前端开发规范
一、HTML
1.语义化标签
HTML5 提供了很多语义化元素,更好地帮助描述内容。希望你能从这些丰富的标签库中受益。
<!-- bad -->
<div id="main">
<div class="article">
<div class="header">
<h1>Blog post</h1>
<p>Published: <span>21st Feb, 2015</span></p>
</div>
<p>…</p>
</div>
</div>
<!-- good -->
<main>
<article>
<header>
<h1>Blog post</h1>
<p>Published: <time datetime="2015-02-21">21st Feb, 2015</time></p>
</header>
<p>…</p>
</article>
</main>
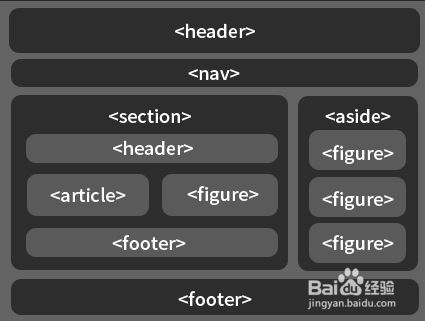

请确保正确使用语义化的标签,错误的用法甚至不如保守的用法。
<!-- bad -->
<h1>
<figure>
<img alt=Company src=logo.png>
</figure>
</h1>
<!-- good -->
<h1>
<img alt=Company src=logo.png>
</h1>
简洁
确保代码简洁,不要再采用XHTML的旧做法。
<!-- bad -->
<!doctype html>
<html lang=en>
<head>
<meta http-equiv=Content-Type content="text/html; charset=utf-8" />
<title>Contact</title>
<link rel=stylesheet href=style.css type=text/css />
</head>
<body>
<h1>Contact me</h1>
<label>
Email address:
<input type=email placeholder=you@email.com required=required />
</label>
<script src=main.js type=text/javascript></script>
</body>
</html>
<!-- good -->
<!doctype html>
<html lang=en>
<meta charset=utf-8>
<title>Contact</title>
<link rel=stylesheet href=style.css>
<h1>Contact me</h1>
<label>
Email address:
<input type=email placeholder=you@email.com required>
</label>
<script src=main.js></script>
</html>
HTML5 doctype
为每个 HTML 页面的第一行添加标准模式(standard mode)的声明,这样能够确保在每个浏览器中拥有一致的展现。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
</head>
</html>
语言属性
根据 HTML5 规范:
强烈建议为 html 根元素指定 lang 属性,从而为文档设置正确的语言。这将有助于语音合成工具确定其所应该采用的发音,有助于翻译工具确定其翻译时所应遵守的规则等等。
更多关于 lang 属性的知识可以从 此规范 中了解。
这里列出了语言代码表。
<html lang="en">
<!-- ... -->
</html>
IE 兼容模式
IE 支持通过特定的 标签来确定绘制当前页面所应该采用的 IE 版本。除非有强烈的特殊需求,否则最好是设置为 edge mode,从而通知 IE 采用其所支持的最新的模式。
阅读这篇 stack overflow 上的文章可以获得更多有用的信息。
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=Edge">
字符编码
通过明确声明字符编码,能够确保浏览器快速并容易的判断页面内容的渲染方式。这样做的好处是,可以避免在 HTML 中使用字符实体标记(character entity),从而全部与文档编码一致(一般采用 UTF-8 编码)。
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
</head>
可用性
可用性不应该是事后才考虑的事情。你可以通过简单的修改做出不错的效果,例如:
- 正确使用alt属性
- 确保链接和按钮正确使用(不要用
<div class=button>这种粗暴的做法) - 不依赖于颜色来传达信息
- 给表单做好lable标记
<!-- bad -->
<h1><img alt="Logo" src="logo.png"></h1>
<!-- good -->
<h1><img alt="My Company, Inc." src="logo.png"></h1>
性能
除非有非要在加载内容前加载脚本的必要性由,不然别这样做,这样会阻碍网页渲染。如果你的样式表很大,必须独立放到一个文件里。两次HTTP 请求不会显著降低性能。
<!-- bad -->
<!doctype html>
<meta charset=utf-8>
<script src=analytics.js></script>
<title>Hello, world.</title>
<p>...</p>
<!-- good -->
<!doctype html>
<meta charset=utf-8>
<title>Hello, world.</title>
<p>...</p>
<script src=analytics.js></script>
属性顺序
HTML 属性应该按照特定的顺序出现以保证易读性。
id class name data-xxx src, for, type, href title, alt aria-xxx, role value style
二、CSS
分号
不能漏写分号
/* bad */
div {
color: red
}
/* good */
div {
color: red;
}
流
尽量不要改变元素默认行为。保持默认的文本流。比如,移出一个图片下面的一个白块,不影响原本的显示:
/* bad */
img {
display: block;
}
/* good */
img {
vertical-align: middle;
}
类似的,尽量不要改变浮动方式。
/* bad */
div {
width: 100px;
position: absolute;
right: 0;
}
/* good */
div {
width: 100px;
margin-left: auto;
}
选择器
紧密耦合DOM选择器,三个层级以上建议加class:
/* bad */
div:first-of-type :last-child > p ~ *
/* good */
div:first-of-type .info
避免不必要的写法:
/* bad */
img[src$=svg], ul > li:first-child {
opacity: 0;
}
/* good */
[src$=svg], ul > :first-child {
opacity: 0;
}
指明
不要让代码难于重写,让选择器更精确,减少ID、避免使用!important
/* bad */
.bar {
color: green !important;
}
.foo {
color: red;
}
/* good */
.foo.bar {
color: green;
}
.foo {
color: red;
}
覆盖
覆盖样式会使维护和调试更困难,所以要尽量避免。
/* bad */
