springboot如何根据配置自动装配组件?
在分析源码之前,我们先了解下自动装配的理论。没有理论的支撑,我们很难了解到源码的精华。
起步依赖
Spring Boot通过起步依赖为项目的依赖管理提供帮助。起步依赖其实就是特殊的Maven依 赖和Gradle依赖,利用了传递依赖解析,把常用库聚合在一起,组成了几个为特定功能而定制 的依赖。
众多的 起步依赖 均配置在spring-boot-starter-parent中:
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.3.1.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
Spring Boot通过提供众多起步依赖降低项目依赖的复杂度。
自动装配
Spring Boot的自动配置是应用程序启动时的过程,考虑了众多因素,才决定Spring配置应该用哪个,不该用哪个。
下面这些情况都是Spring Boot的自动配置要考虑的。
- Spring的
JdbcTemplate是不是在Classpath里?如果是,并且有DataSource的Bean,则自动配置一个JdbcTemplate的Bean。 Spring Security是不是在Classpath里?如果是,则进行一个非常基本的Web安全设置。
每当应用程序启动的时候,Spring Boot的自动配置都要做将近200个这样的决定。所有这些自动配置就是为了尽量不让我们自己写配置。
下面我们具体分析下 JdbcTemplate 和 Spring Security 自动装配的过程:
JdbcTemplate
Spring Boot的 DataSourceAutoConfiguration 中定义的 JdbcTemplate Bean就是一个非常简单的例子,演示了 @ConditionalOnMissingBean 如何工作:
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(JdbcOperations.class)
public JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate() {
return new JdbcTemplate(this.dataSource);
}
jdbcTemplate() 方法上添加了 @Bean 注解,在需要时可以配置出一个 JdbcTemplateBean。
但它上面还加了 @ConditionalOnMissingBean 注解,要求当前不存在 JdbcOperations 类型的Bean时才生效。
如果当前已经有一个 JdbcOperations Bean了,条件即不满足,不会执行 jdbcTemplate() 方法。
Spring Security
Spring Boot自动配置的安全配置时,最重要的一个类是 SpringBootWebSecurityConfiguration 。
以下是其中的一个代码片段:
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass(WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter.class)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter.class)
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = Type.SERVLET)
public class SpringBootWebSecurityConfiguration {
@Configuration
@Order(SecurityProperties.BASIC_AUTH_ORDER)
static class DefaultConfigurerAdapter extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
}
}
首先我们分析下,这些注解。
@ConditionalOnClass的作用为项目中只有引入security相关的包,才会构建这个Bean。@ConditionalOnMissingBean说明当容器中没有WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter实例时,将采用默认配置。@ConditionalOnWebApplication说明这必须是个Web应用,并且类型为servlet。
自定义配置
虽然Spring Boot提供了一些基本的自动配置,但是很多时候我们还是需要自己覆盖一些配置以满足需要。
以security为例,我们自定义配置类,需要继承抽象类 WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter ,并注入到容器即可
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true, securedEnabled = true)
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
}
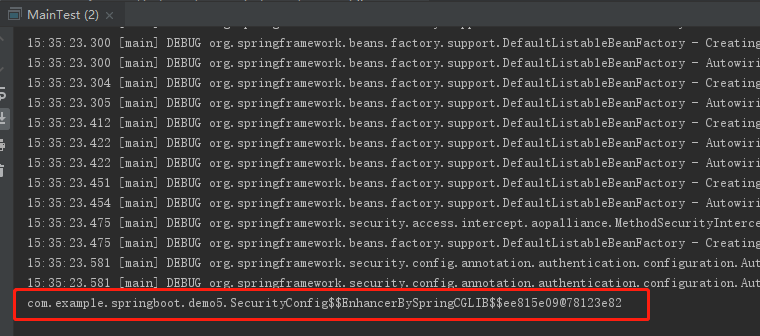
我们测试一下,看是否已经注入到容器
测试类:
public class MainTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SecurityConfig.class);
System.out.println(applicationContext.getBean(WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter.class));
}
}
结果证明已经注入到容器中:
版本
springboot版本:2.3.1.RELEASE
spring版本:5.2.7.RELEASE
源码分析
通过上面理论的描述,接下来我们分析Springboot相关源码,看springboot到底怎么实现的自动装配?
