Flutter 动态化热更新的思考与实践(二)----Dart 代码转换AST
Flutter 动态化热更新的思考与实践(三)---- 解析AST之Runtime
Flutter 动态化热更新的思考与实践(四)---- 解析AST之Widget
Flutter 动态化热更新的思考与实践(五)---- 调用AST动态化的代码
我们在上一篇文章《Flutter动态化热更新的思考与实践》中探讨了在Flutter中实现动态化热更新的可行方案,在本篇文章里我们先来探讨该方案的第一阶段:如何将Dart代码转换成AST描述文件。
1. AST 简介
上一篇文章里也提到了AST,但是没有过多的来解释,那么在本篇文章里先对这个名词做个简单的科普(已经了解的小伙伴可以略过^ ^)。
AST的全称是Abstract Syntax Tree,中文名称叫抽象语法树,是将我们的源代码中的语法以树状结构表现出来。AST不依赖于编程语言,任何编程语言都可以转换为AST结构,关于AST深入的部分在这里就不做展开了,比如AST生成的逻辑步骤等(我本人也还没有了解这部分,涉及到了编译原理的知识,脑壳疼 = =)。想直观了解AST是什么东西的话,Javascript是最合适的语言,有一个在线转换Javascript 到AST的工具AST Explorer, 感兴趣的小伙伴可以自行实验,我贴出一个最简单的例子,比如将这句代码var c = a + 10转换成AST的话,将是下面的样子:

篇幅有限,也只能截取一部分,不过大致可以看到AST的结构是什么样子,通常我们用JSON数据来组织表达,也便于我们读取和解析。
在上面截图的AST数据结构中可以看到,AST结构中会包含很多节点对象,每个节点对象下面会包含各种属性以及其他的节点对象,通常这些节点对象的定义是有标准的,如上所例:
VariableDeclarator一般定义为声明的变量BinaryExpression一般定义为运算表达式Identifier一般定义为标识符名称,这个标识符包括变量名、方法名、类名等诸如此类。NumericLiteral一般定义为数值,包括整型、浮点型等
除此之外还有很多的有特定含义的节点对象,通常这些节点对象都对应描述源代码中的某一个语法,比较官方的定义标准可以在这里查找AST节点对象
2. Dart官方工具 analyzer
对AST有了一些了解和认知后,接下来就要思考,如何将Dart代码转换为AST。好在Dart官方很贴心的提供了一个工具包analyzer,通过这个工具包提供的方法,我们可以将一份Dart源代码生成AST对象。当然,这个工具包除了可以生成AST对象外,还可以做一些代码分析,找出一些语法错误或潜在风险警告等。在官方文档里有介绍,比如代码格式化工具dartfmt、代码文档生成工具dartdoc、代码语法预分析服务Dart Analysis Server等都使用了此工具包。
3. 使用 analyzer
现在我们开始进入正题,就是如何通过analyzer提供的工具方法,将一份Dart代码生成JSON结构的AST数据。我们先看看analyzer提供的方法:
/// Return the result of parsing the file at the given [path].
///
/// If a [resourceProvider] is given, it will be used to access the file system.
///
/// [featureSet] determines what set of features will be assumed by the parser.
/// This parameter is required because the analyzer does not yet have a
/// performant way of computing the correct feature set for a single file to be
/// parsed. Callers that need the feature set to be strictly correct must
/// create an [AnalysisContextCollection], query it to get an [AnalysisContext],
/// query it to get an [AnalysisSession], and then call `getParsedUnit`.
///
/// Callers that don't need the feature set to be strictly correct can pass in
/// `FeatureSet.fromEnableFlags([])` to enable the default set of features; this
/// is much more performant than using an analysis session, because it doesn't
/// require the analyzer to process the SDK.
///
/// If [throwIfDiagnostics] is `true` (the default), then if any diagnostics are
/// produced because of syntactic errors in the [content] an `ArgumentError`
/// will be thrown. If the parameter is `false`, then the caller can check the
/// result to see whether there are any errors.
ParseStringResult parseFile(
{@required String path,
ResourceProvider resourceProvider,
@required FeatureSet featureSet,
bool throwIfDiagnostics = true}){
...
}
首先我们通过parseFile解析一份Dart代码文件,文件的路径作为path参数传值,然后会返回ParseStringResult对象,再来看看对这个类的定义:
/// The result of parsing of a single file. The errors returned include only
/// those discovered during scanning and parsing.
///
/// Similar to [ParsedUnitResult], but does not allow access to an analysis
/// session.
///
/// Clients may not extend, implement or mix-in this class.
abstract class ParseStringResult {
/// The content of the file that was scanned and parsed.