li {
visibility: hidden;
}
li:first-child {
visibility: visible;
}
/* good */
li + li {
visibility: hidden;
}
继承
不要把可继承的样式重复声明:
/* bad */
div h1, div p {
text-shadow: 0 1px 0 #fff;
}
/* good */
div {
text-shadow: 0 1px 0 #fff;
}
简洁性
保持代码的简洁。使用属性缩写。不必要的值不用写。
/* bad */
div {
transition: all 1s;
top: 50%;
margin-top: -10px;
padding-top: 5px;
padding-right: 10px;
padding-bottom: 20px;
padding-left: 10px;
}
/* good */
div {
transition: 1s;
top: calc(50% - 10px);
padding: 5px 10px 20px;
}
语言
能用英文的时候不用数字。
/* bad */
:nth-child(2n + 1) {
transform: rotate(360deg);
}
/* good */
:nth-child(odd) {
transform: rotate(1turn);
}
动画
除了变形和改变透明度用animation,其他尽量使用transition。
/* bad */
div:hover {
animation: move 1s forwards;
}
@keyframes move {
100% {
margin-left: 100px;
}
}
/* good */
div:hover {
transition: 1s;
transform: translateX(100px);
}
单位
可以不用单位时就不用。建议用rem。时间单位用s比ms好。
/* bad */
div {
margin: 0px;
font-size: .9em;
line-height: 22px;
transition: 500ms;
}
/* good */
div {
margin: 0;
font-size: .9rem;
line-height: 1.5;
transition: .5s;
}
颜色
需要做透明效果是用rgba,否则都用16进制表示:
/* bad */
div {
color: hsl(103, 54%, 43%);
}
/* good */
div {
color: #5a3;
}
绘图
减少HTTPS请求,尽量用CSS绘图替代图片:
/* bad */
div::before {
content: url(white-circle.svg);
}
/* good */
div::before {
content: "";
display: block;
width: 20px;
height: 20px;
border-radius: 50%;
background: #fff;
}
注释
/* bad */
div {
// position: relative;
transform: translateZ(0);
}
/* good */
div {
/* position: relative; */
will-change: transform;
}
语法
- 用两个空格来代替制表符(tab) -- 这是唯一能保证在所有环境下获得一致展现的方法。
- 为选择器分组时,将单独的选择器单独放在一行。
- 为了代码的易读性,在每个声明块的左花括号前添加一个空格。
- 声明块的右花括号应当单独成行。
- 每条声明语句的 : 后应该插入一个空格。
- 为了获得更准确的错误报告,每条声明都应该独占一行。
- 所有声明语句都应当以分号结尾。最后一条声明语句后面的分号是可选的,但是,如果省略这个分号,你的代码可能更易出错。
- 对于以逗号分隔的属性值,每个逗号后面都应该插入一个空格(例如,box-shadow)。
- 不要在 rgb()、rgba()、hsl()、hsla() 或 rect() 值的内部的逗号后面插入空格。这样利于从多个属性值(既加逗号也加空格)中区分多个颜色值(只加逗号,不加空格)。
/* Bad CSS */
.selector, .selector-secondary, .selector[type=text] {
padding:15px;
margin:0px 0px 15px;
background-color:rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.5);
box-shadow:0px 1px 2px #CCC,inset 0 1px 0 #FFFFFF
}
/* Good CSS */
.selector,
.selector-secondary,
.selector[type="text"] {
padding: 15px;
margin-bottom: 15px;
background-color: rgba(0,0,0,.5);
box-shadow: 0 1px 2px #ccc, inset 0 1px 0 #fff;
}
id及class命名
*class应以功能过内容命名,不以表现形式命名,通用且有意义的词
*class与id单词字母小写,多个单词组成时,使用中划线“-”分隔
激活及hover的效果class
使用on作为激活状态的class,使用hover作为移上元素(hover)的class
样式的声明顺序
1、定位
2、盒模型
3、关于文字
4、关于颜色,背景
5、其他,如:cursor:pointer
.declaration-order {
/*定位 */
position: absolute;
top: 0;
right: 0;
bottom: 0;
left: 0;
z-index: 100;
/* 盒模型 */
display: block;
box-sizing: border-box;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
padding: 10px;
border: 1px solid #e5e5e5;
border-radius: 3px;
margin: 10px;
float: right;
overflow: hidden;
/* 关于文字 */
font: normal 13px "Helvetica Neue", sans-serif;
line-height: 1.5;
text-align: center;
/* 关于颜色,背景 */
background-color: #f5f5f5;
color: #fff;
opacity: .8;
/*其他 */
cursor: pointer;
}
less语法规范
1.变量,混合的使用
变量,混合,允许我们单独定义一系列通用的样式,然后在需要的时候去调用。所以一些公共的样式规则可以单独在一个less文件中定义,其他地方调用,在做全局样式调整时能很方便的修改
// LESS
@color: #4D926F;
#header {
color: @color;
}
h2 {
color: @color;
}
/* 生成的 CSS */
#header {
color: #4D926F;
}
h2 {
color: #4D926F;
}
//LESS
.bordered {
border-top: dotted 1px black;
border-bottom: solid 2px black;
}
#menu a {
color: #111;
.bordered;
}
.post a {
color: red;
.bordered;
}
/* 生成的 CSS */
#menu a {
color: #111;
border-top: dotted 1px black;