概述
我们先看一张图:
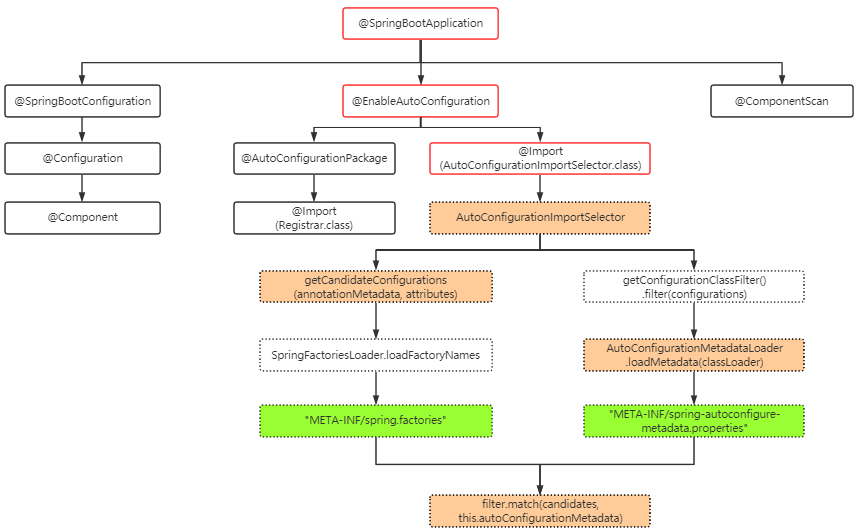
注解:
@SpringBootApplication:这是springboot最核心的注解,当然也是组合注解@EnableAutoConfiguration是自动装配的总开关。我们将以该注解入手,增强对自动配置的理解。@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)导入自动配置的ImportSelectot类。
核心类及方法:
AutoConfigurationImportSelector导入需要自动装配的类或Bean。getCandidateConfigurations获取所有组件的配置类。AutoConfigurationMetadataLoader.loadMetadata加载所有自动装配组件配置类的条件(@Conditional过滤条件)。filter.match(candidates, this.autoConfigurationMetadata)对各组件中全部配置类根据@Conditional进行条件过滤。
配置文件:
META-INF/spring.factories 存放该组件全部配置类的全路径名。
META-INF/spring-autoconfigure-metadata.properties 存储该组件装载配置类时的全部过滤条件。
源码细节
SpringBootApplication
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration // 开启自动装配开关
@ComponentScan(excludeFilters = { @Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class),
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) })
public @interface SpringBootApplication {
}
EnableAutoConfiguration
该注解起到打开自动装配总开关的作用。
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@AutoConfigurationPackage
// 导入selector,识别各组件中的AutoConfigutaion类并装载到容器中
@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)
public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration {
// 自动装配开关,默认true,可在application.properties中设置
String ENABLED_OVERRIDE_PROPERTY = "spring.boot.enableautoconfiguration";
// 不需要装载的bean
Class<?>[] exclude() default {};
// 不需要装载的bean
String[] excludeName() default {};
}
重点 AutoConfigurationImportSelector
该类实现ImportSelector接口,最重要的是实现selectImports方法,该方法的起到的作用是,根据配置文件(spring.factories),将需要注入到容器的bean注入到容器。
@Override
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
// 判断自动装配开关是否打开
if (!isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) {
return NO_IMPORTS;
}
// 获取所有需要装配的bean
AutoConfigurationEntry autoConfigurationEntry = getAutoConfigurationEntry(annotationMetadata);
return StringUtils.toStringArray(autoConfigurationEntry.getConfigurations());
}
首先我们看下,怎样判断自动装配开关的:
protected boolean isEnabled(AnnotationMetadata metadata) {
// 判断当前实例的class
if (getClass() == AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class) {
// 返回 spring.boot.enableautoconfiguration 的值,如果为null,返回true
// spring.boot.enableautoconfiguration 可在配置文件中配置,不配则为null
return getEnvironment().getProperty(EnableAutoConfiguration.ENABLED_OVERRIDE_PROPERTY, Boolean.class, true);
}
return true;
}
接下来,我们看如何获取需要装配的bean:
protected AutoConfigurationEntry getAutoConfigurationEntry(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
// 检查自动装配开关
if (!isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) {
return EMPTY_ENTRY;
}
// 获取EnableAutoConfiguration中的参数,exclude()/excludeName()
AnnotationAttributes attributes = getAttributes(annotationMetadata);
// 获取需要自动装配的所有配置类,读取META-INF/spring.factories
List<String> configurations = getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes);
// 去重,List转Set再转List
configurations = removeDuplicates(configurations);
// 从EnableAutoConfiguration的exclude/excludeName属性中获取排除项
Set<String> exclusions = getExclusions(annotationMetadata, attributes);
// 检查需要排除的类是否在configurations中,不在报错
checkExcludedClasses(configurations, exclusions);
// 从configurations去除exclusions
configurations.removeAll(exclusions);
// 对configurations进行过滤,剔除掉@Conditional条件不成立的配置类
configurations = getConfigurationClassFilter().filter(configurations);
// 把AutoConfigurationImportEvent绑定在所有AutoConfigurationImportListener子类实例上
fireAutoConfigurationImportEvents(configurations, exclusions);
// 返回(configurations, exclusions)组
return new AutoConfigurationEntry(configurations, exclusions);
}
可见selectImports()是AutoConfigurationImportSelector的核心方法
该方法的功能主要是以下三点:
- 获取
META-INF/spring.factories中EnableAutoConfiguration所对应的Configuration类列表 - 由
@EnableAutoConfiguration注解中的exclude/excludeName参数筛选一遍 - 再由私有内部类
ConfigurationClassFilter筛选一遍,即不满足@Conditional的配置类
读取配置文件
META-INF/spring-autoconfigure-metadata.properties:
在私有静态内部类ConfigurationClassFilter的构造器中初始化读取META-INF/spring-autoconfigure-metadata.properties,代码如下
ConfigurationClassFilter(ClassLoader classLoader, List<AutoConfigurationImportFilter> filters) {
this.autoConfigurationMetadata = AutoConfigurationMetadataLoader.loadMetadata(classLoader);
this.filters = filters;
}
AutoConfigurationMetadataLoader:
final class AutoConfigurationMetadataLoader {
protected static final String PATH = "META-INF/spring-autoconfigure-metadata.properties";
private AutoConfigurationMetadataLoader() {
}
static AutoConfigurationMetadata loadMetadata(ClassLoader classLoader) {
return loadMetadata(classLoader, PATH);
}
......
