本篇是笔者解读源码项目 iOS-Framework-Analysis 的开篇,今年计划完成10个优秀第三方源码解读,欢迎star和笔者一起解读这些优秀框架的背后思想,从而提升自己的内功。该篇详细的源码注释已上传 fishhook源码注释,如有需要请自取 🐝🐝。
在iOS平台下,说起Hook首先会想起MethodSwizzling这个苹果提供的工具,利用Objective-C的Runtime的特性,通过在消息转发时交换方法实现(IMP)的机会。但MethodSwizzling只能对Objective-C方法进行Hook,如果要对C/C++方法进行Hook操作,可以使用facebook提供的fishhook框架,本文是对该框架的解读。
初识fishhook
首先,我们需要了解几个常见的概念,有助于后面源码的阅读。
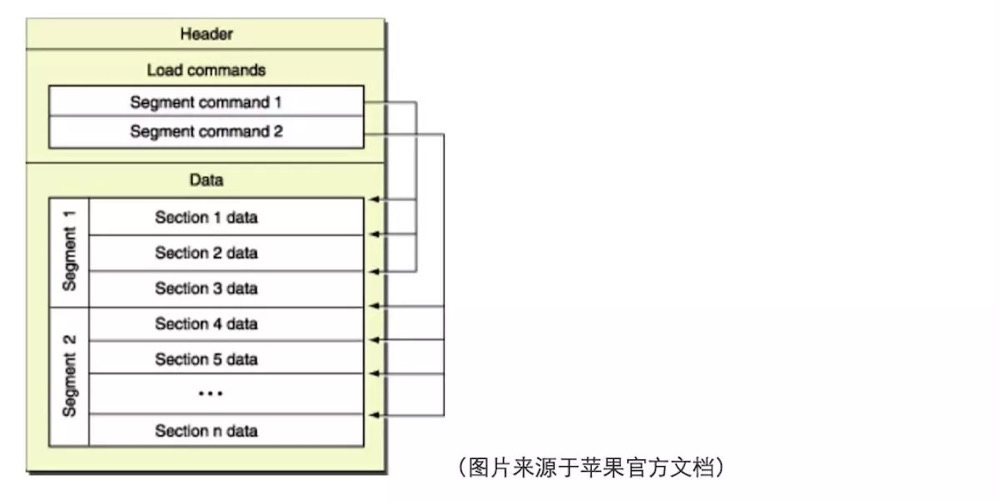
Mach-O: 在iOS和OS X系统下,所有可执行文件、dylib 以及 Bundle都是Mach-O格式。主要有Header、Load Commands和Data组成。
// header
struct mach_header {
uint32_t magic; /* mach magic number identifier */
cpu_type_t cputype; /* cpu specifier */
cpu_subtype_t cpusubtype; /* machine specifier */
uint32_t filetype; /* type of file */
uint32_t ncmds; /* number of load commands */
uint32_t sizeofcmds; /* the size of all the load commands */
uint32_t flags; /* flags */
};
struct mach_header_64 {
uint32_t magic; /* mach magic number identifier */
cpu_type_t cputype; /* cpu specifier */
cpu_subtype_t cpusubtype; /* machine specifier */
uint32_t filetype; /* type of file */
uint32_t ncmds; /* number of load commands */
uint32_t sizeofcmds; /* the size of all the load commands */
uint32_t flags; /* flags */
uint32_t reserved; /* reserved */
};
// load command
struct load_command {
uint32_t cmd; /* type of load command */
uint32_t cmdsize; /* total size of command in bytes */
};
// load command中的segment_command
// 32&64位字段都相同
struct segment_command_64 { /* for 64-bit architectures */
uint32_t cmd; /* LC_SEGMENT_64 */
uint32_t cmdsize; /* includes sizeof section_64 structs*/
char segname[16]; /* segment name */
uint64_t vmaddr; /* memory address of this segment*/
uint64_t vmsize; /* memory size of this segment */
uint64_t fileoff; /* file offset of this segment */
uint64_t filesize; /* amount to map from the file */
vm_prot_t maxprot; /* maximum VM protection */
vm_prot_t initprot; /* initial VM protection */
uint32_t nsects; /* number of sections in segment*/
uint32_t flags; /* flags */
};
// _DATA中的section
// 32&64位字段都相同
struct section_64
{
char sectname[16];
char segname[16];
uint64_t addr;
uint64_t size;
uint32_t offset;
uint32_t align;
uint32_t reloff;
uint32_t nreloc;
uint32_t flags;
uint32_t reserved1;
uint32_t reserved2;
};
dyld ( the dynamic link editor ):负责将各种各样程序需要的镜像加载到程序运行的内存空间中,这个过程发生的时间非常早 — 在 objc 运行时初始化之前。
镜像(image):dyld会将Mach-O文件作为镜像,既镜像就是Mach-O。
_dyld_register_func_for_add_image: 每个镜像被dyld加载时,都会执行系统注册过的回调函数,可以通过该方法注册自定义的回调函数,当调用该函数注册时,会让所有镜像都执行回调函数,无论是否已经加载过。
dyld_stub_binder: 在目标符号(例如 printf)首次被调用时,将其链接到指定的动态链接库 ,找到对应的符号表真实地址进行绑定(printf 符号位于 _DATA 端中的 lazy 符号表中)。
Mach-O的动态绑定机制:编译App时,系统共享库不会编译到Mach-O文件中,而是第一次调用才通过dyld动态绑定,将MACH-O的DATA段符号表中对应的指针指向外部系统共享库中的真正实现
fishhook正是利用动态绑定机制,先确定某一个符号在 _DATA 段中的位置,然后保存原符号对应的函数指针,并使用新的函数指针覆盖原有符号的函数指针,实现替换。
fishhook源码解读
申明