border-bottom: solid 2px black;
}
.post a {
color: red;
border-top: dotted 1px black;
border-bottom: solid 2px black;
}
2.嵌套规则(避免嵌套层级过多)
将嵌套深度限制在2-3级。对于超过3级的嵌套,给予重新评估。这可以避免出现过于详实的CSS选择器。 避免大量的嵌套规则。当可读性受到影响时,将之打断。推荐避免出现多于20行的嵌套规则出现。
#header {
color: black;
.navigation {
font-size: 12px;
}
.logo {
width: 300px;
&:hover { text-decoration: none }
}
}
3.命名空间
有时候,你可能为了更好组织CSS或者单纯是为了更好的封装,将一些变量或者混合模块打包起来, 你可以像下面这样在#bundle中定义一些属性集之后可以重复使用:
#bundle {
.button () {
display: block;
border: 1px solid black;
background-color: grey;
&:hover { background-color: white }
}
.tab { ... }
.citation { ... }
}
/*你只需要在 #header a中像这样引入 .button:*/
#header a {
color: orange;
#bundle > .button;
}
以上HTML和CSS的规范大部分参考github上的frontend-guidelines及编码规范by@mdo(后面几个自己新增
三、JavaScript
javascript规范使用的是Standard标准,其好处可点击超链接查看,npm,github等都是使用的此标准。 下文copy的Standard Style的具体规则,配合eslint使用
1. ==使用两个空格==进行缩进。
eslint: indent
function hello (name) {
console.log('hi', name)
}
2.除需要转义的情况外,==字符串统一使用单引号==。
eslint: quotes
console.log('hello there')
$("<div class='box'>")
3.==不要定义未使用的变量==。
eslint: no-unused-vars
function myFunction () {
var result = something() // ✗ avoid
}
4.==关键字后面加空格==。
eslint: keyword-spacing
if (condition) { ... } // ✓ ok
if(condition) { ... } // ✗ avoid
5.==函数声明时括号与函数名间加空格==。
eslint: space-before-function-paren
function name (arg) { ... } // ✓ ok
function name(arg) { ... } // ✗ avoid
run(function () { ... }) // ✓ ok
run(function() { ... }) // ✗ avoid
6.==始终使用== === 替代 ==。
例外: obj == null 可以用来检查 null || undefined。
eslint: eqeqeq
if (name === 'John') // ✓ ok
if (name == 'John') // ✗ avoid
if (name !== 'John') // ✓ ok
if (name != 'John') // ✗ avoid
7.==字符串拼接操作符== (Infix operators) 之间要==留空格==。
eslint: space-infix-ops
// ✓ ok
var x = 2
var message = 'hello, ' + name + '!'
// ✗ avoid
var x=2
var message = 'hello, '+name+'!'
8.==逗号后面加空格==。
eslint: comma-spacing
// ✓ ok
var list = [1, 2, 3, 4]
function greet (name, options) { ... }
// ✗ avoid
var list = [1,2,3,4]
function greet (name,options) { ... }
9.==else 关键字要与花括号保持在同一行==。
eslint: brace-style
// ✓ ok
if (condition) {
// ...
} else {
// ...
}
// ✗ avoid
if (condition)
{
// ...
}
else
{
// ...
}
10.==多行 if 语句的的括号不能省==。
eslint: curly
// ✓ ok
if (options.quiet !== true) console.log('done')
// ✓ ok
if (options.quiet !== true) {
console.log('done')
}
// ✗ avoid
if (options.quiet !== true)
console.log('done')
11.==不要丢掉异常处理中err参数==。
eslint: handle-callback-err
// ✓ ok
run(function (err) {
if (err) throw err
window.alert('done')
})
// ✗ avoid
run(function (err) {
window.alert('done')
})
12.==使用浏览器全局变量时加上 window. 前缀==。
例外: document, console and navigator
eslint: no-undef
window.alert('hi') // ✓ ok
13.==不允许有连续多行空行==。
eslint: no-multiple-empty-lines
// ✓ ok
var value = 'hello world'
console.log(value)
// ✗ avoid
var value = 'hello world'
console.log(value)
14.==对于三元运算符 ? 和 : 与他们所负责的代码处于同一行==。
eslint: operator-linebreak
// ✓ ok
var location = env.development ? 'localhost' : 'www.api.com'
// ✓ ok
var location = env.development
? 'localhost'
: 'www.api.com'
// ✗ avoid
var location = env.development ?
'localhost' :
'www.api.com'
15.==每个 var 关键字单独声明一个变量==。
eslint: one-var
// ✓ ok
var silent = true
var verbose = true
// ✗ avoid
var silent = true, verbose = true
// ✗ avoid
var silent = true,
verbose = true
16.==条件语句中赋值语句使用括号包起来==。这样使得代码更加清晰可读,而不会认为是将条件判断语句的全等号(===)错写成了等号(=)。
eslint: no-cond-assign
// ✓ ok
while ((m = text.match(expr))) {
// ...
}
// ✗ avoid
while (m = text.match(expr)) {
// ...
