先行好事,再谈前程
1.日志1.1适配器模式1.1.1目标接口1.1.2被适配者1.1.3对象适配器1.2日志优先级2.日志的使用2.1普通使用2.2代理模式总结
Mybatis本身不提供日志实现,而是兼容第三方日志框架,如:slf4J,commonsLoging,Log4J2,Log4J,JdkLog。为了兼容和使用第三方日志框架,Mybatis进行了优秀的设计。
Mybatis的日志模块可以用两个知识点概括:
- 适配器模式
- 代理模式
1.日志
为了兼容第三方日志框架,Mybatis使用了适配器模式,并且使用适配器模式实现中的对象适配器。
1.1适配器模式
对象适配器: 被适配者作为适配器的属性存在
- Target目标接口:期望得到的接口,也是直接使用的接口
- Adapter适配器: 将源接口转为目标接口
- Adaptee被适配者:源接口
1.1.1目标接口
Mybatis 使用日志接口是Log。但是因为Mybatis 本身不实现日志,实际使用的是第三方的日志接口
public interface Log {
boolean isDebugEnabled();
boolean isTraceEnabled();
void error(String s, Throwable e);
void error(String s);
void debug(String s);
void trace(String s);
void warn(String s);
}
1.1.2被适配者
第三方日志接口被Mybatis中适配器适配。
- slf4j日志
- log4j2日志
- log4j日志
- jdklog日志
1.1.3对象适配器
- slf4j适配器:Slf4jLocationAwareLoggerImpl对应1.6版本以上的slf4j日志适配,Slf4jLoggerImpl对应1.6版本以下的slf4j适配器
- Log4j2适配器:Log4j2AbstractLoggerImpl 适配器,Log4j2LoggerImpl适配器
- log4j适配器:Log4jImpl 适配器
- JDK适配器 : Jdk14LoggingImpl
以log4j的适配器Log4jImpl 为例:被适配者作为适配器的属性存在
public class Log4jImpl implements Log {
private static final String FQCN = Log4jImpl.class.getName();
private Logger log;//持有被适配器对象的引用
}
1.2日志优先级
在mybatis中,使用工厂模式来创建日志对象。这样日志的优先级问题也在LogFactory 工厂中处理。
public final class LogFactory {
public static final String MARKER = "MYBATIS";
private static Constructor<? extends Log> logConstructor;
//按优先级
static {
tryImplementation(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
useSlf4jLogging();
}
});
tryImplementation(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
useCommonsLogging();
}
});
tryImplementation(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
useLog4J2Logging();
}
});
tryImplementation(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
useLog4JLogging();
}
});
tryImplementation(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
useJdkLogging();
}
});
tryImplementation(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
useNoLogging();
}
});
}
//尝试设置日志实现
private static void tryImplementation(Runnable runnable) {
if (logConstructor == null) {
try {
runnable.run();
} catch (Throwable t) {
// ignore
}
}
}
//设置日志实现。
private static void setImplementation(Class<? extends Log> implClass) {
try {
Constructor<? extends Log> candidate = implClass.getConstructor(String.class);
Log log = candidate.newInstance(LogFactory.class.getName());
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Logging initialized using '" + implClass + "' adapter.");
}
logConstructor = candidate;
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw new LogException("Error setting Log implementation. Cause: " + t, t);
}
}
优先级就是在静态代码块中指定的。先加载slf4J,如果成功,则构造器logConstructor不为空,那么后续加载的时候发现构造器不为空,后续的其他日志不再设置。这样就实现了优先级
优先级顺序:
slf4j > common logging > log4j2 > log4j > jdk logging > 没有日志
2.日志的使用
Mybatis使用日志分为两种方式
2.1普通使用
所谓普通使用,就是从日志工厂获取一个日志对象然后调用日志打印方法打印
public abstract class BaseExecutor implements Executor {
private static final Log log = LogFactory.getLog(BaseExecutor.class);
