最后更新时间
2020.02.15 15时
背景
在 Android 开发工作中,内存泄露一直是让人比较头疼的问题。首先内存泄露并不是一个 Java 异常,所以我们并不能实时感知到它,一般只有等到内存溢出的时候,我们才会去排除是否发生了内存泄露问题。而往往导致抛异常的代码并不是内存泄露的凶手,而只是压死骆驼的最后一根稻草而已,这是第一个问题。第二个问题则是,当我们想要分析内存问题时,首先需要先 dump 内存快照,通常是以 .hprof 结尾的文件,接着再使用 MAT 等内存分析工具去检测大内存可疑对象,分析对象到 GC Roots 节点的可达性等等。整个流程相对繁琐,这时候我们可能会考虑是否有自动化工具,来帮助我们去分析那些常见的内存泄露场景呢。
LeakCanary
LeakCanary 就是为了解决以上问题而诞生的。2019 年 11 月 的时候,LeakCanary2 正式版发布,和 LeakCanary1 相比,LeakCanary2 有以下改动:
其中,将 Heap 分析模块作为一个独立的模块,是一个非常不错的改动。这意味着,可以基于 Shark 来做很多有意思的事情,比如,用于线上分析或者开发一个"自己"的 LeakCanary。
整体架构
在分析源码之前,我们先看 LeakCanary 的整体结构,这有助于我们对项目整体设计上有一定理解。LeakCanary2 有以下几个模块:
-
leakcanary-android
集成入口模块,提供 LeakCanary 安装,公开 API 等能力
-
leakcanary-android-core
核心模块
-
leakcanary-android-process
和 leakcanary-android 一样,区别是会在单独的进程进行分析
-
leakcanary-android-instrumentation
用于 Android Test 的模块
-
leakcanary-object-watcher-android,leakcanary-object-watcher-android-androidx,leakcanary-watcher-android-support-fragments
对象实例观察模块,在 Activity,Fragment 等对象的生命周期中,注册对指定对象实例的观察,有 Activity,Fragment,Fragment View,ViewModel 等
-
shark-android
提供特定于 Android 平台的分析能力。例如设备的信息,Android 版本,已知的内存泄露问题等
-
shark,shark-test
hprof 文件解析与分析的入口模块,还有对应的 Test 模块
-
shark-graph
分析堆中对象的关系图模块
-
shark-hprof,shark-hprof-test
解析 hprof 文件模块,还有对应的 Test 模块
-
shark-log
日志模块
-
shark-cli
shark-android 的 cli 版本
集成方式
首先,我们从集成方式入手,LeakCanary1 的依赖为:
dependencies {
debugImplementation 'com.squareup.leakcanary:leakcanary-android:1.6.3'
releaseImplementation 'com.squareup.leakcanary:leakcanary-android-no-op:1.6.3'
}
接着在 Application 中调用 LeakCanary.install() 方法。而 LeakCanary2 集成则要简单不少,只需要增加以下依赖即可:
dependencies {
debugImplementation 'com.squareup.leakcanary:leakcanary-android:2.2'
}
也就是说 LeakCanary2 实现了自动调用 install() 方法,实现方式可能大部分人都能猜到,就是使用的 ContentProvider,相关代码位于 leakcanary-object-watcher-android 模块中的 AppWatcherInstaller.kt 中。
AppWatcherInstaller 继承 ContentProvider,重写了 onCreate() 方法,这里利用的是,注册在 Manifest 文件中的 ContentProvider,会在应用启动时,由 ActivityThread 创建并初始化。
override fun onCreate(): Boolean {
val application = context!!.applicationContext as Application
InternalAppWatcher.install(application)
return true
}
AppWatcherInstaller 有两个实现类,一个是 MainProcess,当我们使用 leakcanary-android 模块时,会默认使用这个,表示在当前 App 进程中使用 LeakCanary。另外一个类为 LeakCanaryProcess,当使用 leakcanary-android-process 模块代替 leakcanary-android 模块时,则会使用这个类,我们可以看下 leakcanary-android-process 的 Manifest 文件:
这里利用的 leakcanary-android-process Manifest 优先级要高于 leakcanary-object-watcher-android
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.squareup.leakcanary">
<application>
<service
android:name="leakcanary.internal.HeapAnalyzerService"
android:exported="false"
android:process=":leakcanary" />
<provider
android:name="leakcanary.internal.AppWatcherInstaller$LeakCanaryProcess"
android:authorities="${applicationId}.leakcanary-process.installer"
android:process=":leakcanary"
android:exported="false"/>
</application>
</manifest>
可以看到,HeapAnalyzerService 和 LeakCanaryProcess 都会在运行在 :leakcanary 进程,关于 HeapAnalyzerService 的作用,我们后面会讲到。
这里有个需要注意的是,如果使用 LeakCanaryProcess,默认会禁用 Watcher 功能,这个也很好理解,处于不同进程,是没办法观察到 APP 进程的对象。
internal class LeakCanaryProcess : AppWatcherInstaller() {
override fun onCreate(): Boolean {
super.onCreate()
AppWatcher.config = AppWatcher.config.copy(enabled = false)
return true
}
}
AppWatcher
Watcher 功能的入口位于 InternalAppWatcher.install() 方法中,这个方法的调用时机则是我们上面说到的 AppWatcherInstaller.onCreate() 中。
fun install(application: Application) {
ActivityDestroyWatcher.install(application, objectWatcher, configProvider)
FragmentDestroyWatcher.install(application, objectWatcher, configProvider)
onAppWatcherInstalled(application)
}
这里主要做了两件事,首先是 Activity 和 Fragment 对象的注册观察,这里我们以 ActivityDestroyWatcher 为例,Fragment 的处理也是类似的。
ActivityDestroyWatcher
fun install(
application: Application,
objectWatcher: ObjectWatcher,
configProvider: () -> Config
) {
val activityDestroyWatcher =
ActivityDestroyWatcher(objectWatcher, configProvider)
application.registerActivityLifecycleCallbacks(activityDestroyWatcher.lifecycleCallbacks)
}
调用 registerActivityLifecycleCallbacks() 方法注册 Activity 生命周期回调。
override fun onActivityDestroyed(activity: Activity) {
if (configProvider().watchActivities) {
objectWatcher.watch(
activity, "${activity::class.java.name} received Activity#onDestroy() callback"
)
}
}
在每个 Activity.onDestory 回调中,将每个 Activity 对象加到观察列表中。
private val watchedObjects = mutableMapOf<String, KeyedWeakReference>()
private val queue = ReferenceQueue<Any>()
@Synchronized fun watch(
watchedObject: Any,
description: String
) {
if (!isEnabled()) {
return
}
removeWeaklyReachableObjects()
val key = UUID.randomUUID()
.toString()
val watchUptimeMillis = clock.uptimeMillis()
val reference =
KeyedWeakReference(watchedObject, key, description, watchUptimeMillis, queue)
watchedObjects[key] = reference
checkRetainedExecutor.execute {
moveToRetained(key)
}
}
private fun removeWeaklyReachableObjects() {
var ref: KeyedWeakReference?
