2019-11-24
一、概述
首先需要理解类、对象、对象引用、isa之间的关系。APP 在加载阶段会将 Objective-C 类载入内存的静态区,Objective-C 类本质是 C 语言结构体objc_class,结构体包含了类的超类、协议、成员变量列表、方法列表等类的元数据。类载入内存后,在内存中占据固定空间,因此在看到很多开源代码中,当某个类包含一个Class类型的属性时,经常会将其声明为assign类型,这不是因为Class是基本数据类型,而是因为Class常驻内存,对象不需要持有Class只需将其赋值给属性。
对象的本质是objc_object结构体,objc_object只有一个成员变量isa,通常情况下isa保存对象的Class的内存地址。但是对象占用空间显然不仅仅是保存isa指针的8个字节空间(64位机),实际上还包括了保存实例变量的连续内存空间,也就是 Ivar Layout 空间。构建类的实例,也就是对象,的本质是在堆区为对象分配 其类的instanceSize大小的内存空间,用于保存对象的isa指针以及所有成员变量。对象的引用是指向保存对象的内存空间的一个指针,其本质是对象的内存首地址。
既然初始化主要包括以上内存空间,那么与对象关联的内存引用计数呢?引用计数保存什么地方?Runtime 源代码 NSObject.mm 文件中关于内存管理的代码大量涉及了SideTable数据结构,SideTable是Objective-C实现引用计数内存管理的两个关键点之一,另一个关键点是对象的isa指针。
二、源码分析
2.1 基本数据结构
首先了解SideTable相关的基本数据结构。
-
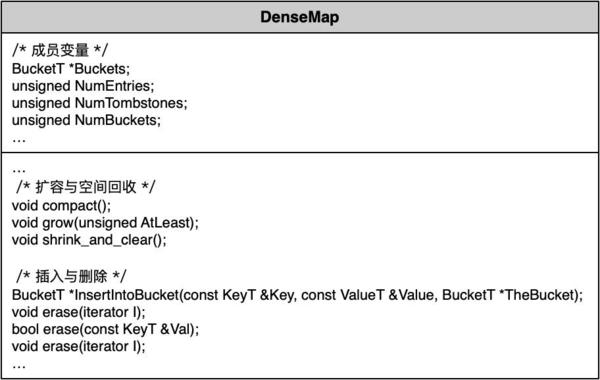
RefcountMap:NSObject.mm的中声明了DenseMap具体类的别名RefcountMap,其中DenseMap是 llvm 定义的用于内存管理的一种数据结构,右图中提取了DenseMap的几个主要成员和方法,可知DenseMap是一种可动态调整容量的,按 Key-Value 方式访问元素,使用二次探测法(基于链表)解决冲突的 Map 数据结构。RefcountMap功能非常明确:保存引用计数; -
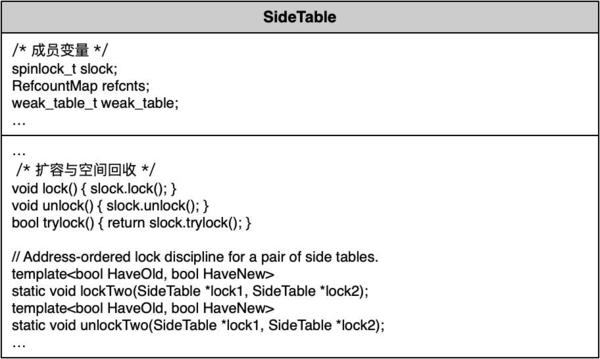
SideTable:SideTable类包含RefcountMap类型的成员变量refcnts,记录全局弱引用计数表的结构体的weak_table,自旋锁slock。SideTable功能是管理单张内存引用技术表; -
StripMap:多个SideTable实例由StripMap类集中管理。StripMap类实例在SideTableInit方法中初始化并保存于SideTableBuf静态变量中,使用SideTables()静态方法获取StripMap实例。
关键代码如下:
/* NSObject.mm */
/* 引用计数相关 */
typedef objc::DenseMap<DisguisedPtr<objc_object>,size_t,true> RefcountMap;
struct SideTable {
spinlock_t slock;
RefcountMap refcnts;
weak_table_t weak_table;
SideTable() {
memset(&weak_table, 0, sizeof(weak_table));
}
~SideTable() {
_objc_fatal("Do not delete SideTable.");
}
void lock() { slock.lock(); }
void unlock() { slock.unlock(); }
bool trylock() { return slock.trylock(); }
template<bool HaveOld, bool HaveNew>
static void lockTwo(SideTable *lock1, SideTable *lock2);
template<bool HaveOld, bool HaveNew>
static void unlockTwo(SideTable *lock1, SideTable *lock2);
};
/* NSObject.mm */
/* 引用计数相关 */
alignas(StripedMap<SideTable>) static uint8_t
SideTableBuf[sizeof(StripedMap<SideTable>)];
static void SideTableInit() {
new (SideTableBuf) StripedMap<SideTable>();
}
static StripedMap<SideTable>& SideTables() {
return *reinterpret_cast<StripedMap<SideTable>*>(SideTableBuf);
}
/* NSObject.mm */
/* 引用计数相关 */
void arr_init(void)
{
AutoreleasePoolPage::init();
SideTableInit();
}
void objc_storeStrong(id *location, id obj)
{
id prev = *location;
if (obj == prev) {
return;
}
objc_retain(obj);
*location = obj;
objc_release(prev);
}
主要类定义如下图所示:

2.2 objc_storeStrong函数逻辑分析
NSObject.mm文件中,void objc_storeStrong(id *location, id obj)函数用于将obj对象的引用存储于location地址,实质上则是将obj的地址存储到location地址,注意调用了objc_retain(obj)增加了obj对象的引用计数,原来存储于location地址的对象prev则调用objc_release将其释放。这里先分析objc_retain的操作,objc_release操作是其反过程。
objc_storeStrong函数调用了objc_retain(id obj),源代码如下。其中,isTaggedPointer()方法用于判定obj是否为tagged pointer。对于一个对象引用(指针),一般情况下该引用的值为对象的内存地址,而tagged pointer则直接在地址中写入对象的类和数据。Tagged pointer使用1 bit标记引用是否为Tagged pointer,Objective-C中为指定最低位;使用3 bit标记对象的类,剩余60bit用于存储对象的value;注意,如果obj是tagged pointer,由于其中已经保存了对象的类型和值,因此若 retain 一个 tagged pointer 则直接返回 tagged pointer 自身,不增加引用计数。objc_retain(id obj)方法调用了retain()方法,retain()方法中的hasCustomRR()方法用于判定对象是否有自定义的retain函数指针,否则调用rootRetain(),本文只分析调用rootRetain()的逻辑分支。
Tagged pointer objects store the class and the object value in the object pointer; the "pointer" does not actually point to anything
#if !SUPPORT_TAGGED_POINTERS || !TARGET_OS_IPHONE
# define SUPPORT_MSB_TAGGED_POINTERS 0
#else
# define SUPPORT_MSB_TAGGED_POINTERS 1
#endif
#if SUPPORT_MSB_TAGGED_POINTERS
# define TAG_MASK (1ULL<<63)
#else
# define TAG_MASK 1
#endif
inline bool objc_object::isTaggedPointer()
{
return ((uintptr_t)this & TAG_MASK);
}
__attribute__((aligned(16)))
id objc_retain(id obj)
{
if (!obj) return obj;
if (obj->isTaggedPointer()) return obj;
return obj->retain();
}
inline id objc_object::retain()
{
assert(!UseGC || ISA()->hasCustomRR());
assert(!isTaggedPointer());
