点击蓝色 “达达前端” 关注我哦!
加个 “星标” ,每天一篇文章,一起学编程

登录注册,说说登录,需要用户名,用户名的提示内容为请输入用户名,密码的提示为8-18位不含特殊字符的数字、字母组合。还有一个点击按钮。
<view class="input-content">
<view class="input-item">
<text class="username">用户名</text>
<input v-model="query.username" placeholder="请输入用户名"/>
</view>
<view class="input-item">
<text class="password">密码</text>
<input v-model="query.password"
placeholder="8-18位不含特殊字符的数字、字母组合"
maxlength="20"
password />
</view>
</view
<button class="confirm-btn" @click="toLogin" >登录</button>
<html>
<head>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="index.css">
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
{{count}}
<button @click='increment'>+</button>
</div>
<script src="index.pack.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
import Vue from 'vue';
import Vuex from 'vuex';
Vue.use(Vuex);
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0
},
mutations: {
}
});
import { mapState } from 'vuex';
new Vue({
el: '#app',
store,
data: {
},
computed: mapState([
'count'
]),
});
vuex是专为vue.js应用程序开发的状态管理模式,它采用集中式存储管理应用的所有组件的状态,并以相应的规则状态以一种可预测的方式发生变化。
什么是状态管理模式?
new Vue({
// state
data () {
return {
count: 0
}
},
// view
template: `
<div>{{ count }}</div>
`,
// actions
methods: {
increment () {
this.count++
}
}
})
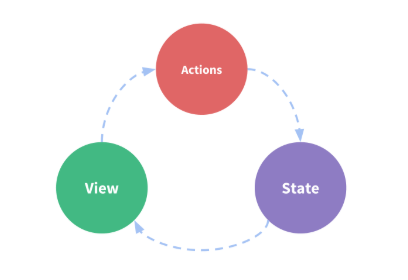
state为驱动应用的数据源,view为以声明方式将state映射到视图,actions为响应在view上的用户输入导致的状态变化。
当我们的应用遇到多个组件共享状态时,单向数据流的简洁性很容易被破坏。
第一,多个视图依赖于同一状态。
第二,来自不同的视图的行为需要变更同一状态。
第一种情况,传参的方法对于多层嵌套的组件将会非常繁琐,并且对于兄弟组件间的状态传递无能为力。
第二种情况,我们会采用父子组件直接引用或者通过事件来变更和同步状态的多份拷贝。
可以把组件的共享状态抽取出来,以一个全局单例模式管理。这样,组件树构成了一个巨大的“视图”,不管在树的哪个位置,任何组件都能获取状态或者触发行为。
通过定义和隔离状态管理中各种概念并通过强制规则维持视图和状态间的独立性。
vuex是专门为vue.js设计的状态管理库,以利用vue.js的细粒度数据响应机制来进行高效的状态更新。
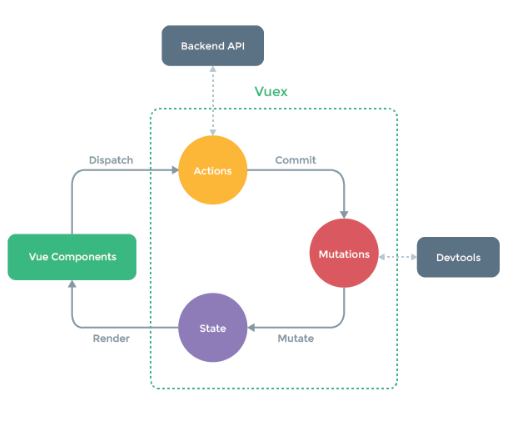
每个vuex应用的核心就是store仓库,store就是一个容器,包含着大部分的状态。
vuex的状态存储是响应式的,当vue组件从store中读取状态的时候,如果store中的状态发生变化,那么相应的组件也会相应地得到更新。
不能直接改变store中的状态,改变store中的状态的唯一途径就是显式地提交commit mutation,可以方便跟踪每一个状态的变化。
Store的认识
安装Vuex后,让我们来创建一个store。
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0
},
mutations: {
increment(state) {
state.count++
}
}
})
可以通过store.state来获取状态对象,然后通过store.commit方法触发状态的变更。
store.commit('increment');
console.log(store.state.count);
通过提交mutation的方式,而非直接改变store.state.count。
核心概念:State,Getter,Mutation,Action,Module。
State单一状态
<html>
<head>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="index.css">
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
{{ count }}
</div>
<script src="index.pack.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
import Vue from 'vue';
import Vuex from 'vuex';
Vue.use(Vuex);
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0
}
});
new Vue({
el: '#app',
store,
computed: {
count () {
return this.$store.state.count
}
}
});
单一状态树,用一个对象包含了全部的应用层级状态。
// 创建一个 Counter 组件
const Counter = {
template: `<div>{{ count }}</div>`,
computed: {
count () {
return store.state.count
}
}
}
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
// 把 store 对象提供给 “store” 选项,这可以把 store 的实例注入所有的子组件
store,
components: { Counter },
template: `
<div class="app">
<counter></counter>
</div>
`
})
通过在根实例总注册store,该store实例会注入根组件下的所有子组件中,且子组件能通过this.$store访问到。
const Counter = {
template: `<div>{{ count }}</div>`,
computed: {
count () {
return this.$store.state.count
}
}
}
mapState辅助函数
// 在单独构建的版本中辅助函数为 Vuex.mapState
import { mapState } from 'vuex'
export default {
// ...