}
17.==单行代码块两边加空格==。
eslint: block-spacing
function foo () {return true} // ✗ avoid
function foo () { return true } // ✓ ok
18.对于变量和函数名统一使用==驼峰命名法==。
eslint: camelcase
function my_function () { } // ✗ avoid
function myFunction () { } // ✓ ok
var my_var = 'hello' // ✗ avoid
var myVar = 'hello' // ✓ ok
19.==不允许有多余的行末逗号==。
eslint: comma-dangle
var obj = {
message: 'hello', // ✗ avoid
}
20.==始终将逗号置于行末==。
eslint: comma-style
var obj = {
foo: 'foo'
,bar: 'bar' // ✗ avoid
}
var obj = {
foo: 'foo',
bar: 'bar' // ✓ ok
}
21.==文件末尾留一空行==。
elint: eol-last
22.==函数调用时标识符与括号间不留间隔==。
eslint: func-call-spacing
console.log ('hello') // ✗ avoid
console.log('hello') // ✓ ok
23.==键值对当中冒号与值之间要留空白==。
eslint: key-spacing
var obj = { 'key' : 'value' } // ✗ avoid
var obj = { 'key' :'value' } // ✗ avoid
var obj = { 'key':'value' } // ✗ avoid
var obj = { 'key': 'value' } // ✓ ok
24.==构造函数要以大写字母开头==。
eslint: new-cap
function animal () {}
var dog = new animal() // ✗ avoid
function Animal () {}
var dog = new Animal() // ✓ ok
25.==无参的构造函数调用时要带上括号==。
eslint: new-parens
function Animal () {}
var dog = new Animal // ✗ avoid
var dog = new Animal() // ✓ ok
26.==对象中定义了存值器,一定要对应的定义取值器==。
eslint: accessor-pairs
var person = {
set name (value) { // ✗ avoid
this.name = value
}
}
var person = {
set name (value) {
this.name = value
},
get name () { // ✓ ok
return this.name
}
}
27.==子类的构造器中一定要调用 super==
eslint: constructor-super
class Dog {
constructor () {
super() // ✗ avoid
}
}
class Dog extends Mammal {
constructor () {
super() // ✓ ok
}
}
28.==使用数组字面量而不是构造器==。
eslint: no-array-constructor
var nums = new Array(1, 2, 3) // ✗ avoid
var nums = [1, 2, 3] // ✓ ok
29.==避免使用 arguments.callee 和 arguments.caller==。
eslint: no-caller
function foo (n) {
if (n <= 0) return
arguments.callee(n - 1) // ✗ avoid
}
function foo (n) {
if (n <= 0) return
foo(n - 1)
}
30.==避免对类名重新赋值==。
eslint: no-class-assign
class Dog {}
Dog = 'Fido' // ✗ avoid
31.==避免修改使用 const 声明的变量==。
eslint: no-const-assign
const score = 100
score = 125 // ✗ avoid
32.==避免使用常量作为条件表达式的条件(循环语句除外)==。
eslint: no-constant-condition
if (false) { // ✗ avoid
// ...
}
if (x === 0) { // ✓ ok
// ...
}
while (true) { // ✓ ok
// ...
}
33.==正则中不要使用控制符==。
eslint: no-control-regex
var pattern = /\x1f/ // ✗ avoid
var pattern = /\x20/ // ✓ ok
34.==不要使用 debugger==。
eslint: no-debugger
function sum (a, b) {
debugger // ✗ avoid
return a + b
}
35.==不要对变量使用 delete 操作==。
eslint: no-delete-var
var name
delete name // ✗ avoid
36.==不要定义冗余的函数参数==。
eslint: no-dupe-args
function sum (a, b, a) { // ✗ avoid
// ...
}
function sum (a, b, c) { // ✓ ok
// ...
}
37.==类中不要定义冗余的属性==。
eslint: no-dupe-class-members
class Dog {
bark () {}
bark () {} // ✗ avoid
}
38.==对象字面量中不要定义重复的属性==。
eslint: no-dupe-keys
var user = {
name: 'Jane Doe',
name: 'John Doe' // ✗ avoid
}
39.==switch 语句中不要定义重复的 case 分支==。
eslint: no-duplicate-case
switch (id) {
case 1:
// ...
case 1: // ✗ avoid
}
40.==同一模块有多个导入时一次性写完==。
eslint: no-duplicate-imports
import { myFunc1 } from 'module'
import { myFunc2 } from 'module' // ✗ avoid
import { myFunc1, myFunc2 } from 'module' // ✓ ok
41.==正则中不要使用空字符==。
eslint: no-empty-character-class
const myRegex = /^abc[]/ // ✗ avoid
const myRegex = /^abc[a-z]/ // ✓ ok
42.==不要解构空值==。
eslint: no-empty-pattern
const { a: {} } = foo // ✗ avoid
const { a: { b } } = foo // ✓ ok
43.==不要使用 eval()==。
eslint: no-eval
eval( "var result = user." + propName ) // ✗ avoid
var result = user[propName] // ✓ ok
44.==catch 中不要对错误重新赋值==。
eslint: no-ex-assign
try {
// ...
} catch (e) {
e = 'new value' // ✗ avoid
}
try {
// ...
} catch (e) {
const newVal = 'new value' // ✓ ok
}
45.==不要扩展原生对象==。
eslint: no-extend-native
Object.prototype.age = 21 // ✗ avoid
46.==避免多余的函数上下文绑定==。
eslint: no-extra-bind
const name = function () {
getName()
}.bind(user) // ✗ avoid
const name = function () {
this.getName()
}.bind(user) // ✓ ok
47.==避免不必要的布尔转换==。
eslint: no-extra-boolean-cast
const result = true
if (!!result) { // ✗ avoid
// ...
}
const result = true
if (result) { // ✓ ok
// ...
