前言
本文介绍一个 nodejs 的爬虫项目,受众对象为初学爬虫不久的小伙伴,通过这个项目能对 node 爬虫有一个简单的认识,也能自己动手写一些简单的爬虫。
项目地址:
启动 koa 服务
🐯最终的数据希望能用于 web 开发,因此我在这里启了一个 web 服务,也是基于 koa。koa 是基于 nodejs 平台的新一代 web 开发框架,使用 koa 启动 node 服务也非常简单,三行代码就能启动一个 http 服务
const Koa = require('koa')
const app = new Koa()
app.listen(8080)
怎么样,是不是看一眼就会,关于 koa 的更多内容可以学习官方文档,只要你能灵活运用 nodejs,koa 也能分分钟上手。
爬虫分析
🕷️爬虫的目的是什么?其实爬虫的目的很简单,就是需要在一个站点中抓取到我们想要的数据。不管用什么方式,用什么语言,只要能把数据抓回来,就达到我们的目的了。但是通过分析站点我们发现,有些网站是静态的,前端无法查看网站中的 api 请求,所以只能通过分析页面去提取数据,这种叫静态抓取。有的页面是前端请求接口渲染数据的,这种我们可以直接拿到 api 地址,而在爬虫中去模拟请求,这种叫动态抓取,基于此,我简单设计了一个通用的爬虫。
全局配置
为了方便,我在全局配置了一些参数方法
const path = require('path')
const base = require('app-root-dir')
// 全局的 require 方式
global.r = (p = base.get(), m = '') => require(path.join(p, m))
// 全局的路径配置
global.APP = {
R: base.get(),
C: path.resolve(base.get(), 'config.js'),
P: path.resolve(base.get(), 'package.json'),
A: path.resolve(base.get(), 'apis'),
L: path.resolve(base.get(), 'lib'),
S: path.resolve(base.get(), 'src'),
D: path.resolve(base.get(), 'data'),
M: path.resolve(base.get(), 'model')
}
为了统一管理,我把所有要抓取的页面地址写到一个配置文件中:
// 所有抓取目标
const targets = {
// 掘金前端相关的文章
juejinFront: {
url: 'https://web-api.juejin.im/query',
method: 'POST',
options: {
headers: {
'X-Agent': 'Juejin/Web',
'X-Legacy-Device-Id': '1559199715822',
'X-Legacy-Token': 'eyJhY2Nlc3NfdG9rZW4iOiJoZ01va0dVNnhLV1U0VGtqIiwicmVmcmVzaF90b2tlbiI6IkczSk81TU9QRjd3WFozY2IiLCJ0b2tlbl90eXBlIjoibWFjIiwiZXhwaXJlX2luIjoyNTkyMDAwfQ==',
'X-Legacy-Uid': '5c9449c15188252d9179ce68'
}
}
},
// 电影天堂的所所有类型的电影
movie: {
url: 'https://www.dy2018.com'
},
// pixabay 图片网站
pixabay: {
url: 'https://pixabay.com'
},
// 豆瓣高分电影
douban: {