#ifndef fishhook_h
#define fishhook_h
#include <stddef.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#if !defined(FISHHOOK_EXPORT)
#define FISHHOOK_VISIBILITY _attribute_((visibility("hidden")))
#else
#define FISHHOOK_VISIBILITY _attribute_((visibility("default")))
#endif
#ifdef _cplusplus
extern "C" {
#endif //_cplusplus
/*
* A structure representing a particular intended rebinding from a symbol
* name to its replacement
*/
struct rebinding {
const char *name; // 被hook的函数名
void *replacement; // 替换的函数指针(IMP)
void **replaced; // 用于存放原函数指针的指针(成功替换后会将原函数指针放入其中)
};
/*
* For each rebinding in rebindings, rebinds references to external, indirect
* symbols with the specified name to instead point at replacement for each
* image in the calling process as well as for all future images that are loaded
* by the process. If rebind_functions is called more than once, the symbols to
* rebind are added to the existing list of rebindings, and if a given symbol
* is rebound more than once, the later rebinding will take precedence.
*/
FISHHOOK_VISIBILITY
// 参数分别是结构体rebinding数组和数组元素个数
int rebind_symbols(struct rebinding rebindings[], size_t rebindings_nel);
/*
* Rebinds as above, but only in the specified image. The header should point
* to the mach-o header, the slide should be the slide offset. Others as above.
*/
FISHHOOK_VISIBILITY
// 在指定的image中进行替换,header为该镜像的header,slider为偏移量,其他如上。
int rebind_symbols_image(void *header,
intptr_t slide,
struct rebinding rebindings[],
size_t rebindings_nel);
#ifdef _cplusplus
}
#endif //_cplusplus
#endif //fishhook_h
实现
#include "fishhook.h"
#include <dlfcn.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <mach/mach.h>
#include <mach/vm_map.h>
#include <mach/vm_region.h>
#include <mach-o/dyld.h>
#include <mach-o/loader.h>
#include <mach-o/nlist.h>
#ifdef _LP64_
typedef struct mach_header_64 mach_header_t;
typedef struct segment_command_64 segment_command_t;
typedef struct section_64 section_t;
typedef struct nlist_64 nlist_t;
//LC_SEGMENT_64:一种command类型表示将文件的64位的段映射到进程地址空间
#define LC_SEGMENT_ARCH_DEPENDENT LC_SEGMENT_64
#else
typedef struct mach_header mach_header_t;
typedef struct segment_command segment_command_t;
typedef struct section section_t;
typedef struct nlist nlist_t;
#define LC_SEGMENT_ARCH_DEPENDENT LC_SEGMENT
#endif
#ifndef SEG_DATA_CONST
#define SEG_DATA_CONST "_DATA_CONST"
#endif
struct rebindings_entry {
struct rebinding *rebindings;
size_t rebindings_nel;
struct rebindings_entry *next;
};
static struct rebindings_entry *_rebindings_head;
首先是引入头文件,按照不同架构定义一些系统结构体,并定义 rebindings_entry 链表节点,创建一个私有的链表头节点 _rebindings_head,每次调用都会将最新的rebindings_entry插入头部。
rebind_symbols
我们从 rebind_symbols(struct rebinding rebindings[], size_t rebindings_nel) 调用入手,看下整个代码逻辑是怎么样的。