if (! ISA()->hasCustomRR()) {
return rootRetain();
}
return ((id(*)(objc_object *, SEL))objc_msgSend)(this, SEL_retain);
}
2.2.1 rootRetain方法逻辑分析
objc_object::rootRetain(bool tryRetain, bool handleOverflow)的处理逻辑比较复杂,源代码如下。可以先不急看代码,后续会按步对其拆分及简化。
ALWAYS_INLINE id
objc_object::rootRetain(bool tryRetain, bool handleOverflow)
{
assert(!UseGC);
if (isTaggedPointer()) return (id)this;
bool sideTableLocked = false;
bool transcribeToSideTable = false;
isa_t oldisa;
isa_t newisa;
do {
transcribeToSideTable = false;
oldisa = LoadExclusive(&isa.bits);
newisa = oldisa;
if (!newisa.indexed) goto unindexed;
if (tryRetain && newisa.deallocating) goto tryfail;
uintptr_t carry;
newisa.bits = addc(newisa.bits, RC_ONE, 0, &carry); // extra_rc++
if (carry) {
if (!handleOverflow) return rootRetain_overflow(tryRetain);
if (!tryRetain && !sideTableLocked) sidetable_lock();
sideTableLocked = true;
transcribeToSideTable = true;
newisa.extra_rc = RC_HALF;
newisa.has_sidetable_rc = true;
}
} while (!StoreExclusive(&isa.bits, oldisa.bits, newisa.bits));
if (transcribeToSideTable) {
sidetable_addExtraRC_nolock(RC_HALF);
}
if (!tryRetain && sideTableLocked) sidetable_unlock();
return (id)this;
tryfail:
if (!tryRetain && sideTableLocked) sidetable_unlock();
return nil;
unindexed:
if (!tryRetain && sideTableLocked) sidetable_unlock();
if (tryRetain) return sidetable_tryRetain() ? (id)this : nil;
else return sidetable_retain();
}
2.2.2 rootRetain分析准备工作
在分析代码之前我们先搞清楚几个问题:
-
LoadExclusive(uintptr_t *src)直接返回*src,即src指针指向的内容。代码中oldisa = LoadExclusive(&isa.bits)看起来是oldisa加载了isa.bits,但是由于isa.bits数据实际上就是isa的数据,因此oldisa实质上是加载了isa,写成oldisa = (isa_t)LoadExclusive(&isa.bits)可以更好理解; -
StoreExclusive(uintptr_t *dst, uintptr_t oldvalue, uintptr_t value)实际调用了__sync_bool_compare_and_swap((void **)dst, (void *)oldvalue, (void *)value),实现功能为:比较oldvalue和dst指针指向的值,若两者相等则将value写入dst指针的内容且返回true,否则不写入且返回false; -
addc(uintptr_t lhs, uintptr_t rhs, uintptr_t carryin, uintptr_t *carryout)实际调用了__builtin_addcl(lhs, rhs, carryin, carryout)函数,实现功能为:计算lhs + rhs + carryin,若64bit上溢出则在输出指针carryout中写入1,例如:uintptr_t result = __builtin_addcl((1ULL<<63), (1ULL<<62), ((1ULL<<62) + 2), &carry),结果为result = 2,carry = 1,结果上溢出;__builtin_addcl((1ULL<<63), (1ULL<<62), (1ULL<<61), &carry),输出carry为0,结果不上溢出; -
id是objc_object*的别名,也就是说对象引用实际上是指向一个objc_object结构体的指针,objc_object结构体只有一个成员——isa_t类型的isa,isa_t是联合体,有两个成员Class cls、uintptr_t bits。bits被指定为占8个字节空间的结构体,其定义根据架构区分(注释中MSB是Most Significant Bit指最高有效位,extra_rc需要处理上溢出情况因此为MSB,LSB是Least Significant Bit,indexed位用来判断isa指针的类型因此为LSB),下面是arm64架构下isa_t的bits的位域分布,图示及源代码如下左高位、右低位,源代码中删除了x86_64及其他架构下的代码:-
indexed:洋红区域右起第1位。0表示普通的isa指针存储类的地址,完全使用SideTable管理引用计数;1表示非指针类型,结合isa中的数据以及SideTable集中管理引用计数; -
has_assoc:洋红区域右起第2位。0表示不存在关联对象;1表示存在关联对象 -
has_cxx_dtor:洋红区域右起第3位。0表示不存在其他析构函数;1表示存在其他析构函数; -
shiftcls:红色区域共33位。保存类的虚拟内存地址。 -
magic:黄色区域共6位,用于非指针类型的isa校验,arm64架构下这6位为固定值0x1a; -
weakly_referenced:青色区域右起第1位。对象是否被弱引用; -
deallocating:青色区域右起第2位。对象是否已执行析构(对象over release相关提示); -
has_sidetable_rc:青色区域右起第3位。表示该对象的引用计数是否过大,以至于在extra_rc空间中上溢出,需要在SideTable中保存 extra reference count; -
extra_rc:绿色区域共19位。记录对象引用计数,在has_sidetable_rc为true时,需要联合SideTable才能获取到对象的确切引用计数;
-

union isa_t
{
isa_t() { }
isa_t(uintptr_t value) : bits(value) { }
Class cls;
uintptr_t bits;
#if SUPPORT_NONPOINTER_ISA
# if __arm64__
# define ISA_MASK 0x0000000ffffffff8ULL
# define ISA_MAGIC_MASK 0x000003f000000001ULL
# define ISA_MAGIC_VALUE 0x000001a000000001ULL
struct {
uintptr_t indexed : 1;
uintptr_t has_assoc : 1;
uintptr_t has_cxx_dtor : 1;
uintptr_t shiftcls : 33; // MACH_VM_MAX_ADDRESS 0x1000000000
uintptr_t magic : 6;
uintptr_t weakly_referenced : 1;
uintptr_t deallocating : 1;
uintptr_t has_sidetable_rc : 1;
uintptr_t extra_rc : 19;
# define RC_ONE (1ULL<<45)
# define RC_HALF (1ULL<<18)
};
# endif
#endif
};
注意:Union联合体的成员之间共享内存空间。以
