主流开源框架源码深入了解第4篇——Leakcanary源码分析。(源码以1.6.1版为准)

简单说两句,又有两个多月没写文章啦,这中间虽然没有继续看源码,不过倒是学了一些性能优化的知识,由于基本都是通过视频、博客等学习,而且自己的笔记也都是学习过程中跟随视频和博客记下的,因此就没有写成文章发布出来。感兴趣的小伙伴可以看一看:github.com/Endless5F/J…
LeakCanary的使用
private static void initLeakCanary(Application sApplication) {
// LeakCanary 初始化(内存泄漏检测)
if (LeakCanary.isInAnalyzerProcess(sApplication)) {
// This process is dedicated to LeakCanary for heap analysis.
// You should not init your app in this process.
return;
}
LeakCanary.install(sApplication);
}
相关知识点以及关联类简析
-
ReferenceQueue:在适当的时候检测到对象的可达性发生改变后,垃圾回收器就将已注册的引用对象添加到此队列中。后面代码里使用一个弱引用连接到你需要检测的对象,然后使用ReferenceQueue来监测这个弱引用可达性的改变
-
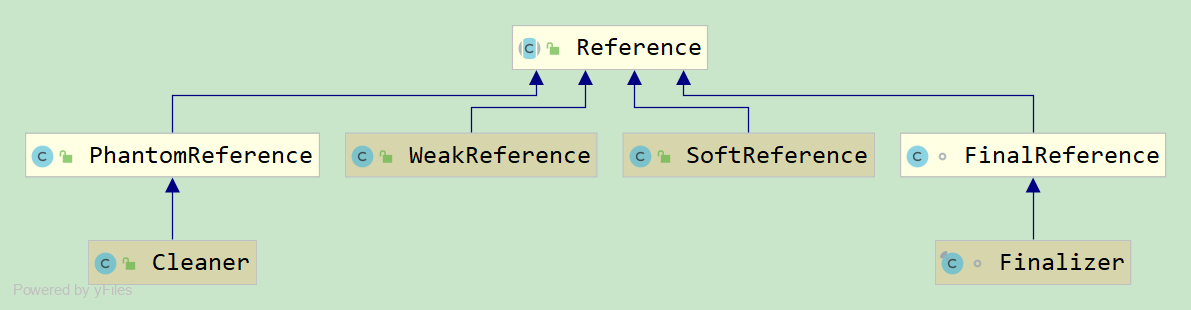
四大引用类型:
- StrongReference强引用:强引用的对象绝对不会被gc回收
- SoftReference软引用:如果物理内存充足则不会被gc回收,如果物理内存不充足则会被gc回收。
- WeakReference弱引用:一旦被gc扫描到则会被回收
- PhantomReference虚引用:不会影响对象的生命周期,形同于无,任何时候都可能被gc回收
- FinalReference:用于收尾机制(finalization)
GC线程扫描它所管辖的内存区域时,一旦发现了只具有弱引用的对象,不管当前内存空间足够与否,都会回收它的内存。由于垃圾回收器是一个优先级很低的线程,因此不一定会很快发现那些只具有弱引用的对象。
除了强引用,其余3种引用均继承自Reference类。Reference其内部提供2个构造函数,一个带queue,一个不带queue。其中queue的意义在于,我们可以在外部对这个queue进行监控。即如果有对象即将被回收,那么相应的reference对象就会被放到这个queue里。我们拿到reference,就可以再作一些事务,执行我们自己的操作(至于什么操作就看你想怎么用了),所以这个队列起到一个对象被回收时通知的作用。如果不带ReferenceQueue的话,要想知道Reference持有的对象是否被回收,就只有不断地轮训reference对象,通过判断里面的get是否返回null(phantomReference对象不能这样作,其get始终返回null,因此它只有带queue的构造函数)。这两种方法均有相应的使用场景,取决于实际的应用。如weakHashMap中就选择去查询queue的数据,来判定是否有对象将被回收;而ThreadLocalMap,则采用判断get()是否为null来作处理。
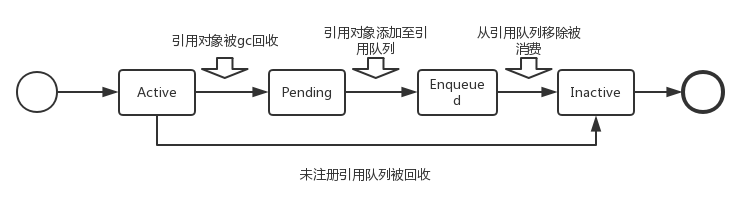
Reference 把内存分为 4 种状态,Active 、 Pending 、 Enqueued 、 Inactive。
- Active 一般说来内存一开始被分配的状态都是 Active
- Pending 快要放入队列(ReferenceQueue)的对象,也就是马上要回收的对象
- Enqueued 对象已经进入队列,已经被回收的对象。方便我们查询某个对象是否被回收
- Inactive 最终的状态,无法变成其他的状态。
LeakCanary种就是WeakReference和ReferenceQueue联合使用,如果弱引用所引用的对象被垃圾回收,Java虚拟机就会把这个弱引用加入到与之关联的引用队列中。
-
ActivityRefWatcher:用于监控Activity,但只能用于Android 4.0及其之上 它通过watchActivities方法将全局的Activity生命周期回调接口 Application.ActivityLifecycleCallbacks注册到application
-
RefWatcher:作用 LeakCanary核心中的核心。RefWatcher的工作就是触发GC,如果对象被回收,那么WeakReference将被放入 ReferenceQueue中,否则就怀疑有泄漏(仅仅是怀疑),然后将内存dump出来,为接下来的深入分析做准备。
-
ExcludedRef:LeakCanary提供了ExcludedRefs来灵活控制是否需要将一些对象排除在考虑之外,因为在Android Framework,手机厂商rom自身也存在一些内存泄漏,对于开发者来说这些泄漏是我们无能为力的,所以在AndroidExcludedRefs中定义了很多排除考虑的类
-
HeapDump.Listener与ServiceHeapDumpListener:ServiceHeapDumpListener实现了HeapDump.Listener接口。当RefWatcher发现可疑引用的之后,它将dump出来的Hprof文件通过 listener传递到HeapAnalyzerService。
-
HeapAnalyzerService:主要是通过HeapAnalyzer.checkForLeak分析对象的引用,计算出到GC root的最短强引用路径。然后将分析结果传递给DisplayLeakService。
-
AbstractAnalysisResultService与DisplayLeakService:DisplayLeakService继承了AbstractAnalysisResultService。它主要是用来处理分析结果,将结果写入文件,然后在通知栏报警。
-
