在 android 项目开发过程中,总会使用到 Collection,对于一些基础的使用方法还是可以的,但是涉及到较深层次的就有点力不从心了,所以打算开始彻底地学习一下 java 集合方面的知识点,做个记录总结,
分析工具
JavaJDK:1.7.0_79
AndroidStudio:3.5
首先来看下 java 集合框架的总图:
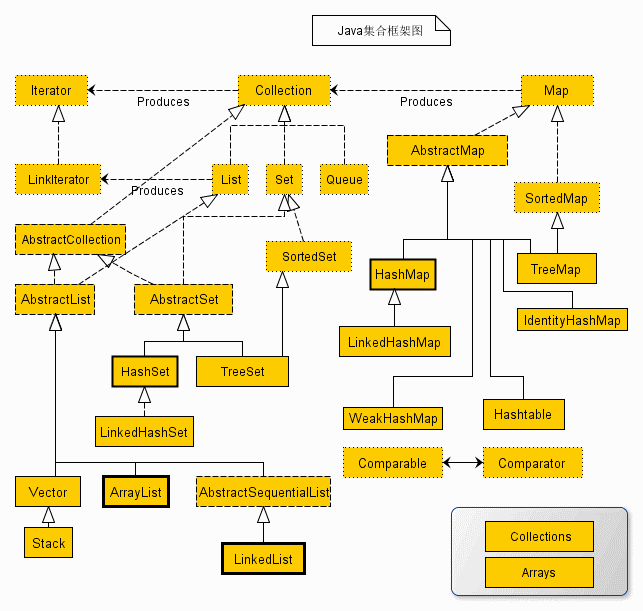
Collection
Collection 是 List、Set 等集合高度抽象出来的接口,它包含了这些集合的基本操作,它主要又分为两大部分:List和Set。
List 接口通常表示一个列表(数组、队列、链表、栈等),其中的元素可以重复,常用实现类为 ArrayList 和 LinkedList,另外还有不常用的 Vector。另外,LinkedList 还是实现了 Queue 接口,因此也可以作为队列使用。
Set 接口通常表示一个集合,其中的元素不允许重复(通过 hashcode 和 equals 函数保证),常用实现类有 HashSet 和 TreeSet,HashSet 是通过 Map 中的HashMap 实现的,而 TreeSet 是通过 Map 中的 TreeMap 实现的。另外,TreeSet 还实现了 SortedSet 接口,因此是有序的集合(集合中的元素要实现 Comparable 接口,并覆写 Compartor 函数才行)。
我们看到,抽象类 AbstractCollection、AbstractList 和 AbstractSet 分别实现了Collection、List 和 Set 接口,这就是在 Java 集合框架中用的很多的适配器设计模式,用这些抽象类去实现接口,在抽象类中实现接口中的若干或全部方法,这样下面的一些类只需直接继承该抽象类,并实现自己需要的方法即可,而不用实现接口中的全部抽象方法。
AbstractList继承AbstractCollection实现List
/**
* {@code AbstractList} is an abstract implementation of the {@code List} interface, optimized
* for a backing store which supports random access. This implementation does
* not support adding or replacing. A subclass must implement the abstract
* methods {@code get()} and {@code size()}, and to create a
* modifiable {@code List} it's necessary to override the {@code add()} method that
* currently throws an {@code UnsupportedOperationException}.
*
* @since 1.2
*/
public abstract class AbstractList<E> extends AbstractCollection<E> implements List<E> {}
AbstractSet 继承AbstractCollection实现Set
/**
* An AbstractSet is an abstract implementation of the Set interface. This
* implementation does not support adding. A subclass must implement the
* abstract methods iterator() and size().
*
* @since 1.2
*/
public abstract class AbstractSet<E> extends AbstractCollection<E> implements Set<E> {}
AbstractCollection实现Collection
/**
* Class {@code AbstractCollection} is an abstract implementation of the {@code
* Collection} interface. A subclass must implement the abstract methods {@code
* iterator()} and {@code size()} to create an immutable collection. To create a
* modifiable collection it's necessary to override the {@code add()} method that
* currently throws an {@code UnsupportedOperationException}.
*
* @since 1.2
*/
public abstract class AbstractCollection<E> implements Collection<E>{}
Map
Map 是一个映射接口,其中的每个元素都是一个 key-value 键值对,同样抽象类 AbstractMap 通过适配器模式实现了 Map 接口中的大部分函数,TreeMap、HashMap、WeakHashMap 等实现类都通过继承 AbstractMap 来实现,另外,不常用的 HashTable 直接实现了 Map 接口,它和 Vector 都是 JDK1.0 就引入的集合类。
TreeMap继承AbstractMap实现NavigableMap
/*
* @since 1.2
*/
public class TreeMap<K, V> extends AbstractMap<K, V>
implements SortedMap<K, V>, NavigableMap<K, V>, Cloneable, Serializable {}
NavigableMap继承SortedMap
public interface NavigableMap<K,V> extends SortedMap<K,V> {}
SortedMap接口继承Map接口
/**
* A map that has its keys ordered. The sorting is according to either the
* natural ordering of its keys or the ordering given by a specified comparator.
*/
public interface SortedMap<K,V> extends Map<K,V> {}
HashMap继承AbstractMap
public class HashMap<K, V> extends AbstractMap<K, V> implements Cloneable, Serializable {}
WeakHashMap继承AbstractMap
/*
* @since 1.2
* @see HashMap
* @see WeakReference
*/
public class WeakHashMap<K, V> extends AbstractMap<K, V> implements Map<K, V> {}
Iterator
Iterator 是遍历集合的迭代器(不能遍历 Map,只用来遍历 Collection),Collection 的实现类都实现了 iterator() 函数,它返回一个 Iterator 对象,用来遍历集合,ListIterator 则专门用来遍历 List。而 Enumeration 则是 JDK1.0 时引入的,作用与 Iterator 相同,但它的功能比 Iterator 要少,它只能再 Hashtable、Vector 和 Stack 中使用。
ListIterator继承Iterator
/**
* An ListIterator is used to sequence over a List of objects. ListIterator can
* move backwards or forwards through the list.
*/
public interface ListIterator<E> extends Iterator<E> {}
以上便是集合的主要内容,我们下面的系列都是按照上面的内容进行详细的分析和总结,欢迎持续关注~
关于作者
专注于 Android 开发多年,喜欢写 blog 记录总结学习经验,blog 同步更新于本人的公众号,欢迎大家关注,一起交流学习~
- GitHub: github.com/crazyandcod…
- 公众号:码农的小世界