isa_t为例,cls成员和bits成员虽然不同,但是两者的值实际在任何时候都是一致的。例如,isa.class = [NSString class]指定了cls指向NSString类的内存地址,此时查看isa.bits会发现其值为NSString类的内存地址;反之,isa.bits = 0xFF,则isa.class的值变为255。
为进一步简化代码,我们考虑把加锁解锁相关的代码移除。在这之前先弄清楚为什么tryRetain的情况下不需要给SideTable加锁(至于加锁的原因太明显不深入讨论,SideTable访问必然涉及多线程竞争问题加锁是必须的)。tryRetain的情况下的逻辑分支调用了sidetable_tryRetain(),其源代码如下。
#define SIDE_TABLE_WEAKLY_REFERENCED (1UL<<0)
#define SIDE_TABLE_DEALLOCATING (1UL<<1) // MSB-ward of weak bit
#define SIDE_TABLE_RC_ONE (1UL<<2) // MSB-ward of deallocating bit
#define SIDE_TABLE_RC_PINNED (1UL<<(WORD_BITS-1))
#define SIDE_TABLE_RC_SHIFT 2
#define SIDE_TABLE_FLAG_MASK (SIDE_TABLE_RC_ONE-1)
bool objc_object::sidetable_tryRetain()
{
#if SUPPORT_NONPOINTER_ISA
assert(!isa.indexed);
#endif
SideTable& table = SideTables()[this];
bool result = true;
RefcountMap::iterator it = table.refcnts.find(this);
if (it == table.refcnts.end()) {
table.refcnts[this] = SIDE_TABLE_RC_ONE;
} else if (it->second & SIDE_TABLE_DEALLOCATING) {
result = false;
} else if (! (it->second & SIDE_TABLE_RC_PINNED)) {
it->second += SIDE_TABLE_RC_ONE;
}
return result;
}
-
首先,最不起眼的前三行预编译代码实际有提供关键信息,预编译判断如果支持非指针类型
isa,则禁止使用非指针类型isa的对象执行tryRetain,即tryRetain只针对使用指针类型的isa的对象(refCount信息只存储于SideTable中的对象); -
其次,调用
SideTables()静态方法,获取管理SideTable的StripedMap,再以对象this为关键字获取对象所对应的SideTable 记为table,table.refcnts为 SideTable 的内存计数表,以this为关键字获取当前对象的内存计数refcntStorage,注意指针isa模式下SideTable中保存数据的位域机构和isa.bits不一样:SideTable中从最低位起第1位SIDE_TABLE_WEAKLY_REFERENCED标记是否若引用,第2位SIDE_TABLE_DEALLOCATING标记对象是否已析构,从第3位开始保存引用计数refCount,因此内存计数递增使用的增量是SIDE_TABLE_RC_ONE即0x04; -
至于为什么不加锁,原因在注释中有提及,
return rootRetain(true)只会被_objc_rootTryRetain()方法调用,且_objc_rootTryRetain()只会被_objc_loadWeak()方法调用,而_objc_loadWeak()方法内的逻辑已经获取了SideTable的锁,因此不必在_objc_rootTryRetain()中重复加锁;
2.2.3 rootRetain逻辑拆分——!isa.index
准备工作完毕,开始分析objc_object::rootRetain(bool tryRetain, bool handleOverflow)的源代码。从源代码中删除加锁解锁逻辑、tryRetain相关逻辑,按照判断逻辑对rootRetain方法进行拆分。剥离出!isa.indexed的逻辑如下:
// rootRetain逻辑拆分——!isa.index
objc_object::rootRetain(bool tryRetain, bool handleOverflow)
{
return sidetable_retain();
}
关键点是sidetable_retain()方法,其源代码如下。首先注意到与sidetable_tryRetain()中相同的预编译语句具有同样的含义,即sidetable_retain ()只针对使用指针类型的isa的对象。条件语句if(! (refcntStorage & SIDE_TABLE_RC_PINNED))用于判断refcntStorage的最高位为0,仅最高位为0才递增refcntStorage。这里table.trylock()是尝试加锁,若 table 已加锁则返回true,此时table不需要重复加锁。sidetable_retain_slow ()的处理逻辑逻辑与sidetable_retain()基本一致,区别仅在于加锁操作。
总结:对于指针类型的isa,内存引用计数仅存储于 SideTable 中。
id objc_object::sidetable_retain()
{
#if SUPPORT_NONPOINTER_ISA
assert(!isa.indexed);
#endif
SideTable& table = SideTables()[this];
if (table.trylock()) {
size_t& refcntStorage = table.refcnts[this];
if (! (refcntStorage & SIDE_TABLE_RC_PINNED)) {
refcntStorage += SIDE_TABLE_RC_ONE;
}
table.unlock();
return (id)this;
}
return sidetable_retain_slow(table);
}
__attribute__((used,noinline,nothrow))
id objc_object::sidetable_retain_slow(SideTable& table)
{
#if SUPPORT_NONPOINTER_ISA
assert(!isa.indexed);
#endif
table.lock();
size_t& refcntStorage = table.refcnts[this];
if (! (refcntStorage & SIDE_TABLE_RC_PINNED)) {
refcntStorage += SIDE_TABLE_RC_ONE;
}
table.unlock();
return (id)this;
}
顺便一提:苹果系列操作系统中,自旋锁
OSSpinLock存在性能缺陷从iOS 10.0开始已经被弃用。
2.2.4 rootRetain逻辑拆分——isa.deallocating
剥离出isanew.deallocating逻辑分支,得到精简后的代码如下。因此,当对象调用rootRetain()方法且isa.isdeallocating为true时,不对 SideTable 和 对象的isa做任何操作,直接返回nil;
总结:对于标记为已析构的对象,调用retain不做关于对象引用计数的任何操作。
// rootRetain逻辑拆分——isa.deallocating
ALWAYS_INLINE id objc_object::rootRetain(bool tryRetain, bool handleOverflow)
{
return nil;
}
2.2.5 rootRetain逻辑拆分——!carry
从2.2.1准备工作中已知addc(uintptr_t lhs, uintptr_t rhs, uintptr_t carryin, uintptr_t *carryout)函数的carryout输出参数用于标记结果是否上溢出。剥离出newisa.isa累加结果不上溢出的代码逻辑如下。newisa.bits = addc(newisa.bits, RC_ONE, 0, &carry)用于递增newisa.bits中的引用计数数据递增量为RC_ONE(递增量取决于extra_rc在isa.bits中的位域),等价于newisa.bits.extra_rc += 1。
总结:对于非指针类型的isa,在对象引用计数不上溢出extra_rc位域的情况下,对象的引用计数直接存储于isa的extra_rc位域。
// rootRetain逻辑拆分——!carry