Heap Dump:Heap Dump也叫堆转储文件,是一个Java进程在某个时间点上的内存快照。
LeakCanary的源码深入
LeakCanary使用非常方便,不过实际上所有操作都是在源码中完成的。
1. LeakCanary.install(sApplication)
public static RefWatcher install(Application application) {
return refWatcher(application) // 获取AndroidRefWatcherBuilder构造者
// 设置监听服务的Class(注意:此处很重要)
.listenerServiceClass(DisplayLeakService.class)
// LeakCanary提供了ExcludedRefs来灵活控制是否需要将一些对象排除在考虑之外,
// 因为在Android Framework,手机厂商rom自身也存在一些内存泄漏,
// 对于开发者来说这些泄漏是我们无能为力的,所以在AndroidExcludedRefs中定义了很多排除考虑的类
.excludedRefs(AndroidExcludedRefs.createAppDefaults().build())
// 构建并装载
.buildAndInstall();
}
我们简单说一下系方法中的几点:
- 该静态方法返回的RefWatcher,都是通过AndroidRefWatcherBuilder这个构造类来配置相关信息的
- listenerServiceClass方法和泄漏分析相关的服务绑定,绑定到DisplayLeakService.class这个类上面,这个类负责分析和通知泄漏消息给开发人员
- excludedRefs方法是排除一些开发可以忽略的泄漏(一般是系统级别BUG),这些枚举在AndroidExcludedRefs这个类当中定义
- buildAndInstall这个方法才是真正构建的重点
2. buildAndInstall()
// AndroidRefWatcherBuilder类:
// 是否观察Activity的内存泄漏
private boolean watchActivities = true;
// 是否观察Fragment的内存泄漏
private boolean watchFragments = true;
public RefWatcher buildAndInstall() {
// LeakCanaryInternals类是LeakCanary的一些类似于工具类的逻辑处理等(都是静态方法)
if (LeakCanaryInternals.installedRefWatcher != null) {
// installedRefWatcher 用于保存是否构建并install过LeakCanary
// 如果重复构建并安装LeakCanary,则会抛出如下异常
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("buildAndInstall() should only be called once" +".");
}
// 实例化RefWatcher对象,这个对象是用来处理泄漏对象的
RefWatcher refWatcher = build();
if (refWatcher != DISABLED) {
// 默认为true
if (watchActivities) {
ActivityRefWatcher.install(context, refWatcher);
}
// 默认为true
if (watchFragments) {
FragmentRefWatcher.Helper.install(context, refWatcher);
}
}
LeakCanaryInternals.installedRefWatcher = refWatcher;
return refWatcher;
}
从代码中可以看出buildAndInstall方法将build部分交给了build()方法,install部分使用ActivityRefWatcher和FragmentRefWatcher.Helper。
1). build部分
// RefWatcherBuilder类中,此类为AndroidRefWatcherBuilder的父类
// 此构建方法中大部分都是获取默认的值
public final RefWatcher build() {
if (isDisabled()) {
return RefWatcher.DISABLED;
}
// 此处不为null
if (heapDumpBuilder.excludedRefs == null) {
heapDumpBuilder.excludedRefs(defaultExcludedRefs());
}
// 这里的this.heapDumpListener 不为null
HeapDump.Listener heapDumpListener = this.heapDumpListener;
if (heapDumpListener == null) {
heapDumpListener = defaultHeapDumpListener();
}
// 下面的默认为null
// 用于查询是否在 debug 调试模式下,调试中不会执行内存泄漏检测。
DebuggerControl debuggerControl = this.debuggerControl;
if (debuggerControl == null) {
debuggerControl = defaultDebuggerControl();
}
// 用于产生内存泄漏分析用的 dump 文件。即 dump 内存 head。
HeapDumper heapDumper = this.heapDumper;
if (heapDumper == null) {
heapDumper = defaultHeapDumper();
}
// 执行内存泄漏检测的 Executor
WatchExecutor watchExecutor = this.watchExecutor;