}
48.==不要使用多余的括号包裹函数==。
eslint: no-extra-parens
const myFunc = (function () { }) // ✗ avoid
const myFunc = function () { } // ✓ ok
49.==switch 一定要使用 break 来将条件分支正常中断==。
eslint: no-fallthrough
switch (filter) {
case 1:
doSomething() // ✗ avoid
case 2:
doSomethingElse()
}
switch (filter) {
case 1:
doSomething()
break // ✓ ok
case 2:
doSomethingElse()
}
switch (filter) {
case 1:
doSomething()
// fallthrough // ✓ ok
case 2:
doSomethingElse()
}
50.==不要省去小数点前面的0==。
eslint: no-floating-decimal
const discount = .5 // ✗ avoid
const discount = 0.5 // ✓ ok
51.==避免对声明过的函数重新赋值==。
eslint: no-func-assign
function myFunc () { }
myFunc = myOtherFunc // ✗ avoid
52.==不要对全局只读对象重新赋值==。
eslint: no-global-assign
window = {} // ✗ avoid
53.==注意隐式的 eval()==。
eslint: no-implied-eval
setTimeout("alert('Hello world')") // ✗ avoid
setTimeout(function () { alert('Hello world') }) // ✓ ok
54.==嵌套的代码块中禁止再定义函数==。
eslint: no-inner-declarations
if (authenticated) {
function setAuthUser () {} // ✗ avoid
}
55.==不要向 RegExp 构造器传入非法的正则表达式==。
eslint: no-invalid-regexp
RegExp('[a-z') // ✗ avoid
RegExp('[a-z]') // ✓ ok
56.==不要使用非法的空白符==。
eslint: no-irregular-whitespace
function myFunc () /*<NBSP>*/{} // ✗ avoid
57.==禁止使用 iterator==。
eslint: no-iterator
Foo.prototype.__iterator__ = function () {} // ✗ avoid
58.==外部变量不要与对象属性重名==。
eslint: no-label-var
var score = 100
function game () {
score: 50 // ✗ avoid
}
59.==不要使用标签语句==
eslint: no-labels
label:
while (true) {
break label // ✗ avoid
}
60.==不要书写不必要的嵌套代码块==。
eslint: no-lone-blocks
function myFunc () {
{ // ✗ avoid
myOtherFunc()
}
}
function myFunc () {
myOtherFunc() // ✓ ok
}
61.==不要混合使用空格与制表符作为缩进==。
eslint: no-mixed-spaces-and-tabs
62.==除了缩进,不要使用多个空格==。
eslint: no-multi-spaces
const id = 1234 // ✗ avoid
const id = 1234 // ✓ ok
63.==不要使用多行字符串==。
eslint: no-multi-str
const message = 'Hello \
world' // ✗ avoid
64.==new 创建对象实例后需要赋值给变量==。
eslint: no-new
new Character() // ✗ avoid
const character = new Character() // ✓ ok
65.==禁止使用 Function 构造器==。
eslint: no-new-func
var sum = new Function('a', 'b', 'return a + b') // ✗ avoid
66.==禁止使用 Object 构造器==。
eslint: no-new-object
let config = new Object() // ✗ avoid
67.==禁止使用 new require==。
eslint: no-new-require
const myModule = new require('my-module') // ✗ avoid
68.==禁止使用 Symbol 构造器==。
eslint: no-new-symbol
const foo = new Symbol('foo') // ✗ avoid
69.==禁止使用原始包装器==。
eslint: no-new-wrappers
const message = new String('hello') // ✗ avoid
70.==不要将全局对象的属性作为函数调用==。
eslint: no-obj-calls
const math = Math() // ✗ avoid
71.==不要使用八进制字面量==。
eslint: no-octal
const num = 042 // ✗ avoid
const num = '042' // ✓ ok
72.==字符串字面量中也不要使用八进制转义字符==。
eslint: no-octal-escape
const copyright = 'Copyright \251' // ✗ avoid
73.==使用 __dirname 和 __filename 时尽量避免使用字符串拼接==。
eslint: no-path-concat
const pathToFile = __dirname + '/app.js' // ✗ avoid
const pathToFile = path.join(__dirname, 'app.js') // ✓ ok
74.==使用 getPrototypeOf 来替代 proto==。
eslint: no-proto
const foo = obj.__proto__ // ✗ avoid
const foo = Object.getPrototypeOf(obj) // ✓ ok
75.==不要重复声明变量==。
eslint: no-redeclare
let name = 'John'
let name = 'Jane' // ✗ avoid
let name = 'John'
name = 'Jane' // ✓ ok
76.==正则中避免使用多个空格==。
eslint: no-regex-spaces
const regexp = /test value/ // ✗ avoid
const regexp = /test {3}value/ // ✓ ok
const regexp = /test value/ // ✓ ok
77.==return 语句中的赋值必需有括号包裹==。
eslint: no-return-assign
function sum (a, b) {
return result = a + b // ✗ avoid
}
function sum (a, b) {
return (result = a + b) // ✓ ok
}
78.==避免将变量赋值给自己==。
eslint: no-self-assign
name = name // ✗ avoid
79.==避免将变量与自己进行比较操作==。
esint: no-self-compare
if (score === score) {} // ✗ avoid
80.==避免使用逗号操作符==。
eslint: no-sequences
if (doSomething(), !!test) {} // ✗ avoid
81.==不要随意更改关键字的值==。
eslint: no-shadow-restricted-names
let undefined = 'value' // ✗ avoid
82.==禁止使用稀疏数组(Sparse arrays)==。
eslint: no-sparse-arrays
let fruits = ['apple',, 'orange'] // ✗ avoid
83.==不要使用制表符==。
eslint: no-tabs
84.==正确使用 ES6 中的字符串模板==。
eslint: no-template-curly-in-string
const message = 'Hello ${name}' // ✗ avoid
const message = `Hello ${name}` // ✓ ok
85.==使用 this 前请确保 super() 已调用==。
eslint: no-this-before-super
class Dog extends Animal {
constructor () {
this.legs = 4 // ✗ avoid
super()
}
}
86.==用 throw 抛错时,抛出 Error 对象而不是字符串==。
eslint: no-throw-literal
throw 'error' // ✗ avoid
throw new Error('error') // ✓ ok
87.==行末不留空格==。
eslint: no-trailing-spaces
88.==不要使用 undefined 来初始化变量==。
eslint: no-undef-init
let name = undefined // ✗ avoid
let name
name = 'value' // ✓ ok
89.==循环语句中注意更新循环变量==。
eslint: no-unmodified-loop-condition
for (let i = 0; i < items.length; j++) {...} // ✗ avoid
for (let i = 0; i < items.length; i++) {...} // ✓ ok
90.==如果有更好的实现,尽量不要使用三元表达式==。
eslint: no-unneeded-ternary
let score = val ? val : 0 // ✗ avoid
let score = val || 0 // ✓ ok
91.==return,throw,continue 和 break 后不要再跟代码==。
eslint: no-unreachable
function doSomething () {
return true
console.log('never called') // ✗ avoid
}
92.==finally 代码块中不要再改变程序执行流程==。
eslint: no-unsafe-finally
try {
// ...