}
META-INF/spring.factories:
通过getCandidateConfigurations方法读取META-INF/spring.factories中配置类:
protected List<String> getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata, AnnotationAttributes attributes) {
// 加载所有META-INF/spring.factories中的配置类
List<String> configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(),
getBeanClassLoader());
Assert.notEmpty(configurations, "No auto configuration classes found in META-INF/spring.factories. If you "
+ "are using a custom packaging, make sure that file is correct.");
return configurations;
}
public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryType, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
String factoryTypeName = factoryType.getName();
return loadSpringFactories(classLoader).getOrDefault(factoryTypeName, Collections.emptyList());
}
// 该方法读取META-INF/spring.factories
private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
MultiValueMap<String, String> result = cache.get(classLoader);
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
try {
// FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION : META-INF/spring.factories
Enumeration<URL> urls = (classLoader != null ?
classLoader.getResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION) :
ClassLoader.getSystemResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION));
result = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>();
while (urls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = urls.nextElement();
UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(url);
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
for (Map.Entry<?, ?> entry : properties.entrySet()) {
String factoryTypeName = ((String) entry.getKey()).trim();
for (String factoryImplementationName : StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String) entry.getValue())) {
result.add(factoryTypeName, factoryImplementationName.trim());
}
}
}
cache.put(classLoader, result);
return result;
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load factories from location [" +
FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION + "]", ex);
}
}
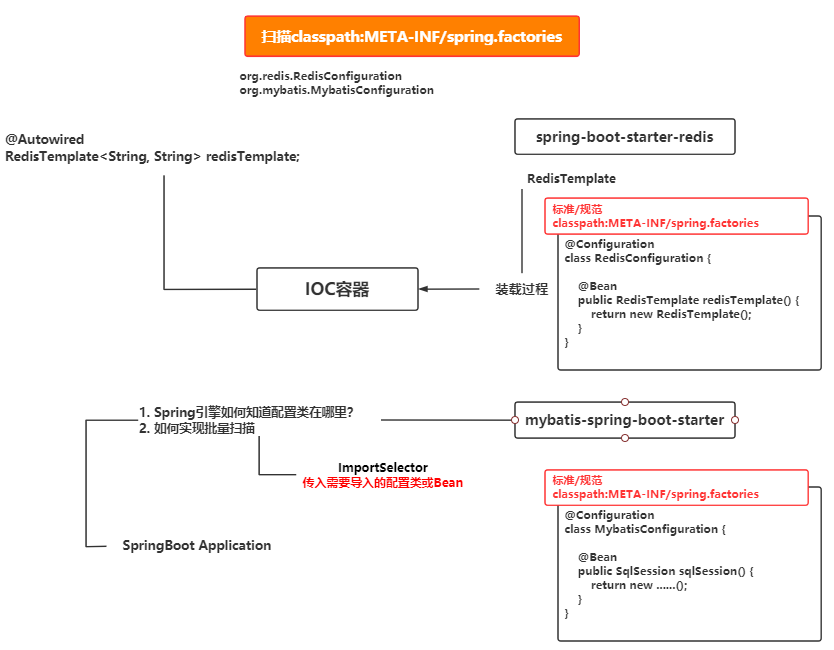
扩展
对于官方组件,是基于condition条件来决定对于类是否要自动装配,对于第三方组件,是采用spi机制 来实现扩展
- 官方包 spring-boot-starter-xxx
- 第三方包 xxx-spring-boot-starter
不论官方组件还是第三方组件都是通过以上机制进行自动装配。
Springboot的自动配置的核心:通过ImportSelector 实现批量导入各组件的配置类到IOC容器中。
知识延伸:
@Conditional 详解:juejin.cn/post/684490…
@Enable* 模块驱动详解:juejin.cn/post/684490…
ImportSelector 批量动态导入Bean详解:juejin.cn/post/684490…