if (watchExecutor == null) {
watchExecutor = defaultWatchExecutor();
}
// GC 开关,调用系统GC。
GcTrigger gcTrigger = this.gcTrigger;
if (gcTrigger == null) {
gcTrigger = defaultGcTrigger();
}
if (heapDumpBuilder.reachabilityInspectorClasses == null) {
heapDumpBuilder.reachabilityInspectorClasses(defaultReachabilityInspectorClasses());
}
// 初始化RefWatcher对象
return new RefWatcher(watchExecutor, debuggerControl, gcTrigger, heapDumper,
heapDumpListener,
heapDumpBuilder);
}
我们看一看build()方法几个变量:
-
heapDumpBuilder.excludedRefs:此变量实际上是在LeakCanary.install方法中通过excludedRefs设置的,用于过滤系统的一些内存泄漏。
-
this.heapDumpListener:此变量实际上同heapDumpBuilder.excludedRefs,是通过listenerServiceClass方法设置的。我们简单看一下其源码:
// 1. AndroidRefWatcherBuilder类: public AndroidRefWatcherBuilder listenerServiceClass( Class<? extends AbstractAnalysisResultService> listenerServiceClass) { return heapDumpListener(new ServiceHeapDumpListener(context, listenerServiceClass)); } // 2. ServiceHeapDumpListener类: public ServiceHeapDumpListener(final Context context, final Class<? extends AbstractAnalysisResultService> listenerServiceClass) { this.listenerServiceClass = checkNotNull(listenerServiceClass, "listenerServiceClass"); this.context = checkNotNull(context, "context").getApplicationContext(); } // 3. RefWatcherBuilder类: public final T heapDumpListener(HeapDump.Listener heapDumpListener) { // 此处就是1中heapDumpListener方法参数初始化的2对象 this.heapDumpListener = heapDumpListener; return self(); }因此heapDumpListener实际上就是ServiceHeapDumpListener对象。
-
其它:其它变量默认都是null,因此设置的都是默认值。
2). install部分
我们已ActivityRefWatcher为例说明:
// ActivityRefWatcher类:
// 通过提供的静态方法初始化ActivityRefWatcher并注册回调
public static void install(Context context, RefWatcher refWatcher) {
Application application = (Application) context.getApplicationContext();
// 初始化ActivityRefWatcher,并将build部分构建的RefWatcher传入
ActivityRefWatcher activityRefWatcher = new ActivityRefWatcher(application, refWatcher);
// 注册Activity的生命周期回调
application.registerActivityLifecycleCallbacks(activityRefWatcher.lifecycleCallbacks);
}
// 生命周期回调
private final Application.ActivityLifecycleCallbacks lifecycleCallbacks =
new ActivityLifecycleCallbacksAdapter() {
@Override
public void onActivityDestroyed(Activity activity) {
// Activity进入Destroy状态时开始监控其引用变化
refWatcher.watch(activity);
}
};
private final Application application;
private final RefWatcher refWatcher;
private ActivityRefWatcher(Application application, RefWatcher refWatcher) {
this.application = application;
// 初始化refWatcher成员
this.refWatcher = refWatcher;
}
我们通过此部分代码,可以看出来,install静态方法中初始化了ActivityRefWatcher的实例对象,并且注册了Activity的生命周期的回调,最终在Activity的onDestroy状态下开始使用refWatcher.watch监控当前Activity是否存在内存泄漏。
3. RefWatcher.watch