do {
ref = queue.poll() as KeyedWeakReference?
if (ref != null) {
watchedObjects.remove(ref.key)
}
} while (ref != null)
}
首先我们要知道 KeyedWeakReference 继承于 WeakReference,弱引用是不会阻止 GC 回收对象的,同时我们可以在构造函数中传递一个 ReferenceQueue,用于对象被 GC 后存放的队列。
class KeyedWeakReference(
referent: Any,
val key: String,
val description: String,
val watchUptimeMillis: Long,
referenceQueue: ReferenceQueue<Any>
) : WeakReference<Any>
所以 removeWeaklyReachableObjects() 方法的作用就是将已经被 GC 的对象从 watchedObjects 集合中删除。
当我们调用 watch() 方法时,先清理已经被 GC 的对象,接着将需要观察的对象,存储为一个 KeyedWeakReference 的弱引用对象,再存放到 watchedObjects 集合中,最后使用 checkRetainedExecutor 安排一次 moveToRetained 任务。
checkRetainedExecutor 是使用 Handler 实现,默认延迟 5s 执行任务。
val watchDurationMillis: Long = TimeUnit.SECONDS.toMillis(5)
private val checkRetainedExecutor = Executor {
mainHandler.postDelayed(it, AppWatcher.config.watchDurationMillis)
}
接下来,我们再来看下 moveToRetained() 的代码:
@Synchronized private fun moveToRetained(key: String) {
removeWeaklyReachableObjects()
val retainedRef = watchedObjects[key]
if (retainedRef != null) {
retainedRef.retainedUptimeMillis = clock.uptimeMillis()
onObjectRetainedListeners.forEach { it.onObjectRetained() }
}
}
同样的,先调用一次 removeWeaklyReachableObjects() 删除已经 GC 的对象,那么剩下的对象就可以认为是被保留(没办法 GC)的对象,会调通知事件。
onAppWatcherInstalled
在 InternalAppWatcher.install() 方法的最后,还有一个 onAppWatcherInstalled 的调用,它是一个方法对象,在 Kotlin 中一切皆对象,包括方法,它的赋值在 init 块中:
init {
val internalLeakCanary = try {
val leakCanaryListener = Class.forName("leakcanary.internal.InternalLeakCanary")
leakCanaryListener.getDeclaredField("INSTANCE")
.get(null)
} catch (ignored: Throwable) {
NoLeakCanary
}
@kotlin.Suppress("UNCHECKED_CAST")
onAppWatcherInstalled = internalLeakCanary as (Application) -> Unit
}
这段代码对不熟悉 Kotlin 的小伙伴来说可能有点绕,首先 internalLeakCanary 是一个方法对象,它的方法签名转化为 Java 代码为:
void invoke(Application) {
}
而这个对象的值是通过反射获取的 InternalLeakCanary.INSTANCE 这是一个单例对象。InternalLeakCanary 位于 leakcanary-android-core 模块,这也是需要反射的原因,这样的处理值得商榷。
当调用 onAppWatcherInstalled() 方法时,实际会调用 InternalLeakCanary.invoke() 方法:
override fun invoke(application: Application) {
this.application = application
AppWatcher.objectWatcher.addOnObjectRetainedListener(this)
val heapDumper = AndroidHeapDumper(application, leakDirectoryProvider)
val gcTrigger = GcTrigger.Default
val configProvider = { LeakCanary.config }
val handlerThread = HandlerThread(LEAK_CANARY_THREAD_NAME)
handlerThread.start()
val backgroundHandler = Handler(handlerThread.looper)
heapDumpTrigger = HeapDumpTrigger(
application, backgroundHandler, AppWatcher.objectWatcher, gcTrigger, heapDumper,
configProvider
)
application.registerVisibilityListener { applicationVisible ->
this.applicationVisible = applicationVisible
heapDumpTrigger.onApplicationVisibilityChanged(applicationVisible)
}
registerResumedActivityListener(application)
addDynamicShortcut(application)
disableDumpHeapInTests()
}
这里做的事情比较多,首先是 addOnObjectRetainedListener() 方法,这里会注册一个 OnObjectRetainedListener 事件,也就是我们上面说到的在 moveToRetained() 方法中的回调事件。
AndroidHeapDumper 则是通过调用 Debug.dumpHprofData() 方法从虚拟机中 dump hprof 文件。
GcTrigger 通过调用 Runtime.getRuntime().gc() 方法触发虚拟机进行 GC 操作。
HeapDumpTrigger 管理触发 Heap Dump 的逻辑,有两个地方会触发 Heap Dump:
-
保留对象超过阙值
这个阙值默认为 5(应用可见的情况下),可以通过
Config配置:val retainedVisibleThreshold: Int = 5当
ObjectWatcher回调onObjectRetained()方法时,HeapDumpTrigger.onObjectRetained()方法会被调用:fun onObjectRetained() { scheduleRetainedObjectCheck( reason = "found new object retained", rescheduling = false ) } private fun scheduleRetainedObjectCheck( reason: String, rescheduling: Boolean, delayMillis: Long = 0L ) { val checkCurrentlyScheduledAt = checkScheduledAt if (checkCurrentlyScheduledAt > 0) { // 同时只会有一个任务 val scheduledIn = checkCurrentlyScheduledAt - SystemClock.uptimeMillis() return } checkScheduledAt = SystemClock.uptimeMillis() + delayMillis backgroundHandler.postDelayed({ checkScheduledAt = 0 checkRetainedObjects(reason) }, delayMillis) } private fun checkRetainedObjects(reason: String) { val config = configProvider() if (!config.dumpHeap) { return } var retainedReferenceCount = objectWatcher.retainedObjectCount if (retainedReferenceCount > 0) { // 先执行一次 GC gcTrigger.runGc() retainedReferenceCount = objectWatcher.retainedObjectCount } // 检测当前保留对象数量 if (checkRetainedCount(retainedReferenceCount, config.retainedVisibleThreshold)) return if (!config.dumpHeapWhenDebugging && DebuggerControl.isDebuggerAttached) { // 默认 debug 时不执行,重新安排到 20s 后 scheduleRetainedObjectCheck( reason = "debugger is attached", rescheduling = true, delayMillis = WAIT_FOR_DEBUG_MILLIS ) return } val now = SystemClock.uptimeMillis() val elapsedSinceLastDumpMillis = now - lastHeapDumpUptimeMillis if (elapsedSinceLastDumpMillis < WAIT_BETWEEN_HEAP_DUMPS_MILLIS) { // 60s 内只会执行一次,重新安排 scheduleRetainedObjectCheck( reason = "previous heap dump was ${elapsedSinceLastDumpMillis}ms ago (< ${WAIT_BETWEEN_HEAP_DUMPS_MILLIS}ms)", rescheduling = true, delayMillis = WAIT_BETWEEN_HEAP_DUMPS_MILLIS - elapsedSinceLastDumpMillis ) return } dismissRetainedCountNotification() // 执行 dump heap dumpHeap(retainedReferenceCount, retry = true) } private fun checkRetainedCount( retainedKeysCount: Int, retainedVisibleThreshold: Int ): Boolean { val countChanged = lastDisplayedRetainedObjectCount != retainedKeysCount lastDisplayedRetainedObjectCount = retainedKeysCount if (retainedKeysCount == 0) { // 没有保留对象 return true } if (retainedKeysCount < retainedVisibleThreshold) { // 低于阙值 if (applicationVisible || applicationInvisibleLessThanWatchPeriod) { // 当前应用可见,或者不可见时间间隔少于 5s,重新安排到 2s 后 scheduleRetainedObjectCheck( reason = "found only $retainedKeysCount retained objects (< $retainedVisibleThreshold while app visible)", rescheduling = true, delayMillis = WAIT_FOR_OBJECT_THRESHOLD_MILLIS ) return true } } return false }上面的代码稍微有点长,所以在关键代码处添加了注释。在执行 heap dump 之前,需要处理几种情况,比如当前是不是处于调试模式,距离上一次执行有没有超过 60s,当前应用是否处于可见状态等等,最终执行的方法是
dumpHeap():private fun dumpHeap( retainedReferenceCount: Int, retry: Boolean ) { val heapDumpFile = heapDumper.dumpHeap() // 因为这些对象我们已经 dump 出来分析了,所以没必要保留它们了 objectWatcher.clearObjectsWatchedBefore(heapDumpUptimeMillis) HeapAnalyzerService.runAnalysis(application, heapDumpFile) } // ObjectWatcher.kt @Synchronized fun clearObjectsWatchedBefore(heapDumpUptimeMillis: Long) { val weakRefsToRemove = watchedObjects.filter { it.value.watchUptimeMillis <= heapDumpUptimeMillis } weakRefsToRemove.values.forEach { it.clear() } watchedObjects.keys.removeAll(weakRefsToRemove.keys) }首先调用
HeapDumper.dumpHeap()获取 hprof 文件,接着调用ObjectWatcher.clearObjectsWatchedBefore()方法清理,最后调用HeapAnalyzerService.runAnalysis()进行分析。
小结
从 ObjectWatcher 保存弱引用对象,再到 HeapDumpTrigger 触发 heap dump,整个过程是非常清晰的。
HeapAnalyzerService
HeapAnalyzerService 是继承于 IntentService,调用 runAnalysis() 方法最终会调用到 analyzeHeap() 方法:
private fun analyzeHeap(
heapDumpFile: File,
config: Config
): HeapAnalysis {
val heapAnalyzer = HeapAnalyzer(this)
val proguardMappingReader = try {
ProguardMappingReader(assets.open(PROGUARD_MAPPING_FILE_NAME))
} catch (e: IOException) {
null
}
return heapAnalyzer.analyze(
heapDumpFile = heapDumpFile,
leakingObjectFinder = config.leakingObjectFinder,
referenceMatchers = config.referenceMatchers,
computeRetainedHeapSize = config.computeRetainedHeapSize,
objectInspectors = config.objectInspectors,
metadataExtractor = config.metadataExtractor,
proguardMapping = proguardMappingReader?.readProguardMapping()
)
}
proguardMappingReader 是用于处理代码混淆的,支持在测试版本打开代码混淆开关,PROGUARD_MAPPING_FILE_NAME 表示 Mapping 文件,这个文件在 leakcanary-deobfuscation-gradle-plugin 模块处理的,具体的可以看 CopyObfuscationMappingFileTask。
HeapAnalyzer.analyze() 这个方法的作用是:从 hprof 文件中搜索泄露对象,然后计算它们到 GC Roots 的最短路径。
Hprof.open(heapDumpFile)
.use { hprof ->
val graph = HprofHeapGraph.indexHprof(hprof, proguardMapping)
val helpers =
FindLeakInput(graph, referenceMatchers, computeRetainedHeapSize, objectInspectors)
helpers.analyzeGraph(
metadataExtractor, leakingObjectFinder, heapDumpFile, analysisStartNanoTime
)
}
解析 hprof 文件
首先,通过调用 Hprof.open() 读取 hprof 文件:
fun open(hprofFile: File): Hprof {
val fileLength = hprofFile.length()
if (fileLength == 0L) {
throw IllegalArgumentException("Hprof file is 0 byte length")
}
val inputStream = hprofFile.inputStream()
val channel = inputStream.channel
val source = Okio.buffer(Okio.source(inputStream))
val endOfVersionString = source.indexOf(0)
val versionName = source.readUtf8(endOfVersionString)
val hprofVersion = supportedVersions[versionName]
// Skip the 0 at the end of the version string.
