前言
之前开发项目写过一些装饰器觉得很不错,比如全局loading的应用,还有一个页面上多种弹窗造成页面的state过于繁重,维护很困难,因此抽离出各种公共组件便于维护,代码也会缩短很多,因此写篇文章深入的记录一下
一、什么是高阶组件 目的是什么
官方解释是:一个传入一个组件,返回另一个组件的函数,其概念与高阶函数的将函数作为参数传入类似。
使用目的
- 将高度相似的部分抽离出来,比如一个常用组件,比如一个弹窗,可能有不同颜色的弹窗,或者只是某些小的地方不同,这样抽离抽离出来便于前端代码的维护
- 生命周期 state 的捕获 渲染劫持
二、使用方法
1.简单的装饰器
- 取到或操作原组件的props✅
- 能否取到或操作state❌
- 能否通过ref访问到原组件中的dom元素❌
- 是否影响原组件生命周期等方法✅
- 是否取到原组件static方法✅
- 劫持原组件生命周期❌
- 渲染劫持❌
// common.js 公共抽离部分
import React from 'react';
const common = WrapperComponet => class extends WrapperComponet {
constructor (props) {
super(props)
this.state = {
...this.state,
list: [],
num: 1
}
}
onClick = () => {
this.setState({ num: this.state.num + 3 });
}
render () {
const newProps = {a: 1};
return <WrapperComponet onClick={this.onClick} { ...newProps}/>
)
}
}
//页面
import React from 'react';
import './App.css';
import common from './common';
@common
class App extends React.Component {
constructor (props) {
super(props)
this.state = {
}
}
render () {
console.log(this.props); // {onClick: ƒ, a: 1} 装饰器里面可以对传入的类进行一些更改
return (
<div className="App">
点击 {this.state.num}
</div>
);
}
}
export default App;
2.利用高阶组件的反向继承,操作state 方法等
不太推荐利用操作反向继承操作state 这样会和原组件造成冲突,最好的应用场景是调试组件,在里面写一些调试代码
- 取到或操作原组件的props✅
- 能否取到或操作state✅
- 能否通过ref访问到原组件中的dom元素✅
- 是否影响原组件生命周期等方法✅
- 是否取到原组件static方法✅
- 劫持原组件生命周期✅
- 渲染劫持✅
反向继承最核心的两个作用,一个是渲染劫持,另一个是覆盖原有的state
(1)覆盖原有state
const common = WrapperComponet => class extends WrapperComponet {
constructor (props) {
super(props)
this.state = {
...this.state,
list: [],
num: 1
}
}
onClick = () => { //被覆盖
this.setState({ num: 100 });
}
render () {
// return <WrapperComponet onClick={this.onClick} { ...newProps}/>
const elementsTree = super.render();
const { children, ...otherProps } = elementsTree.props;
return React.cloneElement(
elementsTree,
otherProps,
...children,
)
}
}
@common
class App extends React.Component {
constructor (props) {
super(props)
this.state = {
}
}
onClick = () => {
this.setState({ num: 99 });
}
render () {
return (
<div className="App" onClick={this.onClick}>
点击 {this.state.num}
</div>
);
}
}
export default App;

(2)渲染劫持
render函数实际是利用react.createElement产生元素 我们可以拿到它 但是我们不能对其进行更改 ,render 函数应该是一个纯函数,完全根据 this.state 和this.props 来决定返回的结果,而且不要产生任何副作用。在 render 函数中去调用 this.setState 毫无疑问是错误的,因为一个纯函数不应该引起状态的改变。 我们只能通过react.cloneElement对其进行增强。
const HOC = (WrappedComponent) => {
return class extends WrappedComponent {
render() {
const tree = super.render();
let newProps = {};
if (tree && tree.type === 'input') {
newProps = { value: 'value被劫持' };
}
const props = { ...tree.props, ...newProps };
const newTree = React.cloneElement(tree, props, tree.props.children);
return newTree;
}
}
}
export default HOC;
3、高阶组件的应用
1.页面复用(工厂模式)
比如一个公共页面 只是某些字段发生改变,可以将这个公共页面设计成工厂
(高阶组件),外部传入一个json配置给这个装饰器的参数,下面举例一个简单的🌰
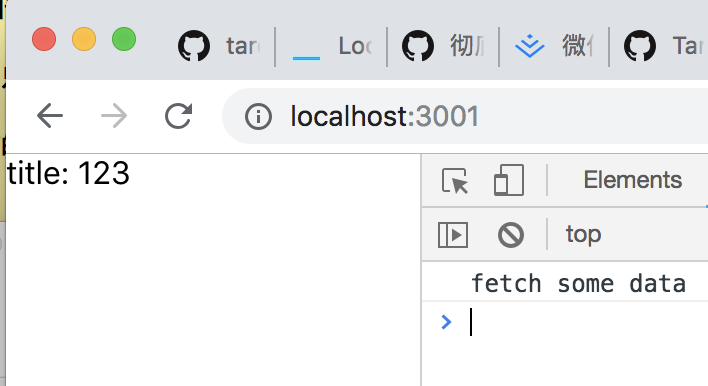
import shopList from './shopList';
const defaultProps = {
fetchData: () => {console.log('fetch some data');},
labelName: 'title',
value: '123'
};
const App = shopList(defaultProps);