String get content;
/// The analysis errors that were computed during analysis.
List<AnalysisError> get errors;
/// Information about lines in the content.
LineInfo get lineInfo;
/// The parsed, unresolved compilation unit for the [content].
CompilationUnit get unit;
}
在这个类结构里,我们需要关注unit这个成员变量,数据类型是CompilationUnit类,注释中已说明是一个“未处理的编译单元”,我们先不从字面上理解这个是什么意思,先来看看CompilationUnit的定义:
/// A compilation unit.
///
/// While the grammar restricts the order of the directives and declarations
/// within a compilation unit, this class does not enforce those restrictions.
/// In particular, the children of a compilation unit will be visited in lexical
/// order even if lexical order does not conform to the restrictions of the
/// grammar.
///
/// compilationUnit ::=
/// directives declarations
///
/// directives ::=
/// [ScriptTag]? [LibraryDirective]? namespaceDirective* [PartDirective]*
/// | [PartOfDirective]
///
/// namespaceDirective ::=
/// [ImportDirective]
/// | [ExportDirective]
///
/// declarations ::=
/// [CompilationUnitMember]*
///
/// Clients may not extend, implement or mix-in this class.
abstract class CompilationUnit implements AstNode {
/// Set the first token included in this node's source range to the given
/// [token].
set beginToken(Token token);
/// Return the declarations contained in this compilation unit.
NodeList<CompilationUnitMember> get declarations;
/// Return the element associated with this compilation unit, or `null` if the
/// AST structure has not been resolved.
CompilationUnitElement get declaredElement;
/// Return the directives contained in this compilation unit.
NodeList<Directive> get directives;
/// Set the element associated with this compilation unit to the given
/// [element].
set element(CompilationUnitElement element);
/// Set the last token included in this node's source range to the given
/// [token].
set endToken(Token token);
/// The set of features available to this compilation unit, or `null` if
/// unknown.
///
/// Determined by some combination of the .packages file, the enclosing
/// package's SDK version constraint, and/or the presence of a `@dart`
/// directive in a comment at the top of the file.
///
/// Might be `null` if, for example, this [CompilationUnit] has been
/// resynthesized from a summary.
FeatureSet get featureSet;
/// Return the line information for this compilation unit.
LineInfo get lineInfo;
/// Set the line information for this compilation unit to the given [info].
set lineInfo(LineInfo info);
/// Return the script tag at the beginning of the compilation unit, or `null`
/// if there is no script tag in this compilation unit.
ScriptTag get scriptTag;
/// Set the script tag at the beginning of the compilation unit to the given
/// [scriptTag].
set scriptTag(ScriptTag scriptTag);
/// Return a list containing all of the directives and declarations in this
/// compilation unit, sorted in lexical order.
List<AstNode> get sortedDirectivesAndDeclarations;
}
(说实话这个类的注释看着着实有些费解,编译原理的知识小白,脑壳疼= =)
不过这并不妨碍我们使用它,我们可以看到这个类实现了AstNode接口,那么大致可以猜测到这个类应该就是用于存储AST数据的,那么在ParseStringResult的unit参数应该就是AST语法树结构的根结点,从这个根节点开始遍历,应该就可以构造出我们想要的JSON结构的AST数据。接下来就是如何遍历,查找了一些资料,了解到CompilationUnit是以访问者模式设计的,那么我们要遍历整棵树的内容就要通过访问者的方式。analyzer工具包中也提供了相关的类,就是AstVisitor<R>,定义如下:
/// An object that can be used to visit an AST structure.
///
/// Clients may not extend, implement or mix-in this class. There are classes
/// that implement this interface that provide useful default behaviors in
/// `package:analyzer/dart/ast/visitor.dart`. A couple of the most useful
/// include
/// * SimpleAstVisitor which implements every visit method by doing nothing,
/// * RecursiveAstVisitor which will cause every node in a structure to be
/// visited, and
/// * ThrowingAstVisitor which implements every visit method by throwing an
/// exception.
abstract class AstVisitor<R> {
...
}
注释中也介绍的很清楚了,用于访问AST结构的对象,并且也提供了几个实现类:
SimpleAstVisitorGeneralizingAstVisitorUnifyingAstVisitorRecursiveAstVisitorThrowingAstVisitor- ...