ALWAYS_INLINE id objc_object::rootRetain(bool tryRetain, bool handleOverflow)
{
bool sideTableLocked = false;
isa_t oldisa;
isa_t newisa;
do {
transcribeToSideTable = false;
oldisa = LoadExclusive(&isa.bits);
newisa = oldisa;
uintptr_t carry;
newisa.bits = addc(newisa.bits, RC_ONE, 0, &carry); // extra_rc++
} while (!StoreExclusive(&isa.bits, oldisa.bits, newisa.bits));
return (id)this;
}
为什么需要do-while循环?
2.2.5 rootRetain逻辑拆分——carry
剥离出newisa.isa累加结果上溢出的代码逻辑如下,保留了原关键注释。关键点在两块if处理逻辑。首先,if (!handleOverflow)中简单调用了rootRetain_overflow ()方法,其内部只是简单调用了rootRetain(tryRetain, true)没有额外处理,因此又会回到rootRetain处理逻辑中。这两行逻辑可以直接忽略。
上溢出的处理过程如下:
- 设置对象的
isa.bits.extra_rc为RC_HALF,也就是保留一半的引用计数在extra_rc位域; - 设置对象的
isa.bits.has_sidetable_rc位为1,表示使用 SideTable 协同保存对象引用计数; - 调用
sidetable_addExtraRC_nolock (RC_HALF)转移另一半的引用计数到 SideTable;
// rootRetain逻辑拆分——carry
ALWAYS_INLINE id objc_object::rootRetain(bool tryRetain, bool handleOverflow)
{
isa_t oldisa;
isa_t newisa;
do {
transcribeToSideTable = false;
oldisa = LoadExclusive(&isa.bits);
newisa = oldisa;
uintptr_t carry;
newisa.bits = addc(newisa.bits, RC_ONE, 0, &carry); // extra_rc++
if (!handleOverflow)
return rootRetain_overflow(tryRetain);
newisa.extra_rc = RC_HALF;
newisa.has_sidetable_rc = true;
} while (!StoreExclusive(&isa.bits, oldisa.bits, newisa.bits));
sidetable_addExtraRC_nolock(RC_HALF);
return (id)this;
}
NEVER_INLINE id objc_object::rootRetain_overflow(bool tryRetain)
{
return rootRetain(tryRetain, true);
}
sidetable_addExtraRC_nolock (RC_HALF)方法的源代码如下。之前讨论过的处理逻辑不再赘述,需要注意:
-
SIDE_TABLE_DEALLOCATING或SIDE_TABLE_WEAKLY_REFERENCED时不调用该方法; -
addc操作将结果写入oldRefcnt,也就是size_t& refcntStorage = table.refcnts[this]内存地址中; -
当累加上溢出时,
refcntStorage = SIDE_TABLE_RC_PINNED | (oldRefcnt & SIDE_TABLE_FLAG_MASK)的含义是保留功能标志位域的内容,计数位域的最高位置为1其余置为0;
bool objc_object::sidetable_addExtraRC_nolock(size_t delta_rc)
{
assert(isa.indexed);
SideTable& table = SideTables()[this];
size_t& refcntStorage = table.refcnts[this];
size_t oldRefcnt = refcntStorage;
assert((oldRefcnt & SIDE_TABLE_DEALLOCATING) == 0);
assert((oldRefcnt & SIDE_TABLE_WEAKLY_REFERENCED) == 0);
if (oldRefcnt & SIDE_TABLE_RC_PINNED) return true;
uintptr_t carry;
size_t newRefcnt =
addc(oldRefcnt, delta_rc << SIDE_TABLE_RC_SHIFT, 0, &carry);
if (carry) {
refcntStorage =
SIDE_TABLE_RC_PINNED | (oldRefcnt & SIDE_TABLE_FLAG_MASK);
return true;
}
else {
refcntStorage = newRefcnt;
return false;
}
}
SIDE_TABLE_RC_PINNED是将 SideTable 中的对象的引用计数的64位数据的最高位作为对象引用计数上溢出的标记,是MSB,引用计数上溢出时,对象的retain、release操作不会改变引用计数位域的值。
2.3 objc_release函数逻辑分析
释放操作调用objc_release(id obj)方法,源代码如下。关键逻辑定位到objc_object::rootRelease(bool performDealloc, bool handleUnderflow)方法。对于指针类型的isa其
__attribute__((aligned(16)))
void objc_release(id obj)
{
if (!obj) return;
if (obj->isTaggedPointer()) return;
return obj->release();
}
inline void objc_object::release()
{
assert(!UseGC || ISA()->hasCustomRR());
assert(!isTaggedPointer());
if (! ISA()->hasCustomRR()) {
rootRelease();
return;
}
((void(*)(objc_object *, SEL))objc_msgSend)(this, SEL_release);
}
ALWAYS_INLINE bool objc_object::rootRelease()
{
return rootRelease(true, false);
}
2.3.1 rootRelease逻辑分析
objc_object::rootRelease(bool performDealloc, bool handleUnderflow)方法源代码如下,代码有点长,但由于有前面打下的知识基础,因此不逐个拆分。
ALWAYS_INLINE bool
objc_object::rootRelease(bool performDealloc, bool handleUnderflow)
{
assert(!UseGC);
if (isTaggedPointer()) return false;
bool sideTableLocked = false;
isa_t oldisa;
isa_t newisa;
retry:
do {
oldisa = LoadExclusive(&isa.bits);
newisa = oldisa;
if (!newisa.indexed) goto unindexed;
uintptr_t carry;
newisa.bits = subc(newisa.bits, RC_ONE, 0, &carry); // extra_rc--
if (carry) goto underflow;
} while (!StoreReleaseExclusive(&isa.bits, oldisa.bits, newisa.bits));
if (sideTableLocked) sidetable_unlock();
return false;
underflow:
newisa = oldisa;
if (newisa.has_sidetable_rc) {
if (!handleUnderflow) {