1. RefWatcher简介
private final WatchExecutor watchExecutor;
private final DebuggerControl debuggerControl;
private final GcTrigger gcTrigger;
private final HeapDumper heapDumper;
private final HeapDump.Listener heapdumpListener;
private final HeapDump.Builder heapDumpBuilder;
private final Set<String> retainedKeys;
private final ReferenceQueue<Object> queue;
- watchExecutor(实际为AndroidWatchExecutor,内部使用Handler):执行内存泄漏检测的Executor。
- debuggerControl:用于查询是否在 debug 调试模式下,调试中不会执行内存泄漏检测。
- gcTrigger:GC 开关,调用系统GC。
- heapDumper(实际为AndroidHeapDumper对象):用于产生内存泄漏分析用的dump文件。
- retainedKeys:保存待检测和产生内存泄漏的引用的 key。
- queue(RefWatcher构造方法中初始化queue):用于保存被gc的弱引用。
- heapdumpListener:用于分析 dump 文件,生成内存泄漏分析报告。
- heapDumpBuilder:通过heapDumper产生的dump文件以及其它信息,来构建分析内存泄漏的HeapDump对象。
2. watch(activity)
// RefWatcher类:
public void watch(Object watchedReference) {
// watchedReference为Activity或者Fragment
watch(watchedReference, "");
}
public void watch(Object watchedReference, String referenceName) {
if (this == DISABLED) {
return;
}
checkNotNull(watchedReference, "watchedReference");
checkNotNull(referenceName, "referenceName");
// 返回的是JVM运行的纳秒数
final long watchStartNanoTime = System.nanoTime();
// key值是用来最终定位泄漏对象用的,用来标识当前Activity或者Fragment的唯一值
String key = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
retainedKeys.add(key);
// 创建一个弱引用,并传入key和queue(引用队列)
// KeyedWeakReference这个弱引用对象使用的是带ReferenceQueue的构造方法
final KeyedWeakReference reference =
new KeyedWeakReference(watchedReference, key, referenceName, queue);
// 继续执行
ensureGoneAsync(watchStartNanoTime, reference);
}
private void ensureGoneAsync(final long watchStartNanoTime, final KeyedWeakReference reference) {
// 实际上使用的是Handler的post方法
// // 在异步线程上开始分析这个弱引用
watchExecutor.execute(new Retryable() {
@Override
public Retryable.Result run() {
return ensureGone(reference, watchStartNanoTime);
}
});
}
Retryable.Result ensureGone(final KeyedWeakReference reference, final long watchStartNanoTime) {
long gcStartNanoTime = System.nanoTime();
long watchDurationMs = NANOSECONDS.toMillis(gcStartNanoTime - watchStartNanoTime);
// 移除弱引用
removeWeaklyReachableReferences();
if (debuggerControl.isDebuggerAttached()) {
// 如果VM正连接到Debuger,忽略这次检测,因为Debugger可能会持有一些在当前上下文中不可见的对象,导致误判
return RETRY;
}
if (gone(reference)) {
// 如果引用已经不存在了则返回
return DONE;
}
gcTrigger.runGc(); // 触发GC
removeWeaklyReachableReferences(); ;// 再次移除弱引用,二次确认
// 如果GC之后引用还是存在,那么就进行深入分析
if (!gone(reference)) {
long startDumpHeap = System.nanoTime();
long gcDurationMs = NANOSECONDS.toMillis(startDumpHeap - gcStartNanoTime);
// dump出内存快照到*.hprof文件
File heapDumpFile = heapDumper.dumpHeap();
if (heapDumpFile == RETRY_LATER) {
// Could not dump the heap.