computed: mapState({
// 箭头函数可使代码更简练
count: state => state.count,
// 传字符串参数 'count' 等同于 `state => state.count`
countAlias: 'count',
// 为了能够使用 `this` 获取局部状态,必须使用常规函数
countPlusLocalState (state) {
return state.count + this.localCount
}
})
}
当映射的计算属性的名称与 state 的子节点名称相同时。
computed: mapState([
// 映射 this.count 为 store.state.count
'count'
])
对象展开运算符
mapState函数返回的是一个对象。
computed: {
localComputed () { /* ... */ },
// 使用对象展开运算符将此对象混入到外部对象中
...mapState({
// ...
})
}
Getter
computed: {
doneTodosCount () {
return this.$store.state.todos.filter(todo => todo.done).length
}
}
getter的返回值会根据它的依赖被缓存起来,且只有当它的依赖值发生了改变才会被重新计算。
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
todos: [
{ id: 1, text: '...', done: true },
{ id: 2, text: '...', done: false }
]
},
getters: {
doneTodos: state => {
return state.todos.filter(todo => todo.done)
}
}
})
通过属性访问
Getter会暴露store.getters对象。
store.getters.doneTodos // -> [{ id: 1, text: '...', done: true }]
getters: {
// ...
doneTodosCount: (state, getters) => {
return getters.doneTodos.length
}
}
store.getters.doneTodosCount
computed: {
doneTodosCount () {
return this.$store.getters.doneTodosCount
}
}
通过方法访问
getters: {
// ...
getTodoById: (state) => (id) => {
return state.todos.find(todo => todo.id === id)
}
}
store.getters.getTodoById(2)
mapGetters辅助函数
mapGetters辅助函数仅仅是将store中的getter映射到局部计算属性。
import { mapGetters } from 'vuex'
export default {
// ...
computed: {
// 使用对象展开运算符将 getter 混入 computed 对象中
...mapGetters([
'doneTodosCount',
'anotherGetter',
// ...
])
}
}
mapGetters({
// 把 `this.doneCount` 映射为 `this.$store.getters.doneTodosCount`
doneCount: 'doneTodosCount'
})
vuex,vue本身自带有store模式,其实就是全局注册一个对象,实现数据共享,适合小型数据少的项目。
vuex的五大核心,state,getters,mutations,actions,module。
vuex四大辅助函数,mapState,mapGetters,mapMutations,mapActions。
vuex的工作流程
客户端操作事件,dispatch调用一个action。
对应的action处理参数,比如接口,逻辑操作,传值,commit的type类型,mutation介绍type类型触发对象的函数,修改state,state更新后中view视图在render的作用下重新渲染。
mapState和mpaGetter的使用只能在computed计算属性中。
mapMutations和mapActions使用的额时候只能在methods中调用。
<script>
import { mapState , mapMutations , mapActions , mapGetters } from 'vuex';
export default {
data(){
return{
}
},
computed:{
...mapState({
counts:(state) => state.count
}),
//mapState就等于下面这个
// counts(){
// return this.$store.state.count
// },
...mapGetters({
getternum:'doneTodos'
}),
//mapGetters就等于下面的这个
// getternum(){
// return this.$store.getters.doneTodos
// }
},
methods:{
...mapMutations({
addnum:'addNum'
}),
//mapMutations就等于下面的这个
// addnum1(){
// this.$store.commit('addNum')
// },
...mapActions({
actionnum:'actionNumAdd'
}),
//mapActions就等于下面的这个
// actionnum6(){
// this.$store.dispatch('actionNumAdd')
// }
}
}
</script>
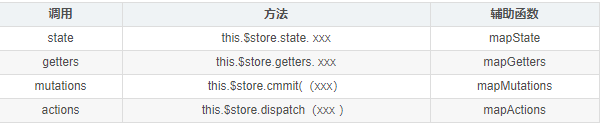
| 调用 | 方法 | 辅助函数 |
|---|---|---|
| state | this.$store.state. xxx | mapState |
| getters | this.$store.getters. xxx | mapGetters |
| mutations | this.$store.cmmit((xxx) | mapMutations |
| actions | this.$store.dispatch(xxx ) | mapActions |
states.js
const state = {
count:0
}
export default state
getter.js
const getters = {
docount:(state,getters) => {
return state.counts
}
}
export default getters
Mutation
更改vuex的store中的状态的唯一方法是提交mutation。每个mutation都有一个字符串的事件类型和一个回调函数。
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 1
},
mutations: {
increment (state) {
// 变更状态
state.count++
}
}
})
store.commit('increment')
提交载荷
// ...