一般我们常用的是前三个类,如果我们需要自定义处理访问的节点数据时,我们可以继承SimpleAstVisitor或GeneralizingAstVisitor这个类,然后重载我们想要自定义处理的方法就好。GeneralizingAstVisitor 或UnifyingAstVisitor一般可以辅助我们分析源代码生成的AST结构是什么样子。如果我们不使用以上实现类,也可以直接实现AstVisitor,但是,AstVisitor里面有121个方法,如果我们自己实现这个类的话,意味着121个方法我们都要重载一遍,即使有很多方法也不会去使用。。所以无特殊要求的话,还是直接继承SimpleAstVisitor或 GeneralizingAstVisitor就基本满足需求了。
了解了遍历AST结构数据的方式后,我们就要开始实现自己的Visitor了:
class MyAstVisitor extends SimpleAstVisitor<Map> {
/// 遍历节点
Map _safelyVisitNode(AstNode node) {
if (node != null) {
return node.accept(this);
}
return null;
}
/// 遍历节点列表
List<Map> _safelyVisitNodeList(NodeList<AstNode> nodes) {
List<Map> maps = [];
if (nodes != null) {
int size = nodes.length;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
var node = nodes[i];
if (node != null) {
var res = node.accept(this);
if (res != null) {
maps.add(res);
}
}
}
}
return maps;
}
}
在我们自己实现的Visitor里,先定义了两个私有方法,分别作为遍历单个节点和遍历节点列表用。接下来我们开始从AST树的根结点遍历并构造Map数据:
class MyAstVisitor extends SimpleAstVisitor<Map> {
/// 遍历节点
Map _safelyVisitNode(AstNode node) {
if (node != null) {
return node.accept(this);
}
return null;
}
/// 遍历节点列表
List<Map> _safelyVisitNodeList(NodeList<AstNode> nodes) {
List<Map> maps = [];
if (nodes != null) {
int size = nodes.length;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
var node = nodes[i];
if (node != null) {
var res = node.accept(this);
if (res != null) {
maps.add(res);
}
}
}
}
return maps;
}
//构造根节点
Map _buildAstRoot(List<Map> body) {
if (body.isNotEmpty) {
return {
"type": "Program",
"body": body,
};
} else {
return null;
}
}
@override
Map visitCompilationUnit(CompilationUnit node) {
return _buildAstRoot(_safelyVisitNodeList(node.declarations));
}
}
根结点下面的内容就要根据我们的源代码来一个一个去解析构造了,我们先举一个简单的例子,比如我们要生成如下代码的AST语法树:
//demo_blog_code2.dart
int incTen(int a) {
int b = a + 10;
return b;
}
首先我们写一个Command-lines 程序,程序中使用上面提到的GeneralizingAstVisitor类来打印输出这段源代码生成的AST语法树中的各节点访问路径是什么样子:
import 'dart:io';
import 'package:analyzer/dart/analysis/features.dart';
import 'package:analyzer/dart/analysis/utilities.dart';
import 'package:analyzer/dart/ast/visitor.dart';
import 'package:analyzer/dart/ast/ast.dart';
import 'package:args/args.dart';
void main(List<String> arguments) {
exitCode = 0; // presume success
final parser = ArgParser()..addFlag("file", negatable: false, abbr: 'f');
var argResults = parser.parse(arguments);
final paths = argResults.rest;
if (paths.isEmpty) {
stdout.writeln('No file found');
} else {
generate(paths[0]);
}
}
class DemoAstVisitor extends GeneralizingAstVisitor<Map> {
@override
Map visitNode(AstNode node) {
//输出遍历AST Node 节点内容
stdout.writeln("${node.runtimeType}<---->${node.toSource()}");
return super.visitNode(node);
}
}
//生成AST
Future generate(String path) async {
if (path.isEmpty) {
stdout.writeln("No file found");
} else {