} catch (e) {
// ...
} finally {
return 42 // ✗ avoid
}
93.==关系运算符的左值不要做取反操作==。
eslint: no-unsafe-negation
if (!key in obj) {} // ✗ avoid
94.==避免不必要的 .call() 和 .apply()==。
eslint: no-useless-call
sum.call(null, 1, 2, 3) // ✗ avoid
95.==避免使用不必要的计算值作对象属性==。
eslint: no-useless-computed-key
const user = { ['name']: 'John Doe' } // ✗ avoid
const user = { name: 'John Doe' } // ✓ ok
96.==禁止多余的构造器==。
eslint: no-useless-constructor
class Car {
constructor () { // ✗ avoid
}
}
97.==禁止不必要的转义==。
eslint: no-useless-escape
let message = 'Hell\o' // ✗ avoid
98.==import, export 和解构操作中,禁止赋值到同名变量==。
eslint: no-useless-rename
import { config as config } from './config' // ✗ avoid
import { config } from './config' // ✓ ok
99.==属性前面不要加空格==。
eslint: no-whitespace-before-property
user .name // ✗ avoid
user.name // ✓ ok
100.==禁止使用 with==。
eslint: no-with
with (val) {...} // ✗ avoid
101.==对象属性换行时注意统一代码风格==。
eslint: object-property-newline
const user = {
name: 'Jane Doe', age: 30,
username: 'jdoe86' // ✗ avoid
}
const user = { name: 'Jane Doe', age: 30, username: 'jdoe86' } // ✓ ok
const user = {
name: 'Jane Doe',
age: 30,
username: 'jdoe86'
}
102.==代码块中避免多余留白==。
eslint: padded-blocks
if (user) {
// ✗ avoid
const name = getName()
}
if (user) {
const name = getName() // ✓ ok
}
103.==展开运算符与它的表达式间不要留空白==。
eslint: rest-spread-spacing
fn(... args) // ✗ avoid
fn(...args) // ✓ ok
104.==遇到分号时空格要后留前不留==。
eslint: semi-spacing
for (let i = 0 ;i < items.length ;i++) {...} // ✗ avoid
for (let i = 0; i < items.length; i++) {...} // ✓ ok
105.==代码块首尾留空格==。
eslint: space-before-blocks
if (admin){...} // ✗ avoid
if (admin) {...} // ✓ ok
106.==圆括号间不留空格==
eslint: space-in-parens
getName( name ) // ✗ avoid
getName(name) // ✓ ok
107.==一元运算符后面跟一个空格==。
eslint: space-unary-ops
typeof!admin // ✗ avoid
typeof !admin // ✓ ok
108.==注释首尾留空格==。
eslint: spaced-comment
//comment // ✗ avoid
// comment // ✓ ok
/*comment*/ // ✗ avoid
/* comment */ // ✓ ok
109.==模板字符串中变量前后不加空格==。
eslint: template-curly-spacing
const message = `Hello, ${ name }` // ✗ avoid
const message = `Hello, ${name}` // ✓ ok
110.==检查 NaN 的正确姿势是使用 isNaN()==。
eslint: use-isnan
if (price === NaN) { } // ✗ avoid
if (isNaN(price)) { } // ✓ ok
111.==用合法的字符串跟 typeof 进行比较操作==。
eslint: valid-typeof
typeof name === 'undefimed' // ✗ avoid
typeof name === 'undefined' // ✓ ok
112.==自调用匿名函数 (IIFEs) 使用括号包裹==。
eslint: wrap-iife
const getName = function () { }() // ✗ avoid
const getName = (function () { }()) // ✓ ok
const getName = (function () { })() // ✓ ok
113.==yield * 中的 * 前后都要有空格==。
eslint: yield-star-spacing
yield* increment() // ✗ avoid
yield * increment() // ✓ ok
114.==请书写优雅的条件语句(avoid Yoda conditions)==。
eslint: yoda
if (42 === age) { } // ✗ avoid
if (age === 42) { } // ✓ ok
115.==使用分号==。
eslint: semi
window.alert('hi') // ✗ avoid
window.alert('hi'); // ✓ ok
116.==不要使用 (, [, or ` 等作为一行的开始==。在没有分号的情况下代码压缩后会导致报错,而坚持这一规范则可避免出错。
** eslint: no-unexpected-multiline **
// ✓ ok
;(function () {
window.alert('ok')
}())
// ✗ avoid
(function () {
window.alert('ok')
}())
// ✓ ok
;[1, 2, 3].forEach(bar)
// ✗ avoid
[1, 2, 3].forEach(bar)
// ✓ ok
;`hello`.indexOf('o')
// ✗ avoid
`hello`.indexOf('o')
备注:上面的写法只能说聪明过头了。
相比更加可读易懂的代码,那些看似投巧的写法是不可取的。
譬如:
;[1, 2, 3].forEach(bar)
建议的写法是:
var nums = [1, 2, 3]
nums.forEach(bar)
es6语法规范
1.==let 取代 var==
ES6 提出了两个新的声明变量的命令:let和const。其中,let完全可以取代var,因为两者语义相同,而且let没有副作用。