source.skip(1)
val identifierByteSize = source.readInt()
// heap dump timestamp
val heapDumpTimestamp = source.readLong()
val byteReadCount = endOfVersionString + 1 + 4 + 8
val reader = HprofReader(source, identifierByteSize, byteReadCount)
return Hprof(
channel, source, reader, heapDumpTimestamp, hprofVersion, fileLength
)
}
关于 hprof 文件
hprof 是由 JVM TI Agent HPROF 生成的一种二进制文件,关于 hprof 文件格式可以看这里。
hprof 文件可以分为以下几个部分:
header
header 中有以下三个部分组成:
文件格式名和版本号
JDK 1.6 的值为 "JAVA PROFILE 1.0.2",在此之前还有 "JAVA PROFILE 1.0" 和 “JAVA PROFILE 1.0.1”,如果是 Android 平台的话,这个值为 "JAVA PROFILE 1.0.3",这也是为什么 MAT 不支持直接解析 Android 平台生成的 hprof 文件了。
identifiers
4 字节,表示 ID 的大小,它的值可能为 4 或者 8,表示一个 ID 需要用 4 字节或者 8 字节来表示。
时间戳
高位 4 字节 + 低位 4 字节
records
record 表示文件中记录的信息,每个 record 都由以下 4 个部分组成:
tag
1 字节,表示 record 的类型,支持的值可以看文档。
time
4 字节,表示 record 的时间戳。
length
4 字节,表示 body 的字节长度。
body
表示 record 中存储的数据。
JVM TI(JVM tool interface)表示虚拟机工具接口,用于提供查询和控制虚拟机中运行的程序。
Agent 表示代理程序,用于调用 JVM TI 的,会运行在 JVM 的进程中,一般通过
java -agentlib或java -agentpath启动。
在了解完 hprof 文件的格式后,我们再来看 LeakCanary 的解析 hprof 文件的代码,同样的,先依次读取 versionName、identifierByteSize、heapDumpTimestamp 后,再创建一个 HprofReader 用于读取 records。HprofReader 的工作方式也是类似的,根据 tag 的值去读取不同的 record,这里我们以 "STRING IN UTF8" 为例:
when (tag) {
STRING_IN_UTF8 -> {
if (readStringRecord) {
val recordPosition = position
val id = readId()
val stringLength = length - identifierByteSize
val string = readUtf8(stringLength)
val record = StringRecord(id, string)
listener.onHprofRecord(recordPosition, record)
} else {
skip(length)
}
}
}
生成 heap graph
HeapGraph 用于表示 heap 中的对象关系图,通过调用 HprofHeapGraph.indexHprof() 生成:
fun indexHprof(
hprof: Hprof,
proguardMapping: ProguardMapping? = null,
indexedGcRootTypes: Set<KClass<out GcRoot>> = setOf(
JniGlobal::class,
JavaFrame::class,
JniLocal::class,
MonitorUsed::class,
NativeStack::class,
StickyClass::class,
ThreadBlock::class,
ThreadObject::class,
JniMonitor::class
)
): HeapGraph {
val index = HprofInMemoryIndex.createReadingHprof(hprof, proguardMapping, indexedGcRootTypes)
return HprofHeapGraph(hprof, index)
}
indexedGcRootTypes 表示我们要收集的 GC Roots 节点,可以作为 GC Roots 节点的有以下对象:
// Traditional.
HPROF_ROOT_UNKNOWN = 0xFF,
// native 中的全局变量
HPROF_ROOT_JNI_GLOBAL = 0x01,
// native 中的局部变量
HPROF_ROOT_JNI_LOCAL = 0x02,
// java 中的局部变量
HPROF_ROOT_JAVA_FRAME = 0x03,
// native 中的入参和出参
HPROF_ROOT_NATIVE_STACK = 0x04,
// 系统类
HPROF_ROOT_STICKY_CLASS = 0x05,
// 活动线程引用的对象
HPROF_ROOT_THREAD_BLOCK = 0x06,
// 调用 wait() 或者 notify(),或者 synchronized 的对象
HPROF_ROOT_MONITOR_USED = 0x07,
// 活动线程
HPROF_ROOT_THREAD_OBJECT = 0x08,
// Android.
// 调用 String.intern() 的对象
HPROF_ROOT_INTERNED_STRING = 0x89,
// 等待 finalizer 调用的对象
HPROF_ROOT_FINALIZING = 0x8a, // Obsolete.
// 用于连接 debugger 的对象
HPROF_ROOT_DEBUGGER = 0x8b,
// 未知
HPROF_ROOT_REFERENCE_CLEANUP = 0x8c, // Obsolete.
// 未知
HPROF_ROOT_VM_INTERNAL = 0x8d,
// 未知
HPROF_ROOT_JNI_MONITOR = 0x8e,
// 不可达,但不是 GC Root
HPROF_UNREACHABLE = 0x90, // Obsolete.
上面的是 JVM 定义的,下面的是 Android 平台特有的,具体可以看 hprof.cc。
虽然存在不少 GC Roots 节点,但 LeakCanary 只选取了部分:
-
HPROF_ROOT_JNI_GLOBAL
native 中的全局变量
-
HPROF_ROOT_JAVA_FRAME
java 中的局部变量
-
HPROF_ROOT_JNI_LOCAL
native 中的局部变量
-
HPROF_ROOT_MONITOR_USED
调用 wait() 或者 notify(),或者 synchronized 的对象
-
HPROF_ROOT_NATIVE_STACK
native 中的入参和出参
-
HPROF_ROOT_STICKY_CLASS
系统类
-
HPROF_ROOT_THREAD_BLOCK
活动线程引用的对象
-
HPROF_ROOT_THREAD_OBJECT
活动线程
-
HPROF_ROOT_JNI_MONITOR
未知,可能是 native 中的同步对象
接着会从 hprof 文件中读取 records,读取原理可以参考 hprof 文件格式。这里有个小细节,LeakCanary 只会读取以下几种类型的 record:
-
STRING IN UTF8
0x01,UTF8 格式的字符串
-
LOAD CLASS
0x02,虚拟机中加载的类
-
HEAP DUMP 中的 CLASS DUMP
0x0C 和 0x20,dump 出来内存中的类实例
hprof 1.0.2 版本会用 HEAP DUMP SEGMENT 0x1C 作用是一样的
-
HEAP DUMP 中的 INSTANCE DUMP
0x0C 和 0x21,dump 出来内存中的对象实例
-
HEAP DUMP 中的 OBJECT ARRAY DUMP
0x0C 和 0x22,dump 出来内存中的对象数组实例
-
HEAP DUMP 中的 PRIMITIVE ARRAY DUMP
0x0C 和 0x23,dump 出来内存中的原始类型数组实例
-
HEAP 中 GC Roots
这里包括了上面定义的所有 GC Roots 对象实例
查询泄露对象
在生成 heap graph 后,我们就可以根据它,来获取泄露对象的 objectIds:
// FindLeakInput.analyzeGraph()
val leakingObjectIds = leakingObjectFinder.findLeakingObjectIds(graph)
LeakingObjectFinder 用于查询泄露对象,它的实现有两个:KeyedWeakReferenceFinder 和 FilteringLeakingObjectFinder,默认为 KeyedWeakReferenceFinder,即通过 KeyedWeakReference 引用的对象,关于 KeyedWeakReference 的作用我们在 AppWatcher 那里有说到。
internal fun findKeyedWeakReferences(graph: HeapGraph): List<KeyedWeakReferenceMirror> {
return graph.context.getOrPut(KEYED_WEAK_REFERENCE.name) {
val addedToContext: List<KeyedWeakReferenceMirror> = graph.instances
.filter { instance ->
val className = instance.instanceClassName