export default App;
import React from 'react';
function CommonPage(config) {
const {
fetchData,
labelName,
value
} = config;
return class extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
data: [],
};
}
render() {
return <div onClick={fetchData}>
{`${labelName}: ${value}`}
</div>
}
};
}
export default CommonPage;
2.页面的选择渲染
比如 一个页面如果根据权限去渲染一些不同的页面 而且这个判断设计很多页面 那么我们不能将这些判断都写在代码中 重复的逻辑应该抽离出出来
import AuthPage from './two';
class App extends React.Component {
componentWillMount() {
// 获取业务数据
}
render() {
return <div>业务页面</div>;
}
}
export default AuthPage(App);
import React from 'react';
const AuthPage = WrappedComponent => class extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
permission: -1,
};
}
componentWillMount() {
// 权限获取接口,在此模拟promise
new Promise(resolve => resolve(0)).then((res) => {
// success
this.setState({
permission: res,
});
});
}
render() {
if (this.state.permission) {// 非0显示特殊页面
return <div>特殊页面</div>;
}
return <WrappedComponent {...this.props} />;
}
}
export default AuthPage;
3.页面的性能指标监控
对某些页面进行时间监控 利用高阶组件防止重复代码
import React from 'react';
function Performance(WrappedComponent) {
return class extends WrappedComponent {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.start = 0;
this.end = 0;
}
componentWillMount() {
super.componentWillMount && super.componentWillMount();
this.start = Date.now();
}
componentDidMount() {
super.componentDidMount && super.componentDidMount();
this.end = Date.now();
console.log(`组件渲染时间为 ${this.end - this.start} ms`);
}
render() {
return super.render();
}
};
}
export default Performance;
import Performance from './three';
class App extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
}
}
componentWillMount() {
// 获取业务数据
}
render() {
return <div>业务页面</div>;
}
}
export default Performance(App);

4.对组件进行二次封装
点击按钮希望请求未回来的时候显示loading状态防止二次请求
import Button from './Button';
class App extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
loading: false
}
}
componentWillMount() {
// 获取业务数据
}
onClick = () => {
// 模拟一个接口
return new Promise(resolve => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve(4);
}, 4000);
}).then((res) => {
console.log(res, '业务代码');
});
}
render() {
return <Button type="primary" onClick={this.onClick}>请求</Button>;
}
}
export default App;
// ButtonWrapper.js
import React from 'react';
const Button = WrappedComponent => class extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
loading: false
};
}
componentWillMount() {
}
handleClick = () => {
// 只有return一个promise才会加载loading状态,否则正常执行,因为判断是否有then必须还要执行一遍onclick,所以暂时只能加try catch
try {
this.setState({ loading: true });
this.props.onClick().then((res) => {
this.setState({ loading: false });
});
}
catch(e) {
this.setState({ loading: false });
}
}
render() {
return <WrappedComponent {...this.props} loading={this.state.loading} onClick={this.handleClick}/>;
}
}
export default Button;
import { Button } from 'antd';
import ButtonWrapper from './ButtonWrapper';
export default ButtonWrapperewButton(Button);