await _handleError(path);
if (exitCode == 2) {
try {
var parseResult =
parseFile(path: path, featureSet: FeatureSet.fromEnableFlags([]));
var compilationUnit = parseResult.unit;
//遍历AST
compilationUnit.accept(DemoAstVisitor());
} catch (e) {
stdout.writeln('Parse file error: ${e.toString()}');
}
}
}
}
Future _handleError(String path) async {
if (await FileSystemEntity.isDirectory(path)) {
stderr.writeln('error: $path is a directory');
} else {
exitCode = 2;
}
}
然后我们运行上面的代码:
dart main.dart -f dsldemos/demo_blog_code2.dart
(demo_blog_code2.dart 为测试源代码文件),输出如下:
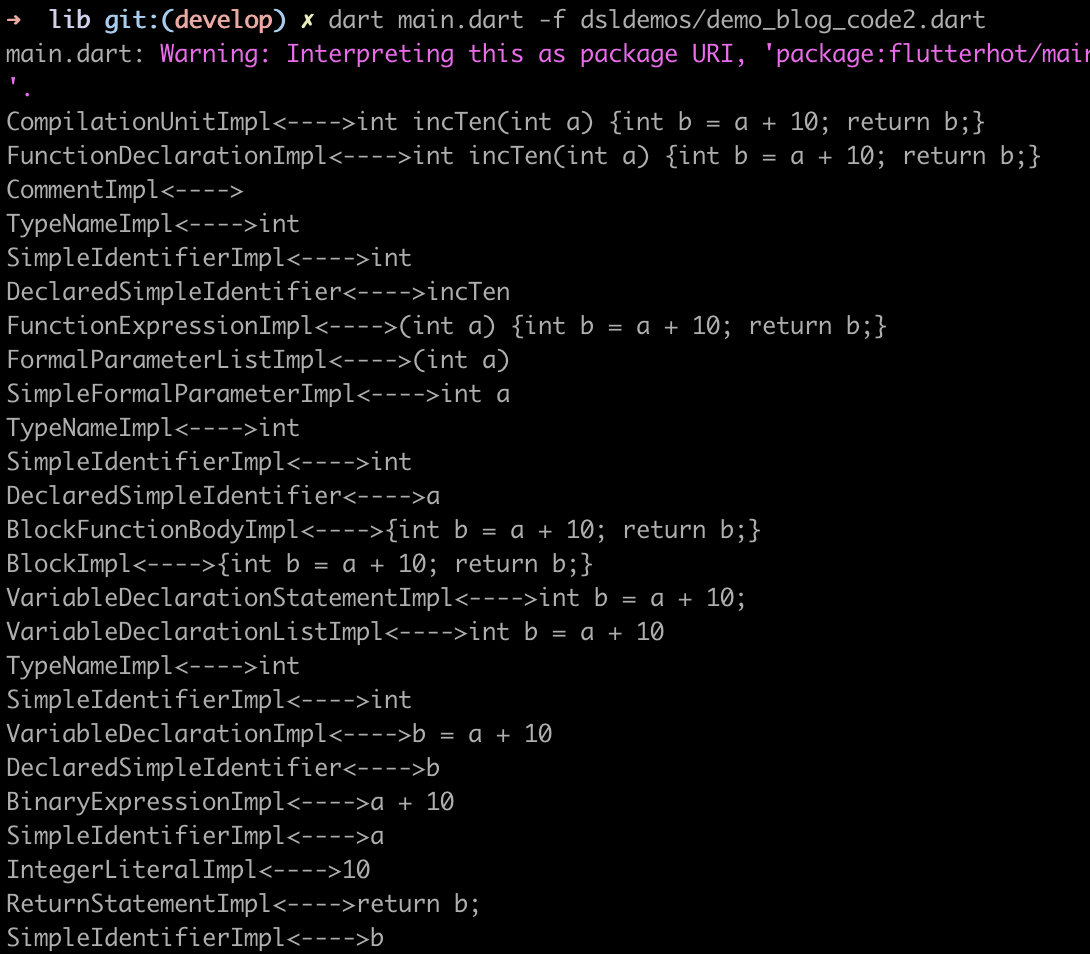
根据这份输出结果,我们大致可以判断需要在Visitor中处理的重载方法都有哪些,最终我们的Visitor实现:
class MyAstVisitor extends SimpleAstVisitor<Map> {
/// 遍历节点
Map _safelyVisitNode(AstNode node) {
if (node != null) {
return node.accept(this);
}
return null;
}
/// 遍历节点列表
List<Map> _safelyVisitNodeList(NodeList<AstNode> nodes) {
List<Map> maps = [];
if (nodes != null) {
int size = nodes.length;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
var node = nodes[i];
if (node != null) {
var res = node.accept(this);
if (res != null) {
maps.add(res);
}
}
}
}
return maps;
}
//构造根节点
Map _buildAstRoot(List<Map> body) {
if (body.isNotEmpty) {
return {
"type": "Program",
"body": body,
};
} else {
return null;
}
}
//构造代码块Bloc 结构
Map _buildBloc(List body) => {"type": "BlockStatement", "body": body};
//构造运算表达式结构
Map _buildBinaryExpression(Map left, Map right, String lexeme) => {
"type": "BinaryExpression",
"operator": lexeme,
"left": left,
"right": right
};
//构造变量声明
Map _buildVariableDeclaration(Map id, Map init) => {
"type": "VariableDeclarator",
"id": id,
"init": init,
};
//构造变量声明
Map _buildVariableDeclarationList(
Map typeAnnotation, List<Map> declarations) =>
{
"type": "VariableDeclarationList",
"typeAnnotation": typeAnnotation,
"declarations": declarations,
};
//构造标识符定义
Map _buildIdentifier(String name) => {"type": "Identifier", "name": name};
//构造数值定义
Map _buildNumericLiteral(num value) =>
{"type": "NumericLiteral", "value": value};
//构造函数声明
Map _buildFunctionDeclaration(Map id, Map expression) => {
"type": "FunctionDeclaration",
"id": id,
"expression": expression,
};
//构造函数表达式
Map _buildFunctionExpression(Map params, Map typeParameters, Map body) => {
"type": "FunctionExpression",
"parameters": params,
"typeParameters": typeParameters,
"body": body,
};
//构造函数参数
Map _buildFormalParameterList(List<Map> parameterList) =>
{"type": "FormalParameterList", "parameterList": parameterList};
//构造函数参数
Map _buildSimpleFormalParameter(Map type, String name) =>
{"type": "SimpleFormalParameter", "paramType": type, "name": name};
//构造函数参数类型
Map _buildTypeName(String name) => {
"type": "TypeName",
"name": name,
};
//构造返回数据定义
Map _buildReturnStatement(Map argument) => {
"type": "ReturnStatement",
"argument": argument,