url: 'https://movie.douban.com/j/search_subjects?type=movie&tag=%E8%B1%86%E7%93%A3%E9%AB%98%E5%88%86&sort=recommend&page_limit=20&page_start=0'
}
}
如上所示,有的抓取静态页面,有的抓取动态 api,而模拟后者请求的时候,需要设置额外的请求头,post 请求还需要传递 json,都在这里统一配置。
通用类库
分析静态页面我采用了 cheerio 库
cheerio 类似于 node 环境中的 jquery,它能解析页面并提取页面中的相关信息,它暴露出的 api 与 jquery 大同小异,可以理解为 服务端的 jq,如下进行了简单的封装
const cheerio = require('cheerio')
const $ = html => cheerio.load(html, {
ignoreWhitespace: true,
xmlMode: true
})
const $select = (html, selector) => $(html)(selector)
// 节点属性
const $attr = (html, attr) => $(html).attr(attr)
module.exports = {
$,
$select,
$attr
}
superagent 是一个功能完善的 服务端 http 库,它可以把静态页面抓回来提供给 cheerio 来分析,也能抓取动态 api 返回数据,基于此我进行了简单的封装
// 封装 superagent 库
const superagent = require('superagent')
const { isEmpty } = require('lodash')
// 页面需要转码 例如 utf-8
const charset = require('superagent-charset')
const debug = require('debug')('superAgent')
charset(superagent)
const allowMethods = ['GET', 'POST']
const errPromise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
return reject('no url or method is not supported')
}).catch(err => err)
/*
* options 包含 post 数据 和 headers, 如
* {
* json: { a: 1 },
* headers: { accept: 'json' }
* }
*/
// mode 区分动态还是静态抓取, unicode 为页面编码方式,静态页面中使用
const superAgent = (url, {method = 'GET', options = {}} = {}, mode = 'dynamic', unicode = 'gbk') => {
if(!url || !allowMethods.includes(method)) return errPromise
const {headers} = options
let postPromise
if(method === 'GET') {
postPromise = superagent.get(url)
if(mode === 'static') {
// 抓取的静态页面需要根据编码模式解码
postPromise = postPromise.charset(unicode)
}
}
if(method === 'POST') {
const {json} = options
// post 请求要求发送一个 json