return rootRelease_underflow(performDealloc);
}
if (!sideTableLocked) {
sidetable_lock();
sideTableLocked = true;
if (!isa.indexed) {
goto unindexed;
}
}
size_t borrowed = sidetable_subExtraRC_nolock(RC_HALF);
if (borrowed > 0) {
newisa.extra_rc = borrowed - 1; too
bool stored = StoreExclusive(&isa.bits, oldisa.bits, newisa.bits);
if (!stored) {
isa_t oldisa2 = LoadExclusive(&isa.bits);
isa_t newisa2 = oldisa2;
if (newisa2.indexed) {
uintptr_t overflow;
newisa2.bits =
addc(newisa2.bits, RC_ONE * (borrowed-1), 0, &overflow);
if (!overflow) {
stored = StoreReleaseExclusive(&isa.bits, oldisa2.bits,
newisa2.bits);
}
}
}
if (!stored) {
sidetable_addExtraRC_nolock(borrowed);
goto retry;
}
sidetable_unlock();
return false;
}
else {
}
}
if (sideTableLocked) sidetable_unlock();
if (newisa.deallocating) {
return overrelease_error();
}
newisa.deallocating = true;
if (!StoreExclusive(&isa.bits, oldisa.bits, newisa.bits)) goto retry;
__sync_synchronize();
if (performDealloc) {
((void(*)(objc_object *, SEL))objc_msgSend)(this, SEL_dealloc);
}
return true;
unindexed:
if (sideTableLocked) sidetable_unlock();
return sidetable_release(performDealloc);
}
objc_object::rootRelease(bool performDealloc, bool handleUnderflow)方法的返回是引用计数是否下溢出,performDealloc参数指定引用计数下溢出时 是否需要向对象发送SEL_dealloc消息,handleUnderflow参数指定是否已经处理了内存引用计数下溢出状况。
rootRelease(bool performDealloc, bool handleUnderflow)方法的处理过程描述如下:
-
指针类型的
isa时,直接走 SideTable 的引用计数递减操作,调用objc_object::sidetable_release(bool performDealloc),并返回sidetable_release的处理结果,下方贴出源代码,处理逻辑大致为sidetable_retain()方法的反操作,只是多了发送SEL_dealloc消息的逻辑; -
非指针类型的
isa时,isa.bits.extra_rc递减RC_ONE; -
isa.bits.extra_rc递减不下溢出时,返回false; -
isa.bits.extra_rc递减下溢出 且isa.bits.has_sidetable_rc为0(无 SideTable 协同保存引用计数)时:若isa.deallocating为1表示对象已释放抛出 over release 异常,否则将isa.bits.deallocating置为1,并通过((void(*)(objc_object *, SEL))objc_msgSend)(this, SEL_dealloc)向对象发送析构消息; -
isa.bits.extra_rc递减下溢出 且isa.bits.has_sidetable_rc为1(有 SideTable 协同保存引用计数)时:这部分逻辑跳转比较多,在接下来的章节做代码单独剥离。
uintptr_t objc_object::sidetable_release(bool performDealloc)
{
#if SUPPORT_NONPOINTER_ISA
assert(!isa.indexed);
#endif
SideTable& table = SideTables()[this];
bool do_dealloc = false;
if (table.trylock()) {
RefcountMap::iterator it = table.refcnts.find(this);
if (it == table.refcnts.end()) {
do_dealloc = true;
table.refcnts[this] = SIDE_TABLE_DEALLOCATING;
} else if (it->second < SIDE_TABLE_DEALLOCATING) {
do_dealloc = true;
it->second |= SIDE_TABLE_DEALLOCATING;
} else if (! (it->second & SIDE_TABLE_RC_PINNED)) {
it->second -= SIDE_TABLE_RC_ONE;
}
table.unlock();
if (do_dealloc && performDealloc) {
((void(*)(objc_object *, SEL))objc_msgSend)(this, SEL_dealloc);
}
return do_dealloc;
}
return sidetable_release_slow(table, performDealloc);
}
2.3.2 rootRelease逻辑拆分——carry && isa.has_sidetable_rc
忽略以下代码,得到精简后的源代码:
-
unindexed相关处理逻辑,underflow中的if (!sideTableLocked)判断是为了保证在获取到SideTable锁之前,有unindexed transition正在进行,因此需要在此处加锁等待,并在获取到锁后重新判断isa.indexed作相应处理; -
加锁解锁相关代码;
-
重新尝试相关逻辑,两个
if (!stored)块中代码,都是为了在更新引用计数失败时,恢复isa.bits及 SideTable 中的引用计数数据并重新尝试; -
handleUnderFlow简单地使用true的handleUnderFlow参数调用自身; -
隐藏isa.deallocating及发送SEL_delloc逻辑代码
// rootRelease逻辑拆分——carry && isa.has_sidetable_rc
ALWAYS_INLINE bool
objc_object::rootRelease(bool performDealloc, bool handleUnderflow)
{
isa_t oldisa;
isa_t newisa;
retry:
do {
oldisa = LoadExclusive(&isa.bits);
newisa = oldisa;
uintptr_t carry;
newisa.bits = subc(newisa.bits, RC_ONE, 0, &carry); // extra_rc--
if (carry) goto underflow;
} while (!StoreReleaseExclusive(&isa.bits, oldisa.bits, newisa.bits));
return false;
underflow:
// newisa恢复到递减前的状态
newisa = oldisa;
if (newisa.has_sidetable_rc) {
size_t borrowed = sidetable_subExtraRC_nolock(RC_HALF);
if (borrowed > 0) {
newisa.extra_rc = borrowed - 1; // redo the original decrement too
StoreExclusive(&isa.bits, oldisa.bits, newisa.bits);
return false;
}
}
// isa.deallocating及发送SEL_delloc逻辑
...
