自定义View的方式将这些代码疯转成1个通用的TabLayoutView。如下:
EnhanceTabLayout.java
/**
* 对 support Design 包中的TabLayout包装
* 主要实现功能:更改indicator 的长度
* Created by zhouwei on 2018/5/18.
*/
public class EnhanceTabLayout extends FrameLayout {
private TabLayout mTabLayout;
private List<String> mTabList;
private List<View> mCustomViewList;
private int mSelectIndicatorColor;
private int mSelectTextColor;
private int mUnSelectTextColor;
private int mIndicatorHeight;
private int mIndicatorWidth;
private int mTabMode;
private int mTabTextSize;
public EnhanceTabLayout(@NonNull Context context) {
super(context);
init(context,null);
}
public EnhanceTabLayout(@NonNull Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
init(context,attrs);
}
public EnhanceTabLayout(@NonNull Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
init(context,attrs);
}
@RequiresApi(api = Build.VERSION_CODES.LOLLIPOP)
public EnhanceTabLayout(@NonNull Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr, int defStyleRes) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr, defStyleRes);
init(context,attrs);
}
private void readAttr(Context context,AttributeSet attrs){
TypedArray typedArray = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs,R.styleable.EnhanceTabLayout);
mSelectIndicatorColor = typedArray.getColor(R.styleable.EnhanceTabLayout_tabIndicatorColor,context.getResources().getColor(R.color.colorAccent));
mUnSelectTextColor = typedArray.getColor(R.styleable.EnhanceTabLayout_tabTextColor, Color.parseColor("#666666"));
mSelectTextColor = typedArray.getColor(R.styleable.EnhanceTabLayout_tabSelectTextColor,context.getResources().getColor(R.color.colorAccent));
mIndicatorHeight = typedArray.getDimensionPixelSize(R.styleable.EnhanceTabLayout_tabIndicatorHeight,1);
mIndicatorWidth = typedArray.getDimensionPixelSize(R.styleable.EnhanceTabLayout_tabIndicatorWidth,0);
mTabTextSize = typedArray.getDimensionPixelSize(R.styleable.EnhanceTabLayout_tabTextSize,13);
mTabMode = typedArray.getInt(R.styleable.EnhanceTabLayout_tab_Mode,2);
typedArray.recycle();
}
private void init(Context context,AttributeSet attrs){
readAttr(context,attrs);
mTabList = new ArrayList<>();
mCustomViewList = new ArrayList<>();
View view = LayoutInflater.from(getContext()).inflate(R.layout.enhance_tab_layout,this,true);
mTabLayout = view.findViewById(R.id.enhance_tab_view);
// 添加属性
mTabLayout.setTabMode(mTabMode == 1 ? TabLayout.MODE_FIXED:TabLayout.MODE_SCROLLABLE);
mTabLayout.addOnTabSelectedListener(new TabLayout.OnTabSelectedListener() {
@Override
public void onTabSelected(TabLayout.Tab tab) {
// onTabItemSelected(tab.getPosition());
// Tab 选中之后,改变各个Tab的状态
for (int i=0;i<mTabLayout.getTabCount();i++){
View view = mTabLayout.getTabAt(i).getCustomView();
if(view == null){
return;
}
TextView text = (TextView) view.findViewById(R.id.tab_item_text);
View indicator = view.findViewById(R.id.tab_item_indicator);
if(i == tab.getPosition()){ // 选中状态
text.setTextColor(mSelectTextColor);
indicator.setBackgroundColor(mSelectIndicatorColor);
indicator.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
}else{// 未选中状态
text.setTextColor(mUnSelectTextColor);
indicator.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE);
}
}
}
@Override
public void onTabUnselected(TabLayout.Tab tab) {
}
@Override
public void onTabReselected(TabLayout.Tab tab) {
}
});
}
public List<View> getCustomViewList(){
return mCustomViewList;
}
public void addOnTabSelectedListener (TabLayout.OnTabSelectedListener onTabSelectedListener){
mTabLayout.addOnTabSelectedListener(onTabSelectedListener);