postPromise = superagent.post(url).send(json)
}
// 需要请求头的话这里设置请求头
if(headers && !isEmpty(headers)) {
postPromise = postPromise.set(headers)
}
return new Promise(resolve => {
return postPromise
.end((err, res) => {
if(err) {
console.log('err', err)
// 不抛错
return resolve(`There is a ${err.status} error has not been resolved`)
}
// 静态页面,返回 text 页面内容
if(mode === 'static') {
debug('output html in static mode')
return resolve(res.text)
}
// api 返回 body 的内容
return resolve(res.body)
})
})
}
module.exports = superAgent
另外抓回来的数据我们需要读写:
const fs = require('fs')
const path = require('path')
const debug = require('debug')('readFile')
// 默认读取 data 文件夹下的文件
module.exports = (filename, filepath = APP.D) => {
const file = path.join(filepath, filename)
if(fs.existsSync(file)) {
return fs.readFileSync(file, 'utf8')
} else {
debug(`Error: the file is not exist`)
}
}
const fs = require('fs')
const path = require('path')
const debug = require('debug')('writeFile')
// 默认都写入 data 文件夹下的对应文件
module.exports = (filename, data, filepath) => {
const writeData = JSON.stringify(data, '', '\t')
const lastPath = path.join(filepath || APP.D, filename)
if(!fs.existsSync(path.join(filepath || APP.D))) {
fs.mkdirSync(path.join(filepath || APP.D))
}
fs.writeFileSync(lastPath, writeData, function(err) {
if(err) {
debug(`Error: some error occured, the status is ${err.status}`)
}
})
}
一切准备就绪之后开始抓取页面
抓取动态 api
以掘金为例,需要分析并模拟请求
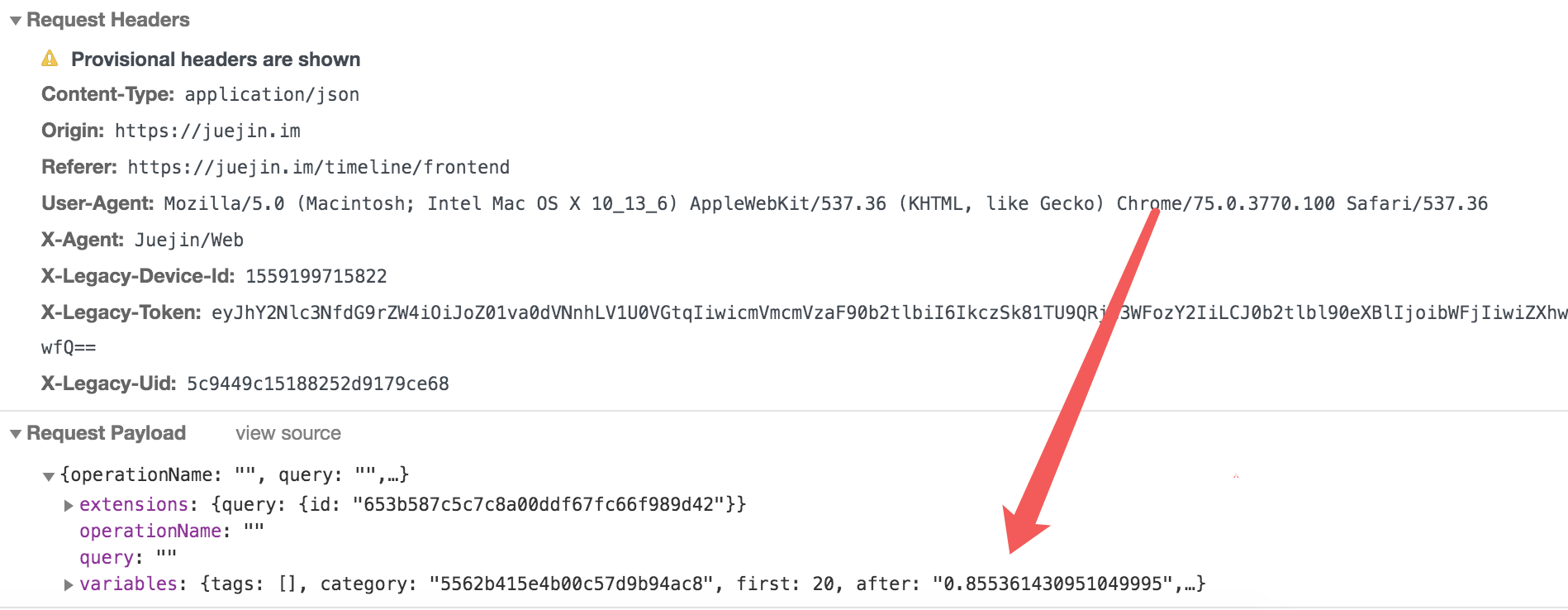

掘金文章的 feed 流是这样实现的,上一页的返回数据中有一个标记after,请求下一页时需要把这个 after 值放在 post 的 json 中,其他的参数是一些静态的,抓取的时候可以先写死
const { get } = require('lodash')
const superAgent = r(APP.L, 'superagent')
const { targets } = r(APP.C)
const writeFile = r(APP.L, 'writeFile')