className == "leakcanary.KeyedWeakReference" || className == "com.squareup.leakcanary.KeyedWeakReference"
}
.map {
KeyedWeakReferenceMirror.fromInstance(
it, heapDumpUptimeMillis
)
}
.filter { it.hasReferent }
.toList()
graph.context[KEYED_WEAK_REFERENCE.name] = addedToContext
addedToContext
}
}
KeyedWeakReferenceFinder 通过过滤 heap dump 中的所有 KeyedWeakReference 实例,来获取泄露对象实例。
而 FilteringLeakingObjectFinder 则是用于我们自定义的泄露对象判断逻辑:
override fun findLeakingObjectIds(graph: HeapGraph): Set<Long> {
return graph.objects
.filter { heapObject ->
filters.any { filter ->
filter.isLeakingObject(heapObject)
}
}
.map { it.objectId }
.toSet()
}
生成泄露对象报告
LeakCanary 定义了两个泄露类型:ApplicationLeak 和 LibraryLeak:
-
ApplicationLeak
表示应用本身导致内存泄露
-
LibraryLeak
表示依赖库导致的内存泄露,例如 Android Framework 等
以上两种泄露都是通过调用 FindLeakInput.findLeaks() 方法来获取的:
private fun FindLeakInput.findLeaks(leakingObjectIds: Set<Long>): Pair<List<ApplicationLeak>, List<LibraryLeak>> {
val pathFinder = PathFinder(graph, listener, referenceMatchers)
val pathFindingResults =
pathFinder.findPathsFromGcRoots(leakingObjectIds, computeRetainedHeapSize)
return buildLeakTraces(pathFindingResults)
}
查询泄露对象到 GC Roots 的路径
这是通过 PathFinder.findPathsFromGcRoots() 方法实现的:
fun findPathsFromGcRoots(
leakingObjectIds: Set<Long>,
computeRetainedHeapSize: Boolean
): PathFindingResults {
val sizeOfObjectInstances = determineSizeOfObjectInstances(graph)
val state = State(leakingObjectIds, sizeOfObjectInstances, computeRetainedHeapSize)
return state.findPathsFromGcRoots()
}
private fun State.findPathsFromGcRoots(): PathFindingResults {
enqueueGcRoots()
// 省略
return PathFindingResults(shortestPathsToLeakingObjects, dominatedObjectIds)
}
State.findPathsFromGcRoots() 的代码有点长,我们一点点分析。
首先是 enqueueGcRoots() 方法,它的作用是将所有 GC Roots 节点放入到队列中:
private fun State.enqueueGcRoots() {
// 将 GC Roots 进行排序
// 排序是为了确保 ThreadObject 在 JavaFrames 之前被访问,这样可以通过 ThreadObject.threadsBySerialNumber 获取它的线程信息
val gcRoots = sortedGcRoots()
// 存储线程名称
val threadNames = mutableMapOf<HeapInstance, String>()
// 存储线程的 SerialNumber,可以通过 SerialNumber 访问对应的线程信息
val threadsBySerialNumber = mutableMapOf<Int, Pair<HeapInstance, ThreadObject>>()
gcRoots.forEach { (objectRecord, gcRoot) ->
if (computeRetainedHeapSize) {
// 计算泄露对象而保留的内存大小
undominateWithSkips(gcRoot.id)
}
when (gcRoot) {
is ThreadObject -> {
// 活动的 Thread 实例
// 缓存 threadsBySerialNumber
threadsBySerialNumber[gcRoot.threadSerialNumber] = objectRecord.asInstance!! to gcRoot
// 入列 NormalRootNode
enqueue(NormalRootNode(gcRoot.id, gcRoot))
}
is JavaFrame -> {
// Java 局部变量
val threadPair = threadsBySerialNumber[gcRoot.threadSerialNumber]
if (threadPair == null) {
// Could not find the thread that this java frame is for.
enqueue(NormalRootNode(gcRoot.id, gcRoot))
} else {
val (threadInstance, threadRoot) = threadPair
val threadName = threadNames[threadInstance] ?: {
val name = threadInstance[Thread::class, "name"]?.value?.readAsJavaString() ?: ""
threadNames[threadInstance] = name
name
}()
// RefreshceMatchers 用于匹配已知的引用节点
// IgnoredReferenceMatcher 表示忽略这个引用节点
// LibraryLeakReferenceMatcher 表示这是库内存泄露对象
val referenceMatcher = threadNameReferenceMatchers[threadName]
if (referenceMatcher !is IgnoredReferenceMatcher) {
val rootNode = NormalRootNode(threadRoot.id, gcRoot)
val refFromParentType = LOCAL
val refFromParentName = ""
val childNode = if (referenceMatcher is LibraryLeakReferenceMatcher) {
LibraryLeakChildNode(
objectId = gcRoot.id,
parent = rootNode,
refFromParentType = refFromParentType,
refFromParentName = refFromParentName,
matcher = referenceMatcher
)
} else {
NormalNode(
objectId = gcRoot.id,
parent = rootNode,
refFromParentType = refFromParentType,
refFromParentName = refFromParentName
)
}
// 入列 LibraryLeakChildNode 或 NormalNode
enqueue(childNode)
}
}
}
is JniGlobal -> {
// Native 全局变量
// 是否匹配已知引用节点
val referenceMatcher = when (objectRecord) {
is HeapClass -> jniGlobalReferenceMatchers[objectRecord.name]
is HeapInstance -> jniGlobalReferenceMatchers[objectRecord.instanceClassName]
is HeapObjectArray -> jniGlobalReferenceMatchers[objectRecord.arrayClassName]
is HeapPrimitiveArray -> jniGlobalReferenceMatchers[objectRecord.arrayClassName]
}
if (referenceMatcher !is IgnoredReferenceMatcher) {
if (referenceMatcher is LibraryLeakReferenceMatcher) {
// 入列 LibraryLeakRootNode
enqueue(LibraryLeakRootNode(gcRoot.id, gcRoot, referenceMatcher))
} else {
// 入列 NormalRootNode
enqueue(NormalRootNode(gcRoot.id, gcRoot))
}
}
}
// 其他 GC Roots,入列 NormalRootNode