return RETRY;
}
long heapDumpDurationMs = NANOSECONDS.toMillis(System.nanoTime() - startDumpHeap);
// 构建HeapDump对象
HeapDump heapDump =
heapDumpBuilder.heapDumpFile(heapDumpFile).referenceKey(reference.key)
.referenceName(reference.name)
.watchDurationMs(watchDurationMs)
.gcDurationMs(gcDurationMs)
.heapDumpDurationMs(heapDumpDurationMs)
.build();
// 对.hprof文件进行分析
heapdumpListener.analyze(heapDump);
}
return DONE;
}
这一大段代码我们分别来分析一下:
-
触发watch动作过程分析:当Activity的onDestroy调用的时候,Application会收到通知,然后调用 lifecycleCallback.onActivityDestroyed()方法,最终RefWatcher的watch方法被触发,也就实现 了Activity内存泄漏自动分析。
-
创建一个弱引用KeyedWeakReference,而当JVM触发GC时,弱引用就会被回收,那么此弱引用添加到引用队列(ReferenceQueue)当中去。(WeakReference构造方法传入ReferenceQueue队列的时候,若引用的对象被回收,则将其加入该队列。)
-
通过两次移除弱引用,第二次之前手动调用gc操作。若还引用还存在,则生成堆内存dump文件,并初始化HeapDump对象,最后调用heapdumpListener.analyze分析并通知内存泄漏。
再来看两个上段代码中的两个方法的具体源码:
private boolean gone(KeyedWeakReference reference) {
// 判断retainedKeys容器中有没有key。
// 若回收了,就不存在key了,那么就没有泄漏,否则就怀疑有泄漏。
return !retainedKeys.contains(reference.key);
}
private void removeWeaklyReachableReferences() {
KeyedWeakReference ref;
// 这个对象作为弱引用,若回收了,那么添加到引用队列(ReferenceQueue)当中去,所以这个函数.poll是出栈的意思,
// 如果成功出栈了,那么说明你加入了引用队列,然后可以认为是已经被回收了
// 然后retainedKeys这个是一个Set容器,在之前会加入生成的唯一key作为标识,这里如果这个对象回收了,那么就移除这个key值。
while ((ref = (KeyedWeakReference) queue.poll()) != null) {
retainedKeys.remove(ref.key);
}
}
4. heapdumpListener.analyze内存快照分析
说明:此处的heapdumpListener就是上面【1). build部分】中的ServiceHeapDumpListener
此部分核心内容使用了另一个库:HaHa
// ServiceHeapDumpListener类:
@Override
public void analyze(HeapDump heapDump) {
checkNotNull(heapDump, "heapDump");
HeapAnalyzerService.runAnalysis(context, heapDump, listenerServiceClass);
}
// HeapAnalyzerService类:
public static void runAnalysis(Context context, HeapDump heapDump
,Class<? extends AbstractAnalysisResultService> listenerServiceClass) {
// Android 禁用与启用 APP 或四大组件
// 请参考:https://blog.csdn.net/ShawnXiaFei/article/details/82020386
setEnabledBlocking(context, HeapAnalyzerService.class, true);
setEnabledBlocking(context, listenerServiceClass, true);
Intent intent = new Intent(context, HeapAnalyzerService.class);
// 此处listenerServiceClass,
// 即【LeakCanary.install(sApplication)】中提到的DisplayLeakService.class
intent.putExtra(LISTENER_CLASS_EXTRA, listenerServiceClass.getName());
intent.putExtra(HEAPDUMP_EXTRA, heapDump);
// 开启前台服务
ContextCompat.startForegroundService(context, intent);
}
@Override
protected void onHandleIntentInForeground(@Nullable Intent intent) {
if (intent == null) {
CanaryLog.d("HeapAnalyzerService received a null intent, ignoring.");
return;
}
// 获取DisplayLeakService.class
String listenerClassName = intent.getStringExtra(LISTENER_CLASS_EXTRA);
HeapDump heapDump = (HeapDump) intent.getSerializableExtra(HEAPDUMP_EXTRA);
// 初始化堆分析仪
HeapAnalyzer heapAnalyzer =
new HeapAnalyzer(heapDump.excludedRefs, this,
heapDump.reachabilityInspectorClasses);
// checkForLeak就是最为关键的方法
AnalysisResult result = heapAnalyzer.checkForLeak(heapDump.heapDumpFile,
heapDump.referenceKey,
heapDump.computeRetainedHeapSize);
// 将结果发送给侦听器
AbstractAnalysisResultService.sendResultToListener(this, listenerClassName, heapDump,result);
}
@Override
public void onProgressUpdate(Step step) {
// 更新分析内存泄漏过程中的进度状态
int percent = (int) ((100f * step.ordinal()) / Step.values().length);
CanaryLog.d("Analysis in progress, working on: %s", step.name());
String lowercase = step.name().replace("_", " ").toLowerCase();
String message = lowercase.substring(0, 1).toUpperCase() + lowercase.substring(1);
// 开启通知显示
showForegroundNotification(100, percent, false, message);
}