public void close(boolean forceRollback) {
try {
} catch (SQLException e) {
//普通使用
log.warn("Unexpected exception on closing transaction. Cause: " + e);
} finally {
}
}
}
2.2代理模式
Mybatis使用日志最多的形式,就是代理模式。
基本方法是:
给需要加日志功能的组件,创建代理对象,并用日志增强器对其进行增强
日志增强器:
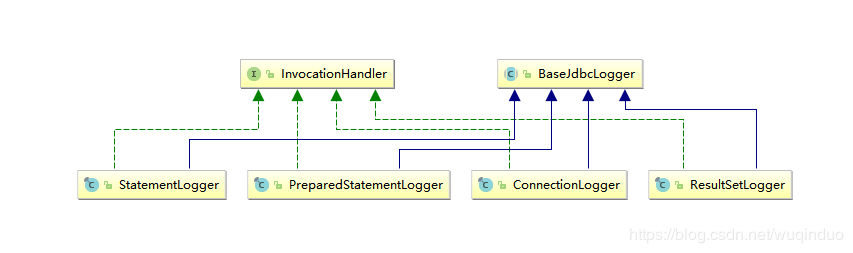
他们对JDBC的几个核心类进行的动态代理增强,使其具有日志打印功能
- ConnectionLogger: 连接日志增强器
- PreparedStatementLogger : PreparedStatement 日志增强器
- ResultSetLogger : 结果集日志增强器
- StatementLogger : Statement日志增强器
我们以ConnectionLogger为例来看看其原理
/*
BaseExecutor
*/
public abstract class BaseExecutor implements Executor {
//获取连接
protected Connection getConnection(Log statementLog) throws SQLException {
Connection connection = transaction.getConnection();
if (statementLog.isDebugEnabled()) {//如果是日志级别是debug模式则创建代理对象。
return ConnectionLogger.newInstance(connection, statementLog, queryStack);
} else {
return connection;
}
}
}
/*
ConnectionLogger
*/
public final class ConnectionLogger extends BaseJdbcLogger implements InvocationHandler {
//为Connection创建代理对象
public static Connection newInstance(Connection conn, Log statementLog, int queryStack) {
InvocationHandler handler = new ConnectionLogger(conn, statementLog, queryStack);
ClassLoader cl = Connection.class.getClassLoader();
return (Connection) Proxy.newProxyInstance(cl, new Class[]{Connection.class}, handler);
}
//增强
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] params)
throws Throwable {
try {
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, params);
}
if ("prepareStatement".equals(method.getName())) {
if (isDebugEnabled()) {
//日志的打印
debug(" Preparing: " + removeBreakingWhitespace((String) params[0]), true);
}
PreparedStatement stmt = (PreparedStatement) method.invoke(connection, params);
stmt = PreparedStatementLogger.newInstance(stmt, statementLog, queryStack);
return stmt;
} else if ("prepareCall".equals(method.getName())) {
if (isDebugEnabled()) {
//日志的打印
debug(" Preparing: " + removeBreakingWhitespace((String) params[0]), true);
}
PreparedStatement stmt = (PreparedStatement) method.invoke(connection, params);
stmt = PreparedStatementLogger.newInstance(stmt, statementLog, queryStack);
return stmt;
} else if ("createStatement".equals(method.getName())) {
Statement stmt = (Statement) method.invoke(connection, params);
stmt = StatementLogger.newInstance(stmt, statementLog, queryStack);
return stmt;
} else {
return method.invoke(connection, params);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
}
}
开启debug模式时,获取的Connection对象是代理对象。当执行其方法时, 会走ConnectionLogger#invoke方法,然后会根据方法名,进行日志的打印。
这样通过代理模式优雅的把日志打印功能加入到JDBC重要组件中,为我们排查问题提供了参考。
总结
Mybatis在日志的设计上可谓是精彩干练。
- 通过适配器模式接入主流的日志框架,兼容万象。
- 通过动态代理模式对JDBC核心类进行日志功能的增强,让它具备日志打印的能力。
关联阅读
0.Mybatis源码系列0-从JDBC到Mybatis
1.Mybatis源码系列1-Mybaits初始化
2.Mybatis源码系列2-Mapper原理
3.Mybatis源码系列3-三种SqlSession的区别
4.Transaction与SqlSession,Connection
5.Mybatis源码系列4-一级缓存
6.Mybatis源码系列5-二级缓存
如果本文任何错误,请批评指教,不胜感激 !
如果觉得文章不错,点个赞吧
微信公众号:源码行动
享学源码,行动起来,来源码行动