}
/**
* 与TabLayout 联动
* @param viewPager
*/
public void setupWithViewPager(@Nullable ViewPager viewPager) {
mTabLayout.addOnTabSelectedListener(new ViewPagerOnTabSelectedListener(viewPager,this));
}
/**
* retrive TabLayout Instance
* @return
*/
public TabLayout getTabLayout(){
return mTabLayout;
}
/**
* 添加tab
* @param tab
*/
public void addTab(String tab){
mTabList.add(tab);
View customView = getTabView(getContext(),tab,mIndicatorWidth,mIndicatorHeight,mTabTextSize);
mCustomViewList.add(customView);
mTabLayout.addTab(mTabLayout.newTab().setCustomView(customView));
}
public static class ViewPagerOnTabSelectedListener implements TabLayout.OnTabSelectedListener{
private final ViewPager mViewPager;
private final WeakReference<EnhanceTabLayout> mTabLayoutRef;
public ViewPagerOnTabSelectedListener(ViewPager viewPager,EnhanceTabLayout enhanceTabLayout) {
mViewPager = viewPager;
mTabLayoutRef = new WeakReference<EnhanceTabLayout>(enhanceTabLayout);
}
@Override
public void onTabSelected(TabLayout.Tab tab) {
mViewPager.setCurrentItem(tab.getPosition());
EnhanceTabLayout mTabLayout = mTabLayoutRef.get();
if(mTabLayoutRef!=null){
List<View> customViewList = mTabLayout.getCustomViewList();
if(customViewList == null || customViewList.size() ==0){
return;
}
for (int i=0;i<customViewList.size();i++){
View view = customViewList.get(i);
if(view == null){
return;
}
TextView text = (TextView) view.findViewById(R.id.tab_item_text);
View indicator = view.findViewById(R.id.tab_item_indicator);
if(i == tab.getPosition()){ // 选中状态
text.setTextColor(mTabLayout.mSelectTextColor);
indicator.setBackgroundColor(mTabLayout.mSelectIndicatorColor);
indicator.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
}else{// 未选中状态
text.setTextColor(mTabLayout.mUnSelectTextColor);
indicator.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE);
}
}
}
}
@Override
public void onTabUnselected(TabLayout.Tab tab) {
// No-op
}
@Override
public void onTabReselected(TabLayout.Tab tab) {
// No-op
}
}
/**
* 获取Tab 显示的内容
*
* @param context
* @param
* @return
*/
public static View getTabView(Context context,String text,int indicatorWidth,int indicatorHeight,int textSize) {
View view = LayoutInflater.from(context).inflate(R.layout.tab_item_layout, null);
TextView tabText = (TextView) view.findViewById(R.id.tab_item_text);
if(indicatorWidth>0){
View indicator = view.findViewById(R.id.tab_item_indicator);
ViewGroup.LayoutParams layoutParams = indicator.getLayoutParams();
layoutParams.width = indicatorWidth;
layoutParams.height = indicatorHeight;
indicator.setLayoutParams(layoutParams);
}
tabText.setTextSize(textSize);
tabText.setText(text);
return view;
}
暴露了一些常用方法和原生TabLayout 的几个重要属性,自定义属性如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<resources>
<declare-styleable name="EnhanceTabLayout">
<attr name="tab_Mode" format="enum">
<enum name="mode_fixed" value="1"/>
<enum name="mode_scrollable" value="2"/>
</attr>
<attr name="tabIndicatorColor" format="color"/>
<attr name="tabSelectTextColor" format="color"/>
<attr name="tabTextColor" format="color"/>
<attr name="tabIndicatorHeight" format="dimension"/>
<attr name="tabIndicatorWidth" format="dimension"/>
<attr name="tabTextSize" format="dimension"/>
</declare-styleable>
</resources>
好了,这样就封装了一个可以改变Indicator 宽度的TabLayout,看一下怎么用,xml布局如下:
<com.example.codoon.customtablayout.EnhanceTabLayout
android:id="@+id/enhance_tab_layout"
android:layout_marginTop="30dp"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
app:tabIndicatorHeight="2dp"
app:tabIndicatorWidth="30dp"