2.==全局常量const==
在全局环境,不应该设置变量,只应设置常量
好处:
const优于let有几个原因。一个是const可以提醒阅读程序的人,这个变量不应该改变;另一个是const比较符合函数式编程思想,运算不改变值,只是新建值,而且这样也有利于将来的分布式运算;最后一个原因是 JavaScript 编译器会对const进行优化,所以多使用const,有利于提高程序的运行效率,也就是说let和const的本质区别,其实是编译器内部的处理不同。 const声明常量还有两个好处,一是阅读代码的人立刻会意识到不应该修改这个值,二是防止了无意间修改变量值所导致的错误。
3.==使用解构赋值==
使用数组成员对变量赋值时,优先使用解构赋值。
const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4];
// bad
const first = arr[0];
const second = arr[1];
// good
const [first, second] = arr;
函数的参数如果是对象的成员,优先使用解构赋值。
// bad
function getFullName(user) {
const firstName = user.firstName;
const lastName = user.lastName;
}
// good
function getFullName(obj) {
const { firstName, lastName } = obj;
}
// best
function getFullName({ firstName, lastName }) {
}
如果函数返回多个值,优先使用对象的解构赋值,而不是数组的解构赋值。这样便于以后添加返回值,以及更改返回值的顺序。
// bad
function processInput(input) {
return [left, right, top, bottom];
}
// good
function processInput(input) {
return { left, right, top, bottom };
}
const { left, right } = processInput(input);
4.==对象==
对象尽量静态化,一旦定义,就不得随意添加新的属性。如果添加属性不可避免,要使用Object.assign方法。
// bad
const a = {};
a.x = 3;
// if reshape unavoidable
const a = {};
Object.assign(a, { x: 3 });
// good
const a = { x: null };
a.x = 3;
如果对象的属性名是动态的,可以在创造对象的时候,使用属性表达式定义。
// bad
const obj = {
id: 5,
name: 'San Francisco',
};
obj[getKey('enabled')] = true;
// good
const obj = {
id: 5,
name: 'San Francisco',
[getKey('enabled')]: true,
};
另外,对象的属性和方法,尽量采用简洁表达法,这样易于描述和书写。
var ref = 'some value';
// bad
const atom = {
ref: ref,
value: 1,
addValue: function (value) {
return atom.value + value;
},
};
// good
const atom = {
ref,
value: 1,
addValue(value) {
return atom.value + value;
},
};
5.==数组==
使用扩展运算符(...)拷贝数组。
// bad
const len = items.length;
const itemsCopy = [];
let i;
for (i = 0; i < len; i++) {
itemsCopy[i] = items[i];
}
// good
const itemsCopy = [...items];
使用 Array.from 方法,将类似数组的对象转为数组。
const foo = document.querySelectorAll('.foo');
const nodes = Array.from(foo);
6.==函数==
立即执行函数可以写成箭头函数的形式。
(() => {
console.log('Welcome to the Internet.');
})();
那些需要使用函数表达式的场合,尽量用箭头函数代替。因为这样更简洁,而且绑定了 this。
// bad
[1, 2, 3].map(function (x) {
return x * x;
});
// good
[1, 2, 3].map((x) => {
return x * x;
});
// best
[1, 2, 3].map(x => x * x);
简单的、单行的、不会复用的函数,建议采用箭头函数。如果函数体较为复杂,行数较多,还是应该采用传统的函数写法。
7.==Map结构==
注意区分 Object 和 Map,只有模拟现实世界的实体对象时,才使用 Object。如果只是需要key: value的数据结构,使用 Map 结构。因为 Map 有内建的遍历机制。
let map = new Map(arr);
for (let key of map.keys()) {
console.log(key);
}
for (let value of map.values()) {
console.log(value);
}
for (let item of map.entries()) {
console.log(item[0], item[1]);
}
8.==class==
总是用 Class,取代需要 prototype 的操作。因为 Class 的写法更简洁,更易于理解。
// bad
function Queue(contents = []) {
this._queue = [...contents];
}
Queue.prototype.pop = function() {
const value = this._queue[0];
this._queue.splice(0, 1);
return value;
}
// good
class Queue {
constructor(contents = []) {
this._queue = [...contents];
}
pop() {
const value = this._queue[0];
this._queue.splice(0, 1);
return value;
}
}
使用extends实现继承,因为这样更简单,不会有破坏instanceof运算的危险。
// bad
const inherits = require('inherits');
function PeekableQueue(contents) {
Queue.apply(this, contents);
}
inherits(PeekableQueue, Queue);
PeekableQueue.prototype.peek = function() {
return this._queue[0];
}
// good
class PeekableQueue extends Queue {
peek() {
return this._queue[0];
}
}