}
精简后的源代码中,underflow块中的核心代码剩下sidetable_subExtraRC_nolock方法,其实就是从 SideTable 中取出delta_rc的引用计数,返回取出的引用计数数量。现在疑问剩下,为什么是newisa.extra_rc = borrowed - 1,这是因为前面newisa = oldisa将newisa恢复到递减前的状态,因此要对其作重新减1处理。
size_t objc_object::sidetable_subExtraRC_nolock(size_t delta_rc)
{
assert(isa.indexed);
SideTable& table = SideTables()[this];
RefcountMap::iterator it = table.refcnts.find(this);
if (it == table.refcnts.end() || it->second == 0) {
return 0;
}
size_t oldRefcnt = it->second;
assert((oldRefcnt & SIDE_TABLE_DEALLOCATING) == 0);
assert((oldRefcnt & SIDE_TABLE_WEAKLY_REFERENCED) == 0);
size_t newRefcnt = oldRefcnt - (delta_rc << SIDE_TABLE_RC_SHIFT);
assert(oldRefcnt > newRefcnt);
it->second = newRefcnt;
return delta_rc;
}
2.3.3 图示对象release向side table借位
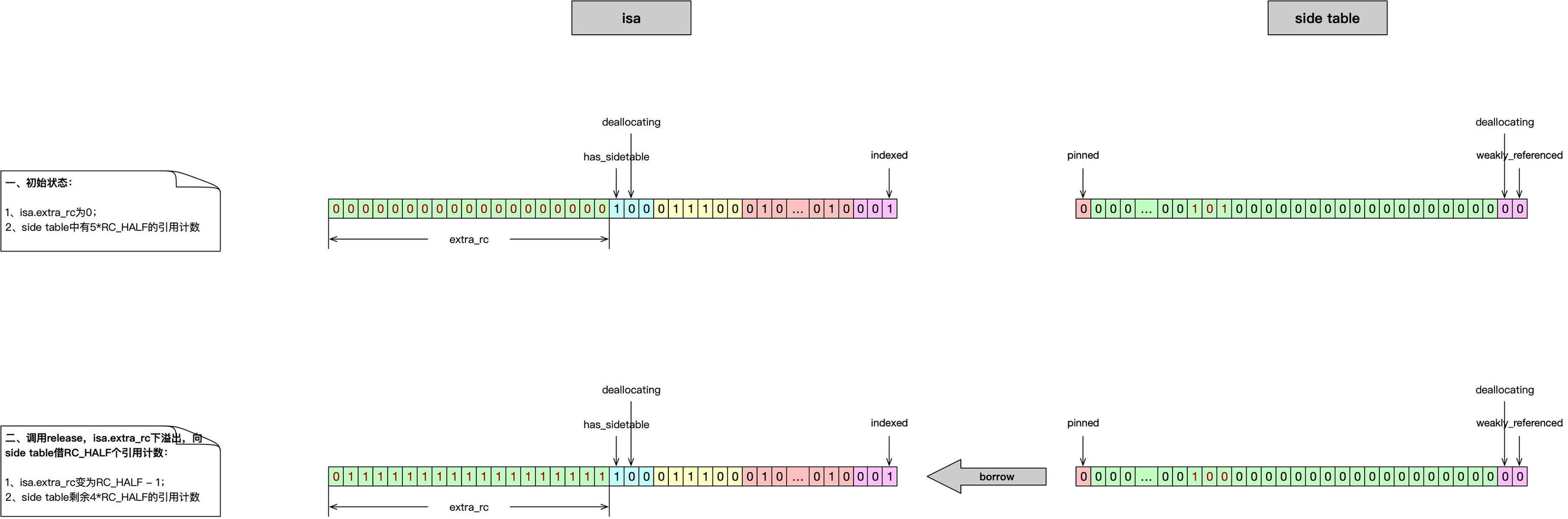
用以下三张图表示 release操作时引用计数下溢出,并向 side table 借位过程。图中,每行左右两条二进制数据分别表示对象的isa.bits、对象在side table中对应的引用计数SideTables[this]. refcnts[this]。左侧:绿色区域表示isa.bits中保存内存引用计数的extra_rc位域,右侧:绿色区域表示 side table 中保存对象的内存引用计数的位域。第一行的初始状态是:对象执行release操作时其非指针类的isa.extra_rc为0。
图一表示isa向 side table 借位成功,完成release操作。
图二表示isa向 side table 借位,side table 的内存计数已减少 RC_HALF,但是向isa.extra_rc中写入数据失败,第二次重新尝试写入isa.extra_rc成功,完成release操作。
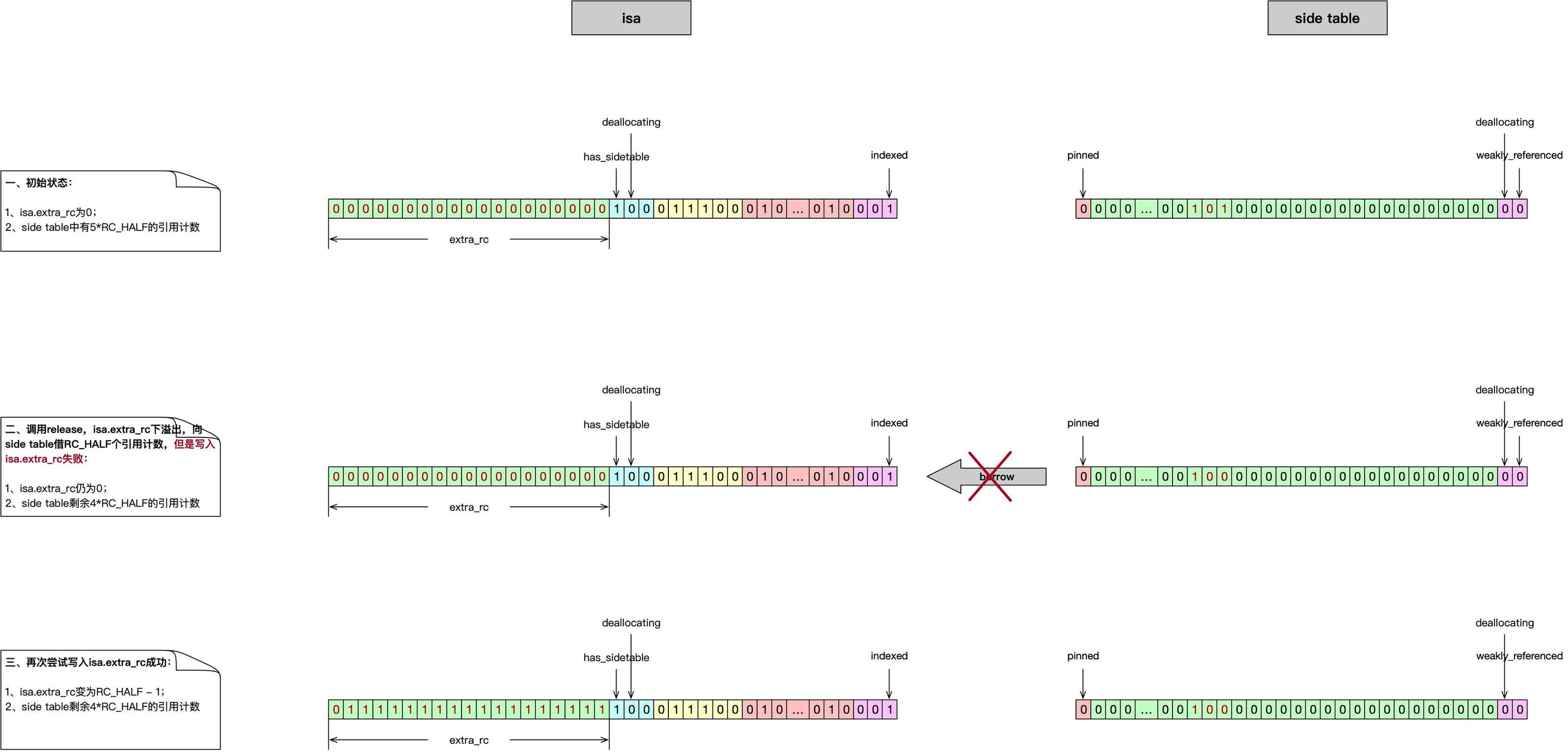
图三表示isa向 side table 借位,side table 的内存计数已减少 RC_HALF,但是向isa.extra_rc中写入数据失败,第二次重新尝试写入isa.extra_rc仍然失败,此时只能将借出的RC_HALF引用计数返还给 side table,返还成功后side table 的内存计数增加RC_HALF回到release前的状态。后续会goto retry重新尝试release操作。
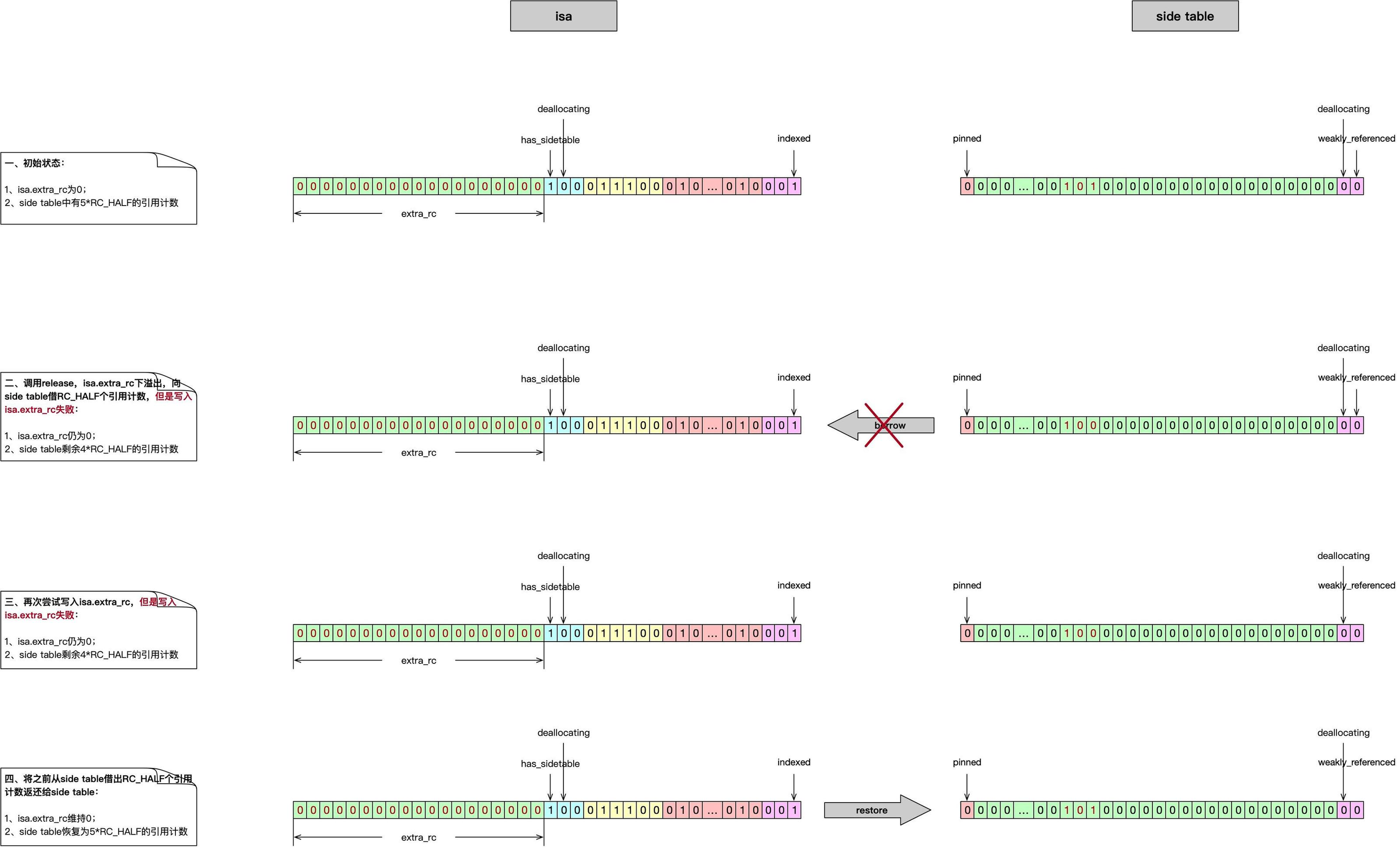