const { juejinFront } = targets
let totalPage = 10 // 只抓取十页
const getPostJson = ({after = ''}) => {
return {
extensions: {query: {id: '653b587c5c7c8a00ddf67fc66f989d42'}},
operationName: '',
query: '',
variables: {limit: 10, category: '5562b415e4b00c57d9b94ac8', after, order: 'POPULAR', first: 20}
}
}
// 保存所有文章数据
let data = []
let paging = {}
const fetchData = async (params = {}) => {
const {method, options: {headers}} = juejinFront
const options = {method, options: {headers, json: getPostJson(params)}}
// 发起请求
const res = await superAgent(juejinFront.url, options)
const resItems = get(res, 'data.articleFeed.items', {})
data = data.concat(resItems.edges)
paging = {
total: data.length,
...resItems.pageInfo
}
pageInfo = resItems.pageInfo
if(resItems.pageInfo.hasNextPage && totalPage > 1) {
fetchData({after: resItems.pageInfo.endCursor})
totalPage--
} else {
// 请求玩之后写入 data 文件夹
writeFile('juejinFront.json', {paging, data})
}
}
module.exports = fetchData
抓取静态 html
以电影天堂为例
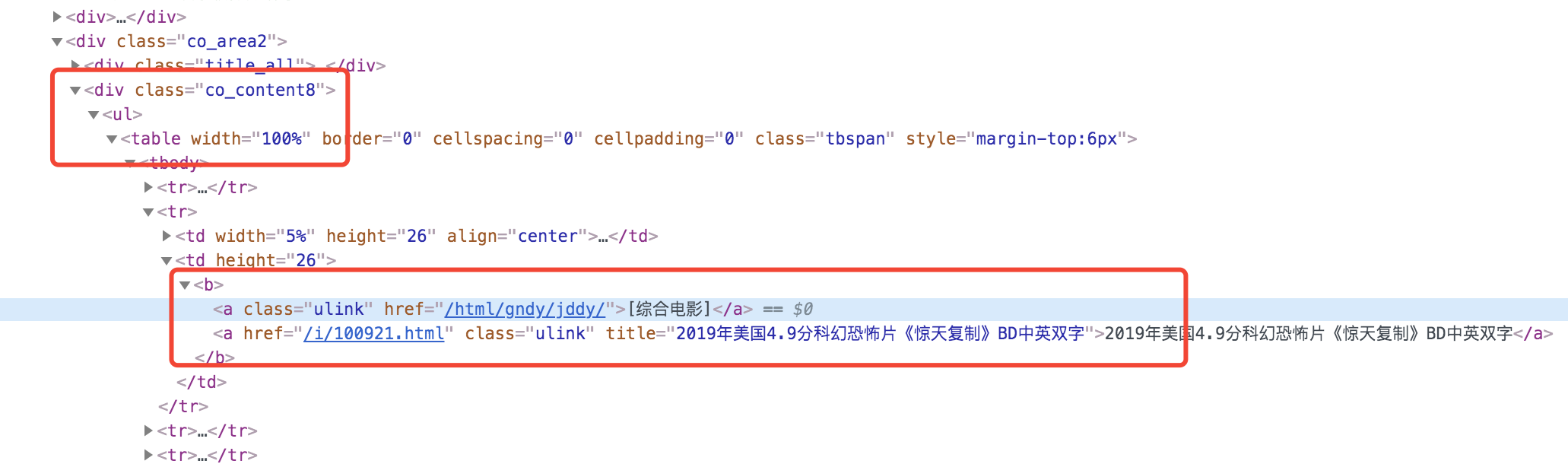
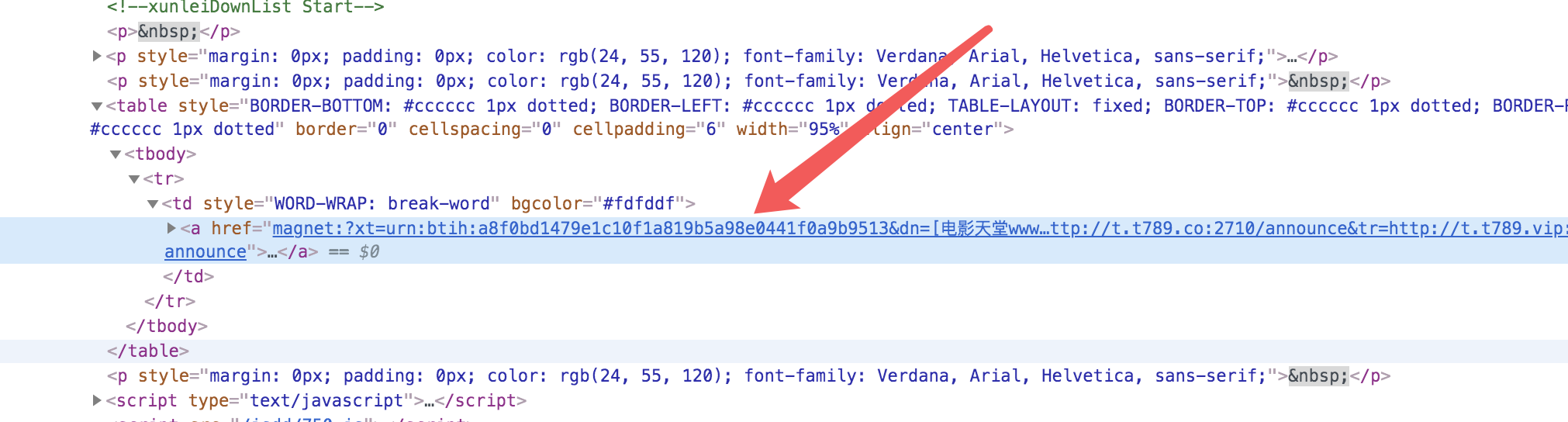
分析电影天堂的页面,有列表页和详情页,要想拿到磁力链接需要进入详情页,而详情页的链接要从列表页进入,因此我们先请求列表页,拿到详情页 url 之后进入详情页解析页面拿到磁力链接。
可以看到列表页中的 url 可以解析 .co_content8 ul table 下的 a 标签,通过 cheerio 拿到的 dom 节点是一个类数组,它的 each() api 相当于 数组的 forEach 方法,我们通过这种方式来抓取链接。进入详情页之后抓取磁力链接和这个类似。这里面涉及到 es7 的 async await 语法,是异步获取数据的一种有效方式。
const path = require('path')
const debug = require('debug')('fetchMovie')
const superAgent = r(APP.L, 'superagent')
const { targets } = r(APP.C)
const writeFile = r(APP.L, 'writeFile')
const {$, $select} = r(APP.L, 'cheerio')
const { movie } = targets
// 各种电影类型,分析网站得到的
const movieTypes = {
0: 'drama',