mutations: {
increment (state, n) {
state.count += n
}
}
store.commit('increment', 10)
载荷大多数是一个对象
// ...
mutations: {
increment (state, payload) {
state.count += payload.amount
}
}
store.commit('increment', {
amount: 10
})
对象风格的提交
store.commit({
type: 'increment',
amount: 10
})
mutations: {
increment (state, payload) {
state.count += payload.amount
}
}
对象展开运算符
state.obj = { ...state.obj, newProp: 123 }
在组件中提交Mutation
this.$store.commit('xxx')
使用 mapMutations 辅助函数
将组件中的 methods 映射为 store.commit 调用
import { mapMutations } from 'vuex'
export default {
// ...
methods: {
...mapMutations([
'increment', // 将 `this.increment()` 映射为 `this.$store.commit('increment')`
// `mapMutations` 也支持载荷:
'incrementBy' // 将 `this.incrementBy(amount)` 映射为 `this.$store.commit('incrementBy', amount)`
]),
...mapMutations({
add: 'increment' // 将 `this.add()` 映射为 `this.$store.commit('increment')`
})
}
}
在vuex中,mutation都是同步事务:
store.commit('increment')
// 任何由 "increment" 导致的状态变更都应该在此刻完成。
Action,action提交的是mutation,而不是直接变更状态。action可以包含任意异步操作。
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0
},
mutations: {
increment (state) {
state.count++
}
},
actions: {
increment (context) {
context.commit('increment')
}
}
})
actions: {
increment ({ commit }) {
commit('increment')
}
}
分发action
action通过store.dispatch分发触发:
store.dispatch('increment')
可以在action内部执行异步操作。
actions: {
incrementAsync ({ commit }) {
setTimeout(() => {
commit('increment')
}, 1000)
}
}
actions支持载荷方式和对象方式:
// 以载荷形式分发
store.dispatch('incrementAsync', {
amount: 10
})
// 以对象形式分发
store.dispatch({
type: 'incrementAsync',
amount: 10
})
在组件中分发action
this.$store.dispatch('xxx') 分发 action
使用 mapActions 辅助函数将组件的 methods 映射为 store.dispatch 调用
import { mapActions } from 'vuex'
export default {
// ...
methods: {
...mapActions([
'increment', // 将 `this.increment()` 映射为 `this.$store.dispatch('increment')`
// `mapActions` 也支持载荷:
'incrementBy' // 将 `this.incrementBy(amount)` 映射为 `this.$store.dispatch('incrementBy', amount)`
]),
...mapActions({
add: 'increment' // 将 `this.add()` 映射为 `this.$store.dispatch('increment')`
})
}
}
module
vuex将store分割成模块,每个模块拥有自己的state,mutation,action,getter。
const moduleA = {
state: { ... },
mutations: { ... },
actions: { ... },
getters: { ... }
}
const moduleB = {
state: { ... },
mutations: { ... },
actions: { ... }
}
const store = new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
a: moduleA,
b: moduleB
}
})
store.state.a // -> moduleA 的状态
store.state.b // -> moduleB 的状态
login.vue
<view class="input-content">
<view class="input-item">
<text class="tit">用户名</text>
<input v-model="query.username" placeholder="请输入用户名" />
</view>
<view class="input-item">
<text class="tit">密码</text>
<input v-model="query.password" placeholder="8-18位不含特殊字符的数字、字母组合" maxlength="20"
password @confirm="toLogin" />
</view>
</view>
<button class="confirm-btn" @click="toLogin" :disabled="logining">登录</button>
import {
mapMutations
}
from 'vuex';
mobile: '', // 手机号
password: '', // 密码
logining: false ,
...mapMutations(['login']),
toLogin() {
this.logining = true;
loginApi(this.query).then(res => {
if(res.data.code === 1) {
this.$api.msg(res.data.msg)
...
}).catch(res => {
this.logining = false;
})
}
store
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: { //全局变量定义处
hasLogin: false, //用户是否登录
userInfo: {}, //用于存放用户账户数据
},
mutations: { //全局方法定义处
login(state, provider) {
},
logout(state) {
},
},
actions: {
}
})
export default store
☆ END ☆
参考文档来源:vuex官方文档https://vuex.vuejs.org/zh/
加群前端交流群
扫码,备注 加群-技术领域-城市-姓名

目前文章内容涉及前端知识点,囊括Vue、JavaScript、数据结构与算法、实战演练、Node全栈一线技术,紧跟业界发展步伐,将 Web前端领域、网络原理等通俗易懂的呈现给小伙伴。更多内容请到达达前端网站进行学习:www.dadaqianduan.cn
推荐阅读
3、一篇文章把你带入到JavaScript中的闭包与高级函数
觉得本文对你有帮助?请分享给更多人
关注「达达前端」加星标,提升前端技能
这是一个有质量,有态度的公众号