以上每张图都必须遵循两个准则:
-
release操作成功时:第一行的**
isa中的引用计数** 与 side table 中的引用计数 之和 必须等于最后一行的**isa中的引用计数** 与 side table 中的引用计数 之和减1。引用计数递减正是release的实现效果; -
release操作失败时:第一行的**
isa中的引用计数** 与 side table 中的引用计数 之和 必须等于最后一行的**isa中的引用计数** 与 side table 中的引用计数 之和。这是为了保证引用计数的数量不会在release操作过程丢失。
2.4 引用计数计算法则
在上面章节介绍了,使用指针类型isa时,当SideTable中该对象的引用计数下溢出,向对象发送析构消息。难道引用计数不是在归零时析构吗?怎么要等到下溢出呢?本章节就是为了回答这个问题。这里同样先给出答案:对象引用计数 = isa.extra_rc + SideTable记录的引用计数 + 1,这就是为何下溢出才析构的原因。
在源代码中,从NSObject的allocWithZone方法开始定位关键代码,经过以下方法:
+ (instancetype)allocWithZone:(struct _NSZone *)zoneid _objc_rootAllocWithZone(Class cls, malloc_zone_t *zone)id class_createInstanceFromZone(Class cls, size_t extraBytes, void *zone)static __attribute__((always_inline)) id _class_createInstanceFromZone(Class cls, size_t extraBytes, void *zone, bool cxxConstruct = true, size_t *outAllocatedSize = nil)inline void objc_object::initIsa(Class cls)inline void objc_object::initIsa(Class cls, bool indexed, bool hasCxxDtor)
最终定位到initIsa(Class cls, bool indexed, bool hasCxxDtor),同时在整个过程中没有出现任何retain的代码,其源代码如下:
inline void objc_object::initIsa(Class cls)
{
initIsa(cls, false, false);
}
inline void objc_object::initIsa(Class cls, bool indexed, bool hasCxxDtor)
{
assert(!isTaggedPointer());
if (!indexed) {
isa.cls = cls;
} else {
assert(!DisableIndexedIsa);
isa.bits = ISA_MAGIC_VALUE;
isa.has_cxx_dtor = hasCxxDtor;
isa.shiftcls = (uintptr_t)cls >> 3;
}
}