};
@override
Map visitCompilationUnit(CompilationUnit node) {
return _buildAstRoot(_safelyVisitNodeList(node.declarations));
}
@override
Map visitBlock(Block node) {
return _buildBloc(_safelyVisitNodeList(node.statements));
}
@override
Map visitBlockFunctionBody(BlockFunctionBody node) {
return _safelyVisitNode(node.block);
}
@override
Map visitVariableDeclaration(VariableDeclaration node) {
return _buildVariableDeclaration(
_safelyVisitNode(node.name), _safelyVisitNode(node.initializer));
}
@override
Map visitVariableDeclarationStatement(VariableDeclarationStatement node) {
return _safelyVisitNode(node.variables);
}
@override
Map visitVariableDeclarationList(VariableDeclarationList node) {
return _buildVariableDeclarationList(
_safelyVisitNode(node.type), _safelyVisitNodeList(node.variables));
}
@override
Map visitSimpleIdentifier(SimpleIdentifier node) {
return _buildIdentifier(node.name);
}
@override
Map visitBinaryExpression(BinaryExpression node) {
return _buildBinaryExpression(_safelyVisitNode(node.leftOperand),
_safelyVisitNode(node.rightOperand), node.operator.lexeme);
}
@override
Map visitIntegerLiteral(IntegerLiteral node) {
return _buildNumericLiteral(node.value);
}
@override
Map visitFunctionDeclaration(FunctionDeclaration node) {
return _buildFunctionDeclaration(
_safelyVisitNode(node.name), _safelyVisitNode(node.functionExpression));
}
@override
Map visitFunctionDeclarationStatement(FunctionDeclarationStatement node) {
return _safelyVisitNode(node.functionDeclaration);
}
@override
Map visitFunctionExpression(FunctionExpression node) {
return _buildFunctionExpression(_safelyVisitNode(node.parameters),
_safelyVisitNode(node.typeParameters), _safelyVisitNode(node.body));
}
@override
Map visitSimpleFormalParameter(SimpleFormalParameter node) {
return _buildSimpleFormalParameter(
_safelyVisitNode(node.type), node.identifier.name);
}
@override
Map visitFormalParameterList(FormalParameterList node) {
return _buildFormalParameterList(_safelyVisitNodeList(node.parameters));
}
@override
Map visitTypeName(TypeName node) {
return _buildTypeName(node.name.name);
}
@override
Map visitReturnStatement(ReturnStatement node) {
return _buildReturnStatement(_safelyVisitNode(node.expression));
}
}
修改下我们的Command-lines程序,使用上面实现的Visitor:
...
try {
var parseResult =
parseFile(path: path, featureSet: FeatureSet.fromEnableFlags([]));
var compilationUnit = parseResult.unit;
//遍历AST
var astData = compilationUnit.accept(MyAstVisitor());
stdout.writeln(jsonEncode(astData));
} catch (e) {
stdout.writeln('Parse file error: ${e.toString()}');
}
...
重新执行后,最终生成的AST数据(部分截图):

这个就是对上面的测试代码生成AST语法树的数据结构了,当然这个AST树经过了一些简化,去掉了一些冗余的节点,主要为了方便我们下一个阶段的工作,解析AST,来做准备,减少我们解析的压力。
好了,本篇文章我们通过一个简单的实例,介绍了如何将Dart代码转换成AST,下一篇文章,我们将探索如果解析生成的AST语法树,来达到和我们源代码同样的执行效果。