int rebind_symbols(struct rebinding rebindings[], size_t rebindings_nel) {
int retval = prepend_rebindings(&_rebindings_head, rebindings, rebindings_nel);
if (retval < 0) {
return retval;
}
// If this was the first call, register callback for image additions (which is also invoked for
// existing images, otherwise, just run on existing images
if (!_rebindings_head->next) {
_dyld_register_func_for_add_image(_rebind_symbols_for_image);
} else {
uint32_t c = _dyld_image_count();
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < c; i++) {
_rebind_symbols_for_image(_dyld_get_image_header(i), _dyld_get_image_vmaddr_slide(i));
}
}
return retval;
}
rebind_symbols 主要做了两件事,首先是调用 prepend_rebindings 将传入的rebindings封装成rebindings_entry,并插入到私有链表的表头。
static int prepend_rebindings(struct rebindings_entry **rebindings_head,
struct rebinding rebindings[],
size_t nel) {
// 创建rebindings_entry节点
struct rebindings_entry *new_entry = (struct rebindings_entry *) malloc(sizeof(struct rebindings_entry));
if (!new_entry) {
return -1;
}
new_entry->rebindings = (struct rebinding *) malloc(sizeof(struct rebinding) * nel);
if (!new_entry->rebindings) {
free(new_entry);
return -1;
}
memcpy(new_entry->rebindings, rebindings, sizeof(struct rebinding) * nel);
new_entry->rebindings_nel = nel;
// 每次都将新创建的rebindings_entry放到链表rebindings_head最前面
new_entry->next = *rebindings_head;
*rebindings_head = new_entry;
return 0;
}
接着通过链表内容判断是否是第一次执行,如果是首次则调用函数 _dyld_register_func_for_add_image 注册自定义回调,系统会在进行dyld链接时自动执行回调。非首次调用则遍历所有镜像(image),手动执行自定义回调方法。
通过自定义回调方法 _rebind_symbols_for_image 实现查找符号在镜像中的位置,并在镜像的 _DATA段 中绑定我们自己的实现。
rebind_symbols_for_image
rebind_symbols_for_image 做的事可以分成两部分,第一部分是在Load Commands找到与符号表相关command,并得到符号表的准备地址,包括在动态符号表、符号表和字符串表。
// 对真正实现方法的简单封装
static void _rebind_symbols_for_image(const struct mach_header *header,
intptr_t slide) {
rebind_symbols_for_image(_rebindings_head, header, slide);
}
static void rebind_symbols_for_image(struct rebindings_entry *rebindings,
const struct mach_header *header,
intptr_t slide) {
Dl_info info;
if (dladdr(header, &info) == 0) {
return;
}
// 找到与符号表相关的 command,包括 linkedit segment command、symtab command 和 dysymtab command
segment_command_t *cur_seg_cmd;
segment_command_t *linkedit_segment = NULL; //LINKEDIT
struct symtab_command* symtab_cmd = NULL; //符号表
struct dysymtab_command* dysymtab_cmd = NULL; //间接符号表
//1. 遍历加载命令,获得MachO中LINKEDIT、符号表、间接符号表三个加载命令
// 每个mach-o由(header、load commands、 data)三块区域组成
// 要去寻找load command,所以这里先跳过sizeof(mach_header_t)大小
uintptr_t cur = (uintptr_t)header + sizeof(mach_header_t);
for (uint i = 0; i < header->ncmds; i++, cur += cur_seg_cmd->cmdsize) {
cur_seg_cmd = (segment_command_t *)cur;
//_LINKEDIT段 含有为动态链接库使用的原始数据,比如符号,字符串,重定位表条目等等
/*
LC_SEGMENT_64 含有为动态链接库使用的原始数据
LC_SYMTAB(符号地址)这个LoadCommand主要提供了两个信息