objc_object::initIsa(Class cls, bool indexed, bool hasCxxDtor)方法用于在对象初始化时,初始化对象的isa。关注表示使用非指针类型isa的else逻辑分支,isa.bits = ISA_MAGIC_VALUE将isa的值设置为ISA_MAGIC_VALUE,ISA_MAGIC_VALUE的值是0x000001a000000001ULL,其extra_rc位域全0,也就是说构建对象实例后isa.extra_rc为0,而此时对象引用计数为1,这就是本章开头答案等式的由来。
initIsa(Class cls)方法中initIsa(cls, false, false)表明,目前默认使用的还是指针类型的isa,即isa直接指向对象的类。
从NSObject的retainCount方法的实现也可以找到答案,先找关键代码,经过:
- (NSUInteger)retainCountinline uintptr_t objc_object::rootRetainCount()
最终定位到inline uintptr_t objc_object::rootRetainCount(),源代码如下。逻辑比较清晰就不再赘述。
inline uintptr_t objc_object::rootRetainCount()
{
assert(!UseGC);
if (isTaggedPointer()) return (uintptr_t)this;
sidetable_lock();
isa_t bits = LoadExclusive(&isa.bits);
if (bits.indexed) {
uintptr_t rc = 1 + bits.extra_rc;
if (bits.has_sidetable_rc) {
rc += sidetable_getExtraRC_nolock();
}
sidetable_unlock();
return rc;
}
sidetable_unlock();
return sidetable_retainCount();
}
三、总结
总结本文要点如下:
-
Objective-C支持使用对象的
isa、全局的多张SideTable单独或联合管理对象引用计数; -
当使用指针类型
isa时,即isa.indexed位为0时:对象的isa是指向对象的Class的指针,此时对象引用计数统一由SideTable管理; -
当使用非指针类型
isa时,即isa.indexed位为1时:对象的isa不是指针而是保存类的地址、内存管理相关的信息的二进制数据,其extra_rc位域保存内存计数,当has_sidetable_rc位为0时,isa.extra_rc即是对象的引用计数,当has_sidetable_rc位为1时,对象引用计数是,SideTable中记录的该对象引用计数 及isa.extra_rc之和; -
当
isa.indexed位为1且has_sidetable_rc位为1时:retain操作若isa.extra递增后上溢出,则转移一半的内存引用计数RC_HALF到SideTable; -
当
isa.indexed位为1且has_sidetable_rc位为1时:release操作若isa.extra递减后下溢出,则向SideTable借出RC_HALF引用计数; -
对象引用计数 =
isa.extra_rc+SideTable记录的引用计数 + 1,对象引用计数归零时向对象发送SEL_dealloc析构消息。