1: 'comedy',
2: 'action',
3: 'love',
4: 'sciFi',
5: 'cartoon',
7: 'thriller',
8: 'horror',
14: 'war',
15: 'crime',
}
const typeIndex = Object.keys(movieTypes)
// 分析页面,得到页面节点选择器,'.co_content8 ul table'
const fetchMovieList = async (type = 0) => {
debug(`fetch ${movieTypes[type]} movie`)
// 存电影数据,title,磁力链接
let data = []
let paging = {}
let currentPage = 1
const totalPage = 30 // 抓取页
while(currentPage <= totalPage) {
const url = movie.url + `/${type}/index${currentPage > 1 ? '_' + currentPage : ''}.html`
const res = await superAgent(url, {}, 'static')
// 拿到一个节点的数组
const $ele = $select(res, '.co_content8 ul table')
// 遍历
$ele.each((index, ele) => {
const li = $(ele).html()
$select(li, 'td b .ulink').last().each(async (idx, e) => {
const link = movie.url + e.attribs.href
// 这里去请求详情页
const { magneto, score } = await fetchMoreInfo(link)
const info = {title: $(e).text(), link, magneto, score}
data.push(info)
// 按评分倒序
data.sort((a, b) => b.score - a.score)
paging = { total: data.length }
})
})
writeFile(`${movieTypes[type]}Movie.json`, { paging, data }, path.join(APP.D, `movie`))
currentPage++
}
}
// 获取磁力链接 '.bd2 #Zoom table a'
const fetchMoreInfo = async link => {
if(!link) return null
let magneto = []
let score = 0
const res = await superAgent(link, {}, 'static')
$select(res, '.bd2 #Zoom table a').each((index, ele) => {
// 不做这个限制了,有些电影没有 magnet 链接
// if(/^magnet/.test(ele.attribs.href)) {}
magneto.push(ele.attribs.href)
})
$select(res, '.position .rank').each((index, ele) => {
score = Math.min(Number($(ele).text()), 10).toFixed(1)
})
return { magneto, score }
}
// 获取所有类型电影,并发
const fetchAllMovies = () => {
typeIndex.map(index => {
fetchMovieList(index)