analyze 方法开启了HeapAnalyzerService堆分析服务,HeapAnalyzerService继承自ForegroundService,而ForegroundService类继承自IntentService。ForegroundService类重写了onHandleIntent方法,并在该方法中调用了自己声明的抽象方法onHandleIntentInForeground。而HeapAnalyzerService类又实现了AnalyzerProgressListener接口,该接口中只有一个方法onProgressUpdate(分析进度状态更新)和分析过程中的状态枚举。因此HeapAnalyzerService服务开启后会直接执行onHandleIntentInForeground方法,最后执行到了一个最重要的方法checkForLeak:
// HeapAnalyzer类:
public AnalysisResult checkForLeak(File heapDumpFile, String referenceKey,
boolean computeRetainedSize) {
long analysisStartNanoTime = System.nanoTime();
if (!heapDumpFile.exists()) {
Exception exception =
new IllegalArgumentException("File does not exist: " + heapDumpFile);
return failure(exception, since(analysisStartNanoTime));
}
try {
// 更新进度状态
listener.onProgressUpdate(READING_HEAP_DUMP_FILE);
// 利用HAHA(基于MAT的堆栈解析库)将之前dump出来的内存文件解析成Snapshot对象
// 根据堆转储文件生成HprofBuffer缓存
HprofBuffer buffer = new MemoryMappedFileBuffer(heapDumpFile);
// Hprof文件解析对象
HprofParser parser = new HprofParser(buffer);
listener.onProgressUpdate(PARSING_HEAP_DUMP);
// 解析过程,是基于google的perflib库,根据hprof的格式进行解析
Snapshot snapshot = parser.parse();
listener.onProgressUpdate(DEDUPLICATING_GC_ROOTS);
// 分析结果进行去重,可减少内存压力
deduplicateGcRoots(snapshot);
listener.onProgressUpdate(FINDING_LEAKING_REF);
// 此方法就是根据我们需要检测的类的key,查询解析结果中是否有我们的对象,获取解析结果中我们检测的对象
Instance leakingRef = findLeakingReference(referenceKey, snapshot);
// 此对象不存在表示已经被gc清除了,不存在泄露因此返回无泄漏
if (leakingRef == null) {
return noLeak(since(analysisStartNanoTime));
}
// 此对象存在也不能确认它内存泄漏了,要检测此对象的gc root
return findLeakTrace(analysisStartNanoTime, snapshot, leakingRef, computeRetainedSize);
} catch (Throwable e) {
return failure(e, since(analysisStartNanoTime));
}
}
private Instance findLeakingReference(String key, Snapshot snapshot) {
// 因为需要监控的类,都构造了一个KeyedWeakReference
// 因此先找到KeyedWeakReference,就可以找到我们的对象
ClassObj refClass = snapshot.findClass(KeyedWeakReference.class.getName());
if (refClass == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Could not find the " + KeyedWeakReference.class.getName() + " class in the " +
"heap dump.");
}
List<String> keysFound = new ArrayList<>();
// 循环所有KeyedWeakReference实例
for (Instance instance : refClass.getInstancesList()) {
List<ClassInstance.FieldValue> values = classInstanceValues(instance);
// 找到KeyedWeakReference里面的key值,此值在我们前面传入的对象唯一标示
Object keyFieldValue = fieldValue(values, "key");
if (keyFieldValue == null) {
keysFound.add(null);
continue;
}
String keyCandidate = asString(keyFieldValue);
// 当key值相等时就表示是我们的检测对象
if (keyCandidate.equals(key)) {
return fieldValue(values, "referent");
}
keysFound.add(keyCandidate);
}
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Could not find weak reference with key " + key + " in " + keysFound);
}
private AnalysisResult findLeakTrace(long analysisStartNanoTime
, Snapshot snapshot,Instance leakingRef, boolean computeRetainedSize) {
listener.onProgressUpdate(FINDING_SHORTEST_PATH);
/**
* 这两行代码是判断内存泄露的关键,我们在上面中分析hprof文件,判断内存泄漏
* 判断的依据是展开调用到gc root,所谓gc root,就是不能被gc回收的对象,
* 查找泄露的最短引用链,gc root有很多类型,我们只要关注两种类型:
* 1.此对象是静态 2.此对象被其他线程使用,并且其他线程正在运行,没有结束
* pathFinder.findPath方法中也就是判断这两种情况
*/
ShortestPathFinder pathFinder = new ShortestPathFinder(excludedRefs);
ShortestPathFinder.Result result = pathFinder.findPath(snapshot, leakingRef);
// 找不到引起内存泄漏的gc root,就表示此对象未泄漏
if (result.leakingNode == null) {
return noLeak(since(analysisStartNanoTime));
}
listener.onProgressUpdate(BUILDING_LEAK_TRACE);
// 生成泄漏的调用栈,为了在通知栏中显示
LeakTrace leakTrace = buildLeakTrace(result.leakingNode);
String className = leakingRef.getClassObj().getClassName();
long retainedSize;
if (computeRetainedSize) {
listener.onProgressUpdate(COMPUTING_DOMINATORS);
// 副作用:计算保留的大小。
snapshot.computeDominators();
Instance leakingInstance = result.leakingNode.instance;
// 计算泄漏的空间大小
retainedSize = leakingInstance.getTotalRetainedSize();
// 检查Android O以上,并查看android.graphics.Bitmap.mBuffer发生了什么
if (SDK_INT <= N_MR1) {