Symbol Table(符号表)的偏移量与Symbol Table中元素的个数
String Table(字符串表)的偏移量与String Table的长度
LC_DYSYMTAB(动态符号表地址)提供了动态符号表的位移和元素个数,还有一些其他的表格索引
*/
if (cur_seg_cmd->cmd == LC_SEGMENT_ARCH_DEPENDENT) {
if (strcmp(cur_seg_cmd->segname, SEG_LINKEDIT) == 0) {
linkedit_segment = cur_seg_cmd;
}
} else if (cur_seg_cmd->cmd == LC_SYMTAB) {
symtab_cmd = (struct symtab_command*)cur_seg_cmd;
} else if (cur_seg_cmd->cmd == LC_DYSYMTAB) {
dysymtab_cmd = (struct dysymtab_command*)cur_seg_cmd;
}
}
if (!symtab_cmd || !dysymtab_cmd || !linkedit_segment ||
!dysymtab_cmd->nindirectsyms) {
return;
}
// 找到符号表的地址
// 本来是:基址=linkedit内存地址 - linkedit的fileoff
// 由于ASLR:真实基址 = linkedit内存地址(vmaddr) + slide - fileoff
uintptr_t linkedit_base = (uintptr_t)slide + linkedit_segment->vmaddr - linkedit_segment->fileoff;
//符号表的地址 = 基址 + 符号表偏移量
nlist_t *symtab = (nlist_t *)(linkedit_base + symtab_cmd->symoff);
//字符串表的地址 = 基址 + 字符串表偏移量
char *strtab = (char *)(linkedit_base + symtab_cmd->stroff);
//动态符号表地址 = 基址 + 动态符号表偏移量
uint32_t *indirect_symtab = (uint32_t *)(linkedit_base + dysymtab_cmd->indirectsymoff);
......
第二部分是遍历镜像_DATA中的section,找到 LAZY_SYMBOL_POINTERS 和 NON_LAZY_SYMBOL_POINTERS,由开头可知,这两个section是在Mach_O的_DATA段中用来绑定non-lazy和lazy 的符号表,最后调用替换方法perform_rebinding_with_section。
为什么要找 LAZY_SYMBOL_POINTERS/NON_LAZY_SYMBOL_POINTERS? NON_LAZY_SYMBOL_POINTERS 非懒加载指针表 LAZY_SYMBOL_POINTERS 懒加载指针表,符号第一次调用时通过 dyld 中的 dyld_stub_binder进行加载到表中 这两个表是_DATA中跟动态符号链接相关的部分,所以需要找到原方法这两个部分的指针去替换链接方法 对于动态链接库里面的C函数,第一次调用的时候,我们会得到函数和实现地址的对应关系,函数的实现地址存放在一个叫 LAZY_SYMBOL_POINTERS 的地方,第二次调用的时候,直接通过 LAZY_SYMBOL_POINTERS 找到函数地址就可以,不再需要繁琐的获取函数地址的过程。
......
//2. 遍历加载命令,得到DATA,然后遍历DATA里面的section,找到nl_symbol_ptr(got)/la_symbol_ptr
cur = (uintptr_t)header + sizeof(mach_header_t);
for (uint i = 0; i < header->ncmds; i++, cur += cur_seg_cmd->cmdsize) {
cur_seg_cmd = (segment_command_t *)cur;
if (cur_seg_cmd->cmd == LC_SEGMENT_ARCH_DEPENDENT) {
//寻找__DATA和__DATA_CONST的section
if (strcmp(cur_seg_cmd->segname, SEG_DATA) != 0 &&
strcmp(cur_seg_cmd->segname, SEG_DATA_CONST) != 0) {
continue;
}
//遍历DATA里面的section,找到nl_symbol_ptr(got)/la_symbol_ptr
for (uint j = 0; j < cur_seg_cmd->nsects; j++) {
//_DATA 加上结构体偏移
//
// struct segment_command_64 { /* for 64-bit architectures */
// uint32_t cmd; /* LC_SEGMENT_64 */
// uint32_t cmdsize; /* includes sizeof section_64 structs*/
// char segname[16]; /* segment name */
// uint64_t vmaddr; /* memory address of this segment*/
// uint64_t vmsize; /* memory size of this segment */
// uint64_t fileoff; /* file offset of this segment */
// uint64_t filesize; /* amount to map from the file */
// vm_prot_t maxprot; /* maximum VM protection */
// vm_prot_t initprot; /* initial VM protection */
// uint32_t nsects; /* number of sections in segment*/
// uint32_t flags; /* flags */
// };
section_t *sect =