})
}
module.exports = fetchAllMovies
数据处理
抓取回来的数据可以存数据库,我目前写在本地,本地的数据也可以作为 api 的数据源,例如电影天堂的数据我可以写一个本地的 api 作为本地开发的 server 来用
const path = require('path')
const router = require('koa-router')()
const readFile = r(APP.L, 'readFile')
const formatPaging = r(APP.M, 'formatPaging')
// router.prefix('/api');
router.get('/movie/:type', async ctx => {
const {type} = ctx.params
const totalData = readFile(`${type}Movie.json`, path.join(APP.D, 'movie'))
const formatData = await formatPaging(ctx, totalData)
ctx.body = formatData
})
module.exports = router.routes()
其中我手动维护了一个分页列表,方便数据给到前端时也实现 feed 流:
// 手动生成分页数据
const {getQuery, addQuery} = r(APP.L, 'url')
const {isEmpty} = require('lodash')
module.exports = (ctx, originData) => {
return new Promise((resolve) => {
const {url, header: {host}} = ctx
if(!url || isEmpty(originData)) {
return resolve({
data: [],
paging: {}
})
}
const {data, paging} = JSON.parse(originData)
const query = getQuery(url)
const limit = parseInt(query.limit) || 10
const offset = parseInt(query.offset) || 0
const isEnd = offset + limit >= data.length
const prev = addQuery(`http://${host}${url}`, {limit, offset: Math.max(offset - limit, 0)})
const next = addQuery(`http://${host}${url}`, {limit, offset: Math.max(offset + limit, 0)})
const formatData = {
data: data.slice(offset, offset + limit),
paging: Object.assign({}, paging, {prev, next, isEnd})
}
return resolve(formatData)
})
}
方便的话大家可以把数据写入数据库,这样就能实现爬虫-后端-前端一条龙了哈哈
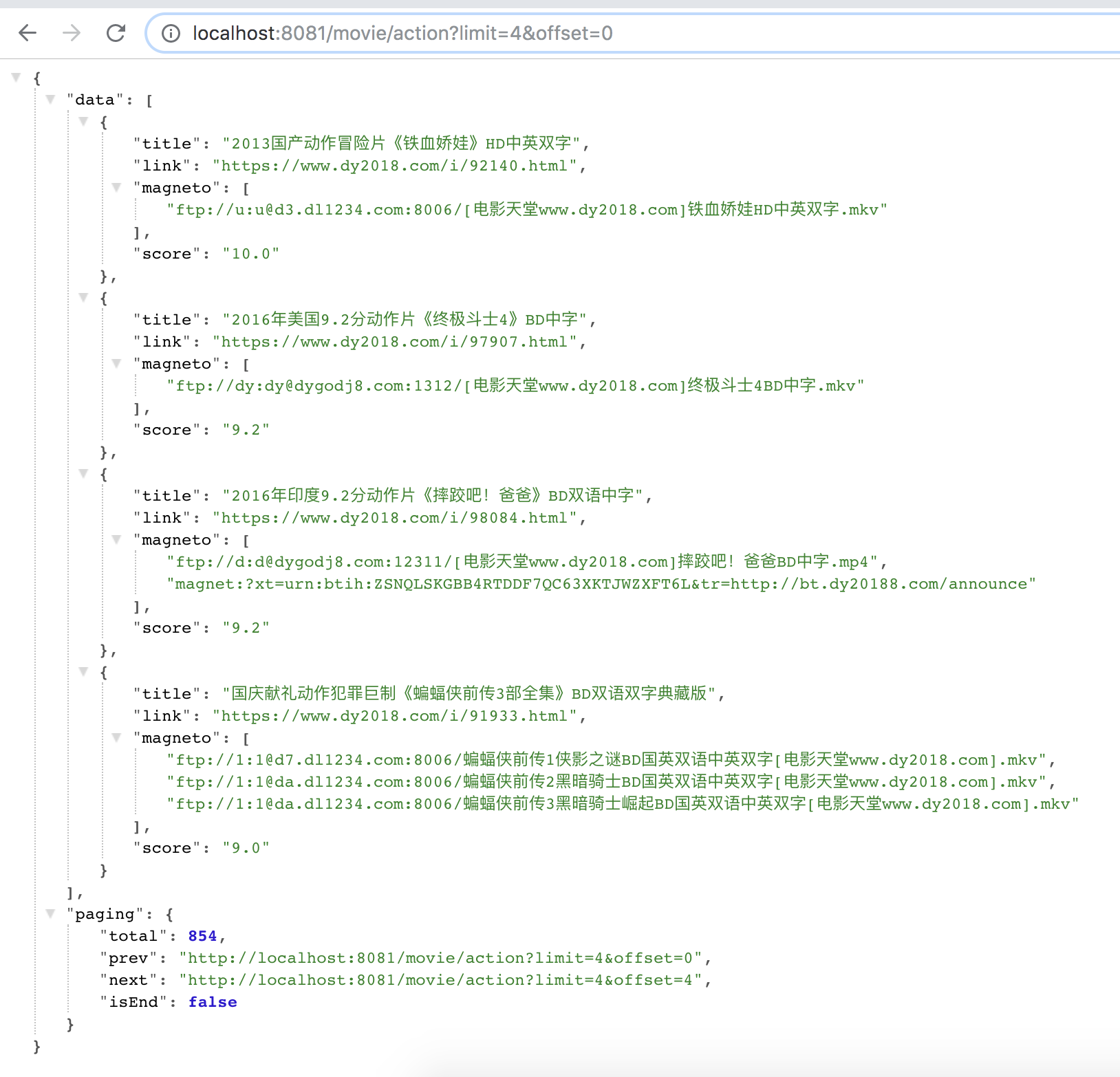
最后的 api,分页由 limit 和 offset 参数控制,可以自定义,请求 next 即可请求下一页实现 feed 流
✨✨✨
当然,关于爬虫能展开讲的东西太多了,有些站点做了爬虫限制,需要构建 ip 池不定时换 ip,有些需要模拟登录,要学习的东西还有很多,喜欢的小伙伴可以提一些 issue 一起交流一起学习