listener.onProgressUpdate(COMPUTING_BITMAP_SIZE);
// 计算忽略的位图保留大小
retainedSize += computeIgnoredBitmapRetainedSize(snapshot, leakingInstance);
}
} else {
retainedSize = AnalysisResult.RETAINED_HEAP_SKIPPED;
}
// 检测到泄漏,构建AnalysisResult分析结果对象返回
return leakDetected(result.excludingKnownLeaks, className, leakTrace, retainedSize,
since(analysisStartNanoTime));
}
第三个分析步骤,解析hprof文件中,是先把这个文件封装成snapshot,然后根据弱引用和前面定义的key值,确定泄漏的对象,最后找到最短泄漏路径,作为结果反馈出来, 那么如果在快照中找不到这个怀疑泄漏的对象,那么就认为这个对象其实并没有泄漏。
最后,当内存泄漏分析完成,则调用AbstractAnalysisResultService.sendResultToListener:
// AbstractAnalysisResultService类:
public static void sendResultToListener(Context context
, String listenerServiceClassName,HeapDump heapDump, AnalysisResult result) {
Class<?> listenerServiceClass;
try {
listenerServiceClass = Class.forName(listenerServiceClassName);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
// 开启DisplayLeakService服务
Intent intent = new Intent(context, listenerServiceClass);
intent.putExtra(HEAP_DUMP_EXTRA, heapDump);
intent.putExtra(RESULT_EXTRA, result);
ContextCompat.startForegroundService(context, intent);
}
内存泄漏分析完成时,会开启DisplayLeakService服务,该服务继承自AbstractAnalysisResultService,而AbstractAnalysisResultService服务又继承自ForegroundService,而AbstractAnalysisResultService重写了ForegroundService服务的onHandleIntentInForeground(该方法是在onHandleIntent中调用),并在onHandleIntentInForeground方法中调用了onHeapAnalyzed方法,最终删除了heapDumpFile文件。
// ForegroundService类:
@Override
protected void onHandleIntent(@Nullable Intent intent) {
onHandleIntentInForeground(intent);
}
// AbstractAnalysisResultService类:
@Override
protected final void onHandleIntentInForeground(Intent intent) {
HeapDump heapDump = (HeapDump) intent.getSerializableExtra(HEAP_DUMP_EXTRA);
AnalysisResult result = (AnalysisResult) intent.getSerializableExtra(RESULT_EXTRA);
try {
onHeapAnalyzed(heapDump, result);
} finally {
//noinspection ResultOfMethodCallIgnored
heapDump.heapDumpFile.delete();
}
}
// DisplayLeakService类:
@Override
protected final void onHeapAnalyzed(HeapDump heapDump, AnalysisResult result) {
String leakInfo = leakInfo(this, heapDump, result, true);
CanaryLog.d("%s", leakInfo);
boolean resultSaved = false;
boolean shouldSaveResult = result.leakFound || result.failure != null;
if (shouldSaveResult) {
heapDump = renameHeapdump(heapDump);
// 保存内存快照和结果
resultSaved = saveResult(heapDump, result);
}
PendingIntent pendingIntent;
String contentTitle;
String contentText;
if (!shouldSaveResult) {
contentTitle = getString(R.string.leak_canary_no_leak_title);
contentText = getString(R.string.leak_canary_no_leak_text);
pendingIntent = null;
} else if (resultSaved) {
pendingIntent = DisplayLeakActivity.createPendingIntent(this, heapDump.referenceKey);
if (result.failure == null) {
if (result.retainedHeapSize == AnalysisResult.RETAINED_HEAP_SKIPPED) {
String className = classSimpleName(result.className);
if (result.excludedLeak) {
contentTitle = getString(R.string.leak_canary_leak_excluded, className);
} else {
contentTitle = getString(R.string.leak_canary_class_has_leaked, className);
}
} else {
String size = formatShortFileSize(this, result.retainedHeapSize);
String className = classSimpleName(result.className);
if (result.excludedLeak) {
contentTitle = getString(R.string.leak_canary_leak_excluded_retaining, className, size);
} else {
contentTitle = getString(R.string.leak_canary_class_has_leaked_retaining, className, size);
}
}
} else {
contentTitle = getString(R.string.leak_canary_analysis_failed);
}
contentText = getString(R.string.leak_canary_notification_message);
} else {
contentTitle = getString(R.string.leak_canary_could_not_save_title);
contentText = getString(R.string.leak_canary_could_not_save_text);
pendingIntent = null;
}
// New notification id every second.