else -> enqueue(NormalRootNode(gcRoot.id, gcRoot))
}
}
}
在将 GC Roots 节点入列的过程,有两个地方值得注意:
-
ReferenceMatcher
ReferenceMatcher用于匹配引用节点,判断是否要忽略它。LeakCanary 支持 4 种类型的匹配:-
类实例字段
缓存在
fieldNameByClassName里,例如,android.os.Message中的obj字段 -
类静态字段
缓存在
staticFieldNameByClassName里,例如,android.app.ActivityManager的mContext字段 -
指定线程
缓存在
threadNames里,例如,FinalizerWatchdogDaemon线程 -
Native 全局变量
缓存在
jniGlobals里,例如,android.widget.Toast\$TN类
内置的引用节点匹配为
AndroidReferenceMatchers.appDefaults。 -
-
VisitQueue
PathFinder中有两个队列,一个优先级更高的toVisitQueue,另外一个是toVisitLastQueue,同时提供toVisitSet和toVisitLastSet用于提供常数级查询。队列中的节点分为两种:
-
RootNode
根节点,它有两个实现类:
-
LibraryLeakRootNode
依赖库的泄露根节点
-
NormalRootNode
普通的根节点
-
-
ChildNode
子节点,可以通过
parent字段访问父节点。它有两个实现类:-
LibraryLeakChildNode
依赖库的泄露子节点
-
NormalNode
普通的字节点
-
以下 3 种情况会将节点放入到
toVisitLastQueue中:- LibraryLeakNode
- GC Root 为 ThreadObject
- 父节点的 GC Root 为 JavaFrame
因为这 3 种导致的内存泄露情况比较少,所以降低它们的访问优先级。
val visitLast = node is LibraryLeakNode || // We deprioritize thread objects because on Lollipop the thread local values are stored // as a field. (node is RootNode && node.gcRoot is ThreadObject) || (node is NormalNode && node.parent is RootNode && node.parent.gcRoot is JavaFrame) -
在将所有的 GC Roots 节点入列后,使用广度优先遍历所有的节点,当访问节点是泄露节点,则添加到 shortestPathsToLeakingObjects 中:
val shortestPathsToLeakingObjects = mutableListOf<ReferencePathNode>()
visitingQueue@ while (queuesNotEmpty) {
val node = poll()
if (checkSeen(node)) {
throw IllegalStateException(
"Node $node objectId=${node.objectId} should not be enqueued when already visited or enqueued"
)
}
if (node.objectId in leakingObjectIds) {
shortestPathsToLeakingObjects.add(node)
// Found all refs, stop searching (unless computing retained size)
if (shortestPathsToLeakingObjects.size == leakingObjectIds.size) {
if (computeRetainedHeapSize) {
listener.onAnalysisProgress(FINDING_DOMINATORS)
} else {
break@visitingQueue
}
}
}
when (val heapObject = graph.findObjectById(node.objectId)) {
is HeapClass -> visitClassRecord(heapObject, node)
is HeapInstance -> visitInstance(heapObject, node)
is HeapObjectArray -> visitObjectArray(heapObject, node)
}
}
在遍历子节点时,有 3 种情况需要考虑:
-
HeapClass
当节点表示 HeapClass,我们将它的静态变量入列:
val node = when (val referenceMatcher = ignoredStaticFields[fieldName]) { null -> NormalNode( objectId = objectId, parent = parent, refFromParentType = STATIC_FIELD, refFromParentName = fieldName ) is LibraryLeakReferenceMatcher -> LibraryLeakChildNode( objectId = objectId, parent = parent, refFromParentType = STATIC_FIELD, refFromParentName = fieldName, matcher = referenceMatcher ) // 忽略 IgnoredReferenceMatcher is IgnoredReferenceMatcher -> null } if (node != null) { enqueue(node) } -
HeapInstance
当节点表示 HeapInstance,我们将它的实例变量入列:
val fieldNamesAndValues = instance.readFields() .filter { it.value.isNonNullReference } .toMutableList() fieldNamesAndValues.sortBy { it.name } fieldNamesAndValues.forEach { field -> val objectId = field.value.asObjectId!! if (computeRetainedHeapSize) { updateDominatorWithSkips(parent.objectId, objectId) } val node = when (val referenceMatcher = fieldReferenceMatchers[field.name]) { null -> NormalNode( objectId = objectId, parent = parent, refFromParentType = INSTANCE_FIELD, refFromParentName = field.name ) is LibraryLeakReferenceMatcher -> LibraryLeakChildNode( objectId = objectId, parent = parent, refFromParentType = INSTANCE_FIELD, refFromParentName = field.name, matcher = referenceMatcher ) // 忽略 IgnoredReferenceMatcher is IgnoredReferenceMatcher -> null } if (node != null) { enqueue(node) } } -
HeapObjectArray
当节点表示 HeapObjectArray,我们将它的非空元素入列:
val nonNullElementIds = record.elementIds.filter { objectId -> objectId != ValueHolder.NULL_REFERENCE && graph.objectExists(objectId) } nonNullElementIds.forEachIndexed { index, elementId -> if (computeRetainedHeapSize) { updateDominatorWithSkips(parent.objectId, elementId) } val name = index.toString() enqueue( NormalNode( objectId = elementId, parent = parent, refFromParentType = ARRAY_ENTRY, refFromParentName = name ) ) }
这里不需要考虑 HeapPrimitiveArray 的情况,因为原始类型不能导致内存泄露。
至此,我们通过调用 findPathsFromGcRoots() 方法将所有泄露对象的引用节点都查询出来了。
最短路径
在通过 findPathsFromGcRoots() 获取的节点中,一个泄露对象可能会有多个引用路径,所以我们还需要做一次遍历,找到每个泄露对象的最短路径(导致泄露的可能性最大)。
private fun deduplicateShortestPaths(inputPathResults: List<ReferencePathNode>): List<ReferencePathNode> {
val rootTrieNode = ParentNode(0)
for (pathNode in inputPathResults) {
// Go through the linked list of nodes and build the reverse list of instances from
// root to leaking.