app:tabTextColor="#999999"
app:tab_Mode="mode_scrollable"
app:tabSelectTextColor="@color/colorPrimary"
app:tabIndicatorColor="@color/colorPrimary"
app:tabTextSize="6sp"
>
</com.example.codoon.customtablayout.EnhanceTabLayout>
Activity中代码如下:
mEnhanceTabLayout = findViewById(R.id.enhance_tab_layout);
mEnhanceTabLayout.addOnTabSelectedListener(new TabLayout.OnTabSelectedListener() {
@Override
public void onTabSelected(TabLayout.Tab tab) {
Log.e("log","onTabSelected");
}
@Override
public void onTabUnselected(TabLayout.Tab tab) {
}
@Override
public void onTabReselected(TabLayout.Tab tab) {
}
});
for(int i=0;i<sTitle.length;i++){
mEnhanceTabLayout.addTab(sTitle[i]);
}
mEnhanceTabLayout.setupWithViewPager(mViewPager);
List<Fragment> fragments = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=0;i<sTitle.length;i++){
fragments.add(ItemFragment.newInstance(sTitle[i]));
}
MyAdapter adapter = new MyAdapter(getSupportFragmentManager(),fragments, Arrays.asList(sTitle));
mViewPager.setAdapter(adapter);
mViewPager.addOnPageChangeListener(new TabLayout.TabLayoutOnPageChangeListener(mEnhanceTabLayout.getTabLayout()));
mEnhanceTabLayout.setupWithViewPager(mViewPager);
注意,如果是配合ViewPager使用,需要下面两行代码,单独使用则不需要:
mViewPager.addOnPageChangeListener(new TabLayout.TabLayoutOnPageChangeListener(mEnhanceTabLayout.getTabLayout()));
mEnhanceTabLayout.setupWithViewPager(mViewPager);
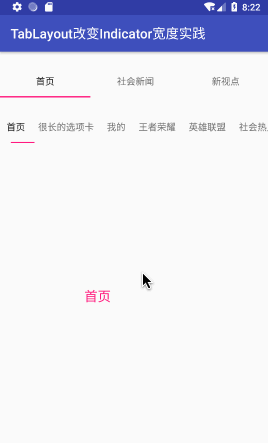
最后看一下效果:(图中第二个TabLayout)
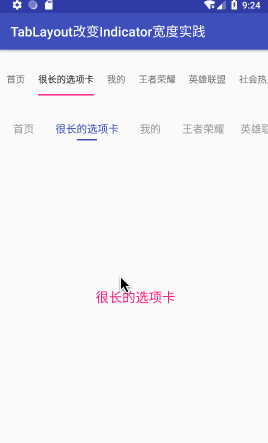
三、第三方开源库
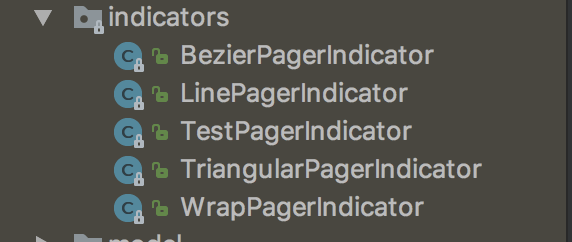
如果前面2中方式都满足不了你的需求的话,你可以使用第三方库,也有一些不错的开源库,这里推荐2个。 **1 , MagicIndicator **
github:https://github.com/hackware1993/MagicIndicator star:4.4k
MagicIndicator ,使用方便,还有多种模式可以选择。包括:
repositories {
...
maven {
url "https://jitpack.io"
}
}
dependencies {
...
compile 'com.github.hackware1993:MagicIndicator:1.5.0'
}
布局文件:
<net.lucode.hackware.magicindicator.MagicIndicator
android:id="@+id/magic_indicator"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="49dp">
</net.lucode.hackware.magicindicator.MagicIndicator>
代码中:
MagicIndicator magicIndicator = (MagicIndicator) findViewById(R.id.magic_indicator);
CommonNavigator commonNavigator = new CommonNavigator(this);
commonNavigator.setAdapter(new CommonNavigatorAdapter() {
@Override
public int getCount() {
return sTitle == null ? 0 : sTitle.length;
}
@Override
public IPagerTitleView getTitleView(Context context, final int index) {
ColorTransitionPagerTitleView colorTransitionPagerTitleView = new ColorTransitionPagerTitleView(context);
colorTransitionPagerTitleView.setNormalColor(Color.GRAY);
colorTransitionPagerTitleView.setSelectedColor(Color.BLACK);
colorTransitionPagerTitleView.setText(sTitle[index]);
colorTransitionPagerTitleView.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
mViewPager.setCurrentItem(index);
}
});
return colorTransitionPagerTitleView;
}
@Override
public IPagerIndicator getIndicator(Context context) {
LinePagerIndicator indicator = new LinePagerIndicator(context);
indicator.setMode(LinePagerIndicator.MODE_EXACTLY);
//设置indicator的宽度
indicator.setLineWidth(TabUtils.dp2px(context,20));
return indicator;
}
});
magicIndicator.setNavigator(commonNavigator);
ViewPagerHelper.bind(magicIndicator,mViewPager);
效果图如下,图中最后一个TabLayout:

2 , FlycoTabLayout github:https://github.com/H07000223/FlycoTabLayout star:6.5k
功能和MagicIndicator差不多,都支持多种Indicator效果:

具体使用请看github 详细介绍。
四、总结
本文总结了改变TabLayout下划线(indicator)宽度的几种方式,使用的时候根据自己的需求选择,在原生控件能做的情况下,尽量使用原生控件,毕竟导入三方库需要一些额外的成本。如果你还有更好的方式,欢迎评论区留言讨论。
更多Android干货文章,关注公众号 【Android技术杂货铺】