int notificationId = (int) (SystemClock.uptimeMillis() / 1000);
// 重点看这个方法
showNotification(this, contentTitle, contentText, pendingIntent, notificationId);
afterDefaultHandling(heapDump, result, leakInfo);
}
// LeakCanaryInternals类:
public static void showNotification(Context context
, CharSequence contentTitle, CharSequence contentText, PendingIntent pendingIntent, int notificationId) {
Notification.Builder builder = new Notification.Builder(context)
.setContentText(contentText)
.setContentTitle(contentTitle)
.setAutoCancel(true)
.setContentIntent(pendingIntent);
Notification notification = buildNotification(context, builder);
NotificationManager notificationManager =
(NotificationManager) context.getSystemService(Context.NOTIFICATION_SERVICE);
notificationManager.notify(notificationId, notification);
}
内存泄漏分析完成后,开启DisplayLeakService服务,并调用onHeapAnalyzed方法,最终弹出通知告知 开发者内存泄漏的引用了,堆引用路径。

LeakCanary的自定义保存泄漏信息
对于Android开发来说,用leakcanary来检测内存泄漏很是方便与快捷的。不过若LeakCanary无法满足需求,可以自定义将内存泄漏结果保存本地。
在LeakCanary中的DisplayLeakService.java类中有一个空方法,如下:
/**
* 您可以重写此方法,并对服务器进行阻塞调用以上传泄漏跟踪和堆转储。
* 不要忘记先检查{@link AnalysisResult#leakFound and AnalysisResult#excludedLeak }
*/
protected void afterDefaultHandling(HeapDump heapDump, AnalysisResult result, String leakInfo) {
}
-
继承DisplayLeakService类,重写afterDefaultHandling()方法,实现自己的泄漏信息处理
public class LeadCanaryService extends DisplayLeakService { @Override protected void afterDefaultHandling(HeapDump heapDump, AnalysisResult result, String leakInfo) { super.afterDefaultHandling(heapDump, result, leakInfo); // 泄漏信息上传云端或者保存本地 saveLocal(result, leakInfo); } private void saveLocal(AnalysisResult result, String leakInfo) { if (result != null) { String leakPath = getApplication().getCacheDir().getAbsolutePath() + "/LeakCanary" + "/LeakCanary.log"; File file = new File(leakPath); FileUtils.createFileDir(file); SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"); String leadMessage = "Time" + simpleDateFormat.toString() + "\\n AnalysisResult{" + "leakFound=" + result.leakFound + ", excludedLeak=" + result.excludedLeak + ", className='" + result.className + '\'' + ", leakTrace=" + result.leakTrace + ", failure=" + result.failure + ", retainedHeapSize=" + result.retainedHeapSize + ", analysisDurationMs=" + result.analysisDurationMs + "} \\r\\n"; ByteArrayInputStream byteArrayInputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream(leadMessage.getBytes()); try { FileUtils.writeFile(byteArrayInputStream, file); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } -
AndroidManifest.xml中注册自定义服务LeadCanaryService
<service android:name=".service.LeadCanaryService"/> -
Application中引用自定义服务LeadCanaryService
LeakCanary.refWatcher(this).listenerServiceClass(LeadCanaryService.class) .excludedRefs(AndroidExcludedRefs.createAppDefaults().build()) .buildAndInstall();
到此,LeakCanary分析就结束啦,对性能优化的小伙伴可以看一下我的Github:github.com/Endless5F/J… ,有详细的文档和代码参考。
参考链接
注:若有什么地方阐述有误,敬请指正。期待您的点赞哦!!!