9.==使用promise时==
一般来说,不要在then方法里面定义失败状态的回调函数(即then的第二个参数),总是使用catch方法
// bad
promise
.then(function(data) {
// success
}, function(err) {
// error
});
// good
promise
.then(function(data) { //cb
// success
})
.catch(function(err) {
// error
});
新增
i++
尽量不要使用i++,尽量使用i+=1;(除了for循环)
四、vue规范
1.vue方法放置顺序
1.1 components
1.2 props
1.3 data
1.4 created
1.5 mounted
1.6 activited
1.7 update
1.8 beforeRouteUpdate
1.9 metods
1.10 filter
1.11 computed
1.12 watch
2.method 自定义方法命名
2.1 动宾短语(good:jumpPage、openCarInfoDialog)(bad:go、nextPage、show、open、login)
2.2 ajax 方法以 get、post 开头,以 data 结尾(good:getListData、postFormData)(bad:takeData、confirmData、getList、postForm)
2.3 事件方法以 on 开头(onTypeChange、onUsernameInput)
2.4 init、refresh 单词除外
2.5 尽量使用常用单词开头(set、get、open、close、jump)
2.6 驼峰命名(good: getListData)(bad: get_list_data、getlistData)
3.生命周期方法注意点
3.1 不在 mounted、created 之类的方法写逻辑,取 ajax 数据,
3.2 在 created 里面监听 Bus 事件
4.基于模块开发
原则:每一个vue组件首先必须专注于解决一个单一的问题,独立的,可复用的,微小的和可测试的。 如果你的组件做了太多的事或是变得臃肿,请将其拆成更小的组件并保持单一的原则。
5.Vue 组件命名
- 有意义的: 不过于具体,也不过于抽象
- 简短: 2 到 3 个单词
- 具有可读性: 以便于沟通交流
<!-- 推荐 -->
<app-header></app-header>
<user-list></user-list>
<range-slider></range-slider>
<!-- 避免 -->
<btn-group></btn-group> <!-- 虽然简短但是可读性差. 使用 `button-group` 替代 -->
<ui-slider></ui-slider> <!-- ui 前缀太过于宽泛,在这里意义不明确 -->
<slider></slider> <!-- 与自定义元素规范不兼容 -->
6.验证组件的props
- 提供默认值。
- 使用 type 属性校验类型。
- 使用 props 之前先检查该 prop 是否存在。
<template>
<input type="range" v-model="value" :max="max" :min="min">
</template>
<script type="text/javascript">
export default {
props: {
max: {
type: Number, // 这里添加了数字类型的校验
default() { return 10; },
},
min: {
type: Number,
default() { return 0; },
},
value: {
type: Number,
default() { return 4; },
},
},
};
</script>
7.只在需要时创建组件
Vue.js 是一个基于组件的框架。如果你不知道何时创建组件可能会导致以下问题:
- 如果组件太大, 可能很难重用和维护;
- 如果组件太小,你的项目就会(因为深层次的嵌套而)被淹没,也更难使组件间通信;
规则
-
首先,尽可能早地尝试构建出诸如模态框、提示框、工具条、菜单、头部等这些明显的(通用型)组件。总之,你知道的这些组件以后一定会在当前页面或者是全局范围内需要。
-
第二,在每一个新的开发项目中,对于一整个页面或者其中的一部分,在进行开发前先尝试思考一下。如果你认为它有一部分应该是一个组件,那么就创建它吧。
-
最后,如果你不确定,那就不要。避免那些“以后可能会有用”的组件污染你的项目。它们可能会永远的只是(静静地)待在那里,这一点也不聪明。注意,一旦你意识到应该这么做,最好是就把它打破,以避免与项目的其他部分构成兼容性和复杂性。
注释规范
1.在vscode中使用vscode-fileheader插件,生成头部文件注释
2.普通的注释
2.1 总是在单行注释符后留一个空格
// this is comment
2.2 总是在多行注释的结束符前留一个空格(使星号对齐)
/*
*/
2.3 不要把注释写在多行注释的开始符、结束符所在行
// bad
/* start
end */
// good
/*
here is line 1
here is line 2
*/
2.4 不要编写无意义的注释
// 初始化value变量为0
var value = 0;
2.5 如果某段代码有功能未实现,或者有待完善,必须添加“TODO”标记,“TODO”前后应留一个空格
// TODO 未处理IE6-8的兼容性
function setOpacity(node, val) {
node.style.opacity = val;
}
3.文档注释
文档注释将会以预定格式出现在API文档中。它以“/**”开头,以“/”结束,其间的每一行均以“”开头(均与开始符的第一个“”对齐),且注释内容与“”间留一个空格。
3.1 @module。声明模块
/**
* 模块说明
* @module 模块名
*/
/**
* Core模块提供最基础、最核心的接口
* @module Core
*/
3.2 @class。声明类
/**
* 类说明
* @class 类名
* @constructor
*/
@class必须搭配@constructor或@static使用,分别标记非静态类与静态类。
/**
* 节点集合类
* @class NodeList
* @constructor
* @param {ArrayLike<Element>} nodes 初始化节点
*/
3.3 @method。声明函数或类方法
/**
* 方法说明
* @method 方法名
* @for 所属类名
* @param {参数类型} 参数名 参数说明
* @return {返回值类型} 返回值说明
*/
没有指定@for时,表示此函数为全局或模块顶层函数。当函数为静态函数时,必须添加@static;当函数有参数时,必须使用@param;当函数有返回值时,必须使用@return。
/**
* 返回当前集合中指定位置的元素
* @method
* @for NodeList
* @param {Number} [i=0] 位置下标。如果为负数,则从集合的最后一个元素开始倒数
* @return {Element} 指定元素
*/
- @param。声明函数参数,必须与@method搭配使用。
- 当参数出现以下情况时,使用对应的格式:[参数名]
- 参数有默认值 [参数名 = 默认值]
3.4 @property。声明类属性
/**
* 属性说明
* @property {属性类型} 属性名
*/