(section_t *)(cur + sizeof(segment_command_t)) + j;
//寻找__la_symbol_ptr区
if ((sect->flags & SECTION_TYPE) == S_LAZY_SYMBOL_POINTERS) {
perform_rebinding_with_section(rebindings, sect, slide, symtab, strtab, indirect_symtab);
}
//寻找__nl_symbol_ptr
if ((sect->flags & SECTION_TYPE) == S_NON_LAZY_SYMBOL_POINTERS) {
perform_rebinding_with_section(rebindings, sect, slide, symtab, strtab, indirect_symtab);
}
}
}
}
}
perform_rebinding_with_section
该方法根据传入的 NON-Lazy 或 Lazy 数据段,遍历该数据段的符号,找到其对应的符号名并与传入的符号名进行匹配,命中则进行替换。
static void perform_rebinding_with_section(struct rebindings_entry *rebindings,
section_t *section,
intptr_t slide,
nlist_t *symtab, // 符号表
char *strtab, // 字符串表
uint32_t *indirect_symtab // 动态符号表
) {
const bool isDataConst = strcmp(section->segname, "__DATA_CONST") == 0;
// 符号表访问指针地址替换
// `nl_symbol_ptr`和`la_symbol_ptr`section中的`reserved1`字段指明对应在`indirect symbol table`起始的index
// 获得该section符号表的起始地址
uint32_t *indirect_symbol_indices = indirect_symtab + section->reserved1;
// 得到该section段的所有函数地址
void **indirect_symbol_bindings = (void **)((uintptr_t)slide + section->addr);
vm_prot_t oldProtection = VM_PROT_READ;
if (isDataConst) {
oldProtection = get_protection(rebindings);
// protect()函数可以用来修改一段指定内存区域的保护属性。
// 这里暂时将常量区权限改成可读可写
mprotect(indirect_symbol_bindings, section->size, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE);
}
for (uint i = 0; i < section->size / sizeof(void *); i++) {
// 从动态符号表中取得符号在符号表中的位置
uint32_t symtab_index = indirect_symbol_indices[i];
if (symtab_index == INDIRECT_SYMBOL_ABS || symtab_index == INDIRECT_SYMBOL_LOCAL ||
symtab_index == (INDIRECT_SYMBOL_LOCAL | INDIRECT_SYMBOL_ABS)) {
continue;
}
//获取每一个需要动态解析的符号在字符串表中的偏移量
uint32_t strtab_offset = symtab[symtab_index].n_un.n_strx;
//通过字符串表偏移量获取符号对应的字符串(符号的名字)
char *symbol_name = strtab + strtab_offset;
bool symbol_name_longer_than_1 = symbol_name[0] && symbol_name[1];
// 遍历rebindings数组,比较符号,相同则进行替换
struct rebindings_entry *cur = rebindings;
while (cur) {
for (uint j = 0; j < cur->rebindings_nel; j++) {
if (symbol_name_longer_than_1 &&
strcmp(&symbol_name[1], cur->rebindings[j].name) == 0) {
// 判断原实现是否有被保存过,既实现和现在表中的实现是否一致
if (cur->rebindings[j].replaced != NULL &&
indirect_symbol_bindings[i] != cur->rebindings[j].replacement) {
*(cur->rebindings[j].replaced) = indirect_symbol_bindings[i];
}
// 更改函数为新的实现
indirect_symbol_bindings[i] = cur->rebindings[j].replacement;
goto symbol_loop;
}
}
cur = cur->next;
}
symbol_loop:;
}
// 恢复常量区的访问权限
if (isDataConst) {
int protection = 0;
if (oldProtection & VM_PROT_READ) {
protection |= PROT_READ; // 按位或后赋值
}
if (oldProtection & VM_PROT_WRITE) {
protection |= PROT_WRITE;
}
if (oldProtection & VM_PROT_EXECUTE) {
protection |= PROT_EXEC;
}
mprotect(indirect_symbol_bindings, section->size, protection);
}
}
总结