val path = mutableListOf<Long>()
var leakNode: ReferencePathNode = pathNode
while (leakNode is ChildNode) {
// 从父节点 -> 子节点
path.add(0, leakNode.objectId)
leakNode = leakNode.parent
}
path.add(0, leakNode.objectId)
// 这里的作用是构建树
updateTrie(pathNode, path, 0, rootTrieNode)
}
val outputPathResults = mutableListOf<ReferencePathNode>()
findResultsInTrie(rootTrieNode, outputPathResults)
return outputPathResults
}
private fun updateTrie(
pathNode: ReferencePathNode,
path: List<Long>,
pathIndex: Int,
parentNode: ParentNode
) {
val objectId = path[pathIndex]
if (pathIndex == path.lastIndex) {
// 当前已经是叶子节点
// 替换已存在的节点,当前路径更短
parentNode.children[objectId] = LeafNode(objectId, pathNode)
} else {
val childNode = parentNode.children[objectId] ?: {
val newChildNode = ParentNode(objectId)
parentNode.children[objectId] = newChildNode
newChildNode
}()
if (childNode is ParentNode) {
// 递归更新
updateTrie(pathNode, path, pathIndex + 1, childNode)
}
}
}
通过遍历泄露对象节点的父节点,构建出一棵树,多个相同泄露对象节点的不同路径,最终获取最短路径的树。多条最短路径(不同泄露对象)最终合并成一棵树。
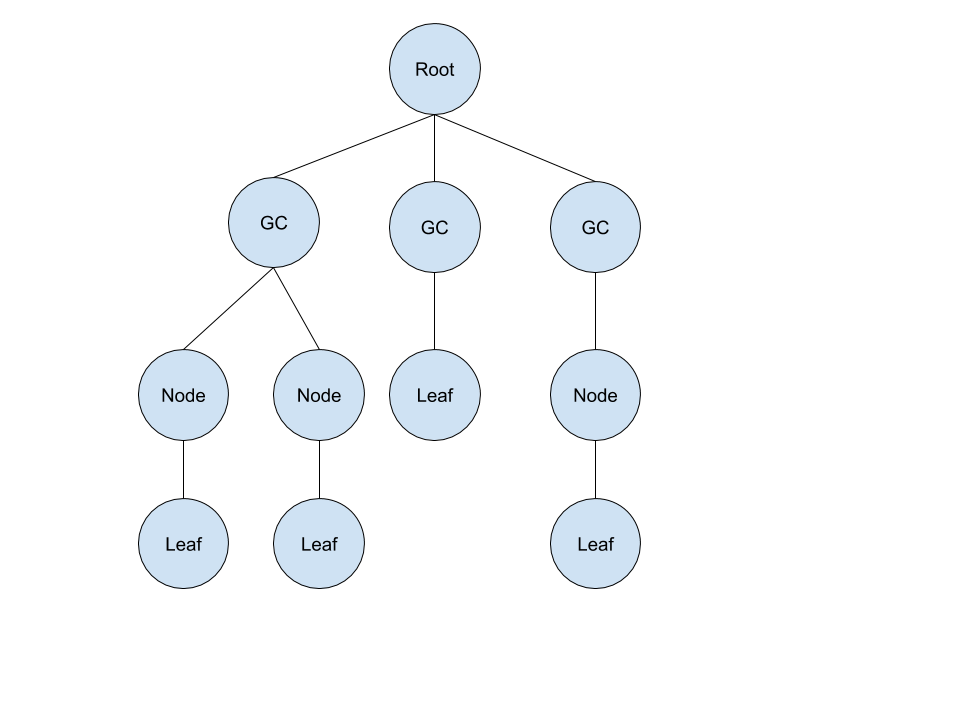
生成 LeakTrace
从上面生成泄露对象路径 ReferencePathNode 到最终的 LeakTrace,这里只是又做了一层包装,比如通过 HeapGraph.findObjectById() 将 objectId 转成对应的 HeapObject:
var node: ReferencePathNode = retainedObjectNode
while (node is ChildNode) {
shortestChildPath.add(0, node)
pathHeapObjects.add(0, graph.findObjectById(node.objectId))
node = node.parent
}
val rootNode = node as RootNode
pathHeapObjects.add(0, graph.findObjectById(rootNode.objectId))
有两个地方需要注意下:
-
ObjectInspector
通过调用
ObjectInspector.inspect(),可以对每个ObjectReporter添加一些说明。例如,判断Activity对象是否泄露:override fun inspect( reporter: ObjectReporter ) { reporter.whenInstanceOf("android.app.Activity") { instance -> val field = instance["android.app.Activity", "mDestroyed"] if (field != null) { if (field.value.asBoolean!!) { leakingReasons += field describedWithValue "true" } else { notLeakingReasons += field describedWithValue "false" } } } }我们也可以通过
Config.objectInspectors添加自定义的ObjectInspector。 -
LeakingStatus
通过调用
HeapAnalyzer.computeLeakStatuses()来计算路径上每个节点的泄露状态:private fun computeLeakStatuses(leakReporters: List<ObjectReporter>): List<Pair<LeakingStatus, String>> { val lastElementIndex = leakReporters.size - 1 var lastNotLeakingElementIndex = -1 var firstLeakingElementIndex = lastElementIndex val leakStatuses = ArrayList<Pair<LeakingStatus, String>>() for ((index, reporter) in leakReporters.withIndex()) { // 通过判断是否存在 leakingReasons 来判断是否为泄露节点 val resolvedStatusPair = resolveStatus(reporter, leakingWins = index == lastElementIndex).let { statusPair -> if (index == lastElementIndex) { // 叶子节点肯定为泄露状态 when (statusPair.first) { LEAKING -> statusPair UNKNOWN -> LEAKING to "This is the leaking object" NOT_LEAKING -> LEAKING to "This is the leaking object. Conflicts with ${statusPair.second}" } } else statusPair } leakStatuses.add(resolvedStatusPair) val (leakStatus, _) = resolvedStatusPair // firstLeakingElementIndex 第一个泄露节点的下标 // lastNotLeakingElementIndex 最后一个非泄露节点的下标 if (leakStatus == NOT_LEAKING) { lastNotLeakingElementIndex = index // Reset firstLeakingElementIndex so that we never have // firstLeakingElementIndex < lastNotLeakingElementIndex