1.All IT eBooks多线程-写在前面
对一个爬虫爱好者来说,或多或少都有这么一点点的收集癖 ~ 发现好的图片,发现好的书籍,发现各种能存放在电脑上的东西,都喜欢把它批量的爬取下来。 然后放着,是的,就这么放着.......然后慢慢的遗忘掉.....
All IT eBooks多线程-爬虫分析
打开网址 http://www.allitebooks.com/ 发现特别清晰的小页面,一看就好爬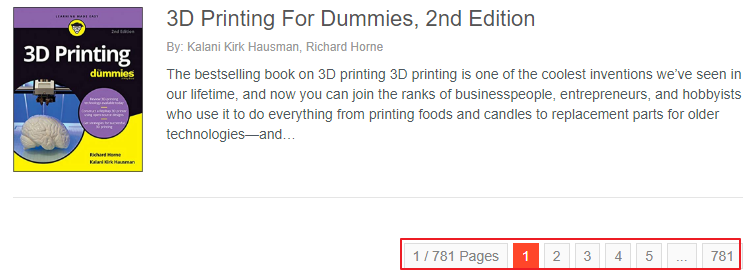
在点击一本图书进入,发现下载的小链接也很明显的展示在了我们面前,小激动一把,这么清晰无广告的网站不多见了。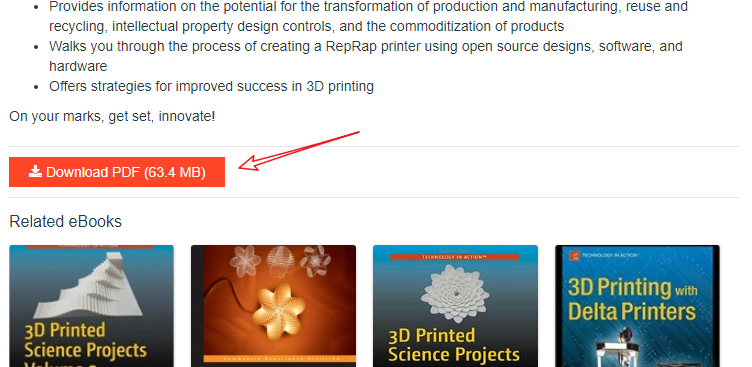
All IT eBooks多线程-撸代码
这次我采用了一个新的模块 requests-html 这个模块的作者之前开发了一款 requests,你应该非常熟悉了,线程控制采用的 queue
安装 requests-html 模块
pip install requests-html
关于这个模块的使用,你只需要使用搜索引擎搜索一下这个模块名称,那文章也是很多滴,作为能学到这篇博客的你来说,是很简单的拉~
我们编写一下核心的内容
from requests_html import HTMLSession
from queue import Queue
import requests
import random
import threading
CARWL_EXIT = False
DOWN_EXIT = False
#####
# 其他代码
####
if __name__ == '__main__':
page_queue = Queue(5)
for i in range(1,6):
page_queue.put(i) # 把页码存储到page_queue里面
# 采集结果
data_queue = Queue()
# 记录线程列表
thread_crawl = []
# 每次开启5个线程
craw_list = ["采集线程1号","采集线程2号","采集线程3号","采集线程4号","采集线程5号"]
for thread_name in craw_list:
c_thread = ThreadCrawl(thread_name,page_queue,data_queue)
c_thread.start()
thread_crawl.append(c_thread)
while not page_queue.empty():
pass
# 如果page_queue为空,采集线程退出循环
CARWL_EXIT = True
for thread in thread_crawl:
thread.join()
print("抓取线程结束")上面就是爬取图书详情页面的线程了,我开启了5个线程爬取,页码也只爬取了5 页,如果你需要更多的,只需要修改
page_queue = Queue(5)
for i in range(1,6):
page_queue.put(i) # 把页码存储到page_queue里面下面我们把 ThreadCrawl 类编写完毕
session = HTMLSession()
# 这个地方是 User_Agents 以后我把他配置到服务器上面,就可以远程获取了 这个列表里面有很多项,你自己去源码里面找吧
USER_AGENTS = [
"Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_7_3) AppleWebKit/535.20 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/19.0.1036.7 Safari/535.20"
]
# 获取图书下载链接的线程类
class ThreadCrawl(threading.Thread):
# 构造函数
def __init__(self,thread_name,page_queue,data_queue):
super(ThreadCrawl,self).__init__()
self.thread_name = thread_name
self.page_queue = page_queue
self.data_queue = data_queue
self.page_url = "http://www.allitebooks.com/page/{}" #URL拼接模板
def run(self):
print(self.thread_name+" 启动*********")
while not CARWL_EXIT:
try:
page = self.page_queue.get(block=False)
page_url = self.page_url.format(page) # 拼接URL操作
self.get_list(page_url) # 分析页面链接
except Exception as e:
print(e)
break
# 获取当前列表页所有图书链接
def get_list(self,url):
try:
response = session.get(url)
except Exception as e:
print(e)
raise e
all_link = response.html.find('.entry-title>a') # 获取页面所有图书详情链接
for link in all_link:
self.get_book_url(link.attrs['href']) # 获取图书链接
# 获取图书下载链接
def get_book_url(self,url):
try:
response = session.get(url)
except Exception as e:
print(e)
raise e
download_url = response.html.find('.download-links a', first=True)
if download_url is not None: # 如果下载链接存在,那么继续下面的爬取工作
link = download_url.attrs['href']
self.data_queue.put(link) # 把图书下载地址 存储到 data_queue里面,准备后面的下载
print("抓取到{}".format(link))上述代码一个非常重要的内容就是把图书的下载链接存储到了data_queue 里面,这些数据 在另一个下载线程里面是最基本的数据。
下面开始 编写图书下载的类和方法。
我开启了4个线程,操作和上面的非常类似
class ThreadDown(threading.Thread):
def __init__(self, thread_name, data_queue):
super(ThreadDown, self).__init__()
self.thread_name = thread_name
self.data_queue = data_queue
def run(self):
print(self.thread_name + ' 启动************')
while not DOWN_EXIT:
try:
book_link = self.data_queue.get(block=False)
self.download(book_link)
except Exception as e:
pass
def download(self,url):
# 随机浏览器User-Agent
headers = {"User-Agent":random.choice(USER_AGENTS)}
# 获取文件名字
filename = url.split('/')[-1]
# 如果url里面包含pdf
if '.pdf' in url or '.epub' in url:
file = 'book/'+filename # 文件路径已经写死,请在跟目录先创建好一个book文件夹
with open(file,'wb') as f: # 开始二进制写文件
print("正在下载 {}".format(filename))
response = requests.get(url,stream=True,headers=headers)
# 获取文件大小
totle_length = response.headers.get("content-length")
# 如果文件大小不存在,则直接写入返回的文本
if totle_length is None:
f.write(response.content)
else:
for data in response.iter_content(chunk_size=4096):
f.write(data)
else:
f.close()
print("{}下载完成".format(filename))
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 其他代码在上面
thread_image = []
image_list = ['下载线程1号', '下载线程2号', '下载线程3号', '下载线程4号']
for thread_name in image_list:
d_thread = ThreadDown(thread_name, data_queue)
d_thread.start()
thread_image.append(d_thread)
while not data_queue.empty():
pass
DOWN_EXIT = True
for thread in thread_image:
thread.join()
print("下载线程结束")如果你把我上面的代码都组合完毕,那么应该可以很快速的去爬取图书了,当然这些图书都是英文了,下载下来你能不能读....... 我就不知道了。
来源:阿里云开发者社区
原文链接:developer.aliyun.com/article/700…