firstLeakingElementIndex = lastElementIndex } else if (leakStatus == LEAKING && firstLeakingElementIndex == lastElementIndex) { firstLeakingElementIndex = index } } val simpleClassNames = leakReporters.map { reporter -> recordClassName(reporter.heapObject).lastSegment('.') } // lastNotLeakingElementIndex 之前节点不会是泄露状态 for (i in 0 until lastNotLeakingElementIndex) { val (leakStatus, leakStatusReason) = leakStatuses[i] val nextNotLeakingIndex = generateSequence(i + 1) { index -> if (index < lastNotLeakingElementIndex) index + 1 else null }.first { index -> leakStatuses[index].first == NOT_LEAKING } // Element is forced to NOT_LEAKING val nextNotLeakingName = simpleClassNames[nextNotLeakingIndex] leakStatuses[i] = when (leakStatus) { UNKNOWN -> NOT_LEAKING to "$nextNotLeakingName↓ is not leaking" NOT_LEAKING -> NOT_LEAKING to "$nextNotLeakingName↓ is not leaking and $leakStatusReason" LEAKING -> NOT_LEAKING to "$nextNotLeakingName↓ is not leaking. Conflicts with $leakStatusReason" } } // firstLeakingElementIndex 之后的节点为泄露状态 if (firstLeakingElementIndex < lastElementIndex - 1) { // We already know the status of firstLeakingElementIndex and lastElementIndex for (i in lastElementIndex - 1 downTo firstLeakingElementIndex + 1) { val (leakStatus, leakStatusReason) = leakStatuses[i] val previousLeakingIndex = generateSequence(i - 1) { index -> if (index > firstLeakingElementIndex) index - 1 else null }.first { index -> leakStatuses[index].first == LEAKING } // Element is forced to LEAKING val previousLeakingName = simpleClassNames[previousLeakingIndex] leakStatuses[i] = when (leakStatus) { UNKNOWN -> LEAKING to "$previousLeakingName↑ is leaking" LEAKING -> LEAKING to "$previousLeakingName↑ is leaking and $leakStatusReason" NOT_LEAKING -> throw IllegalStateException("Should never happen") } } } return leakStatuses }
小结
至此,我们已经把 HeapAnalyzerService.analyzeHeap() 方法分析完了,下面我们用时序图把这个调用关系再加深下印象:
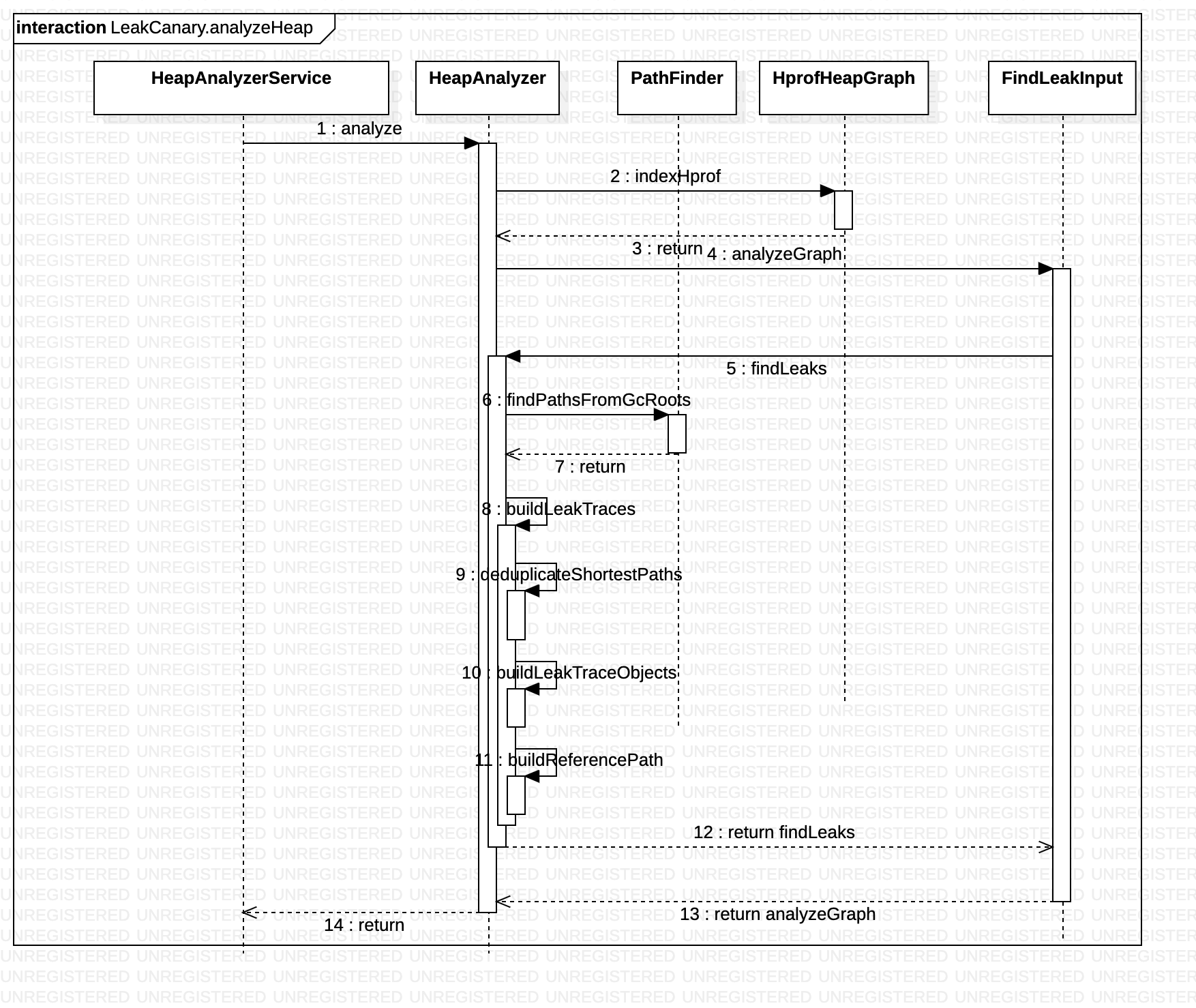
UI 展现
在默认实现的 DefaultOnHeapAnalyzedListener 中,当前 hprof 文件分析成功后,会回调 onHeapAnalyzed() 方法:
override fun onHeapAnalyzed(heapAnalysis: HeapAnalysis) {
// 入库
val id = LeaksDbHelper(application).writableDatabase.use { db ->
HeapAnalysisTable.insert(db, heapAnalysis)
}
val (contentTitle, screenToShow) = when (heapAnalysis) {
is HeapAnalysisFailure -> application.getString(
R.string.leak_canary_analysis_failed
) to HeapAnalysisFailureScreen(id)
is HeapAnalysisSuccess -> {
val retainedObjectCount = heapAnalysis.allLeaks.sumBy { it.leakTraces.size }
val leakTypeCount = heapAnalysis.applicationLeaks.size + heapAnalysis.libraryLeaks.size
application.getString(
R.string.leak_canary_analysis_success_notification, retainedObjectCount, leakTypeCount
) to HeapDumpScreen(id)
}
}
if (InternalLeakCanary.formFactor == TV) {
showToast(heapAnalysis)
printIntentInfo()
} else {
// 显示通知栏消息
showNotification(screenToShow, contentTitle)
}
}
当点击通知栏消息后,再跳转到 LeakActivity:
val pendingIntent = LeakActivity.createPendingIntent(
application, arrayListOf(HeapDumpsScreen(), screenToShow)
)
总结
从源码把 LeakCanary 的核心流程分析下来,可以看到整个项目中,不管是模块的划分,代码的风格都是非常清晰,特别是用了 kotlin 重写后,具备了很多 Java 没有的语法糖,让代码的篇幅也非常精简。总的来说,这个是一个非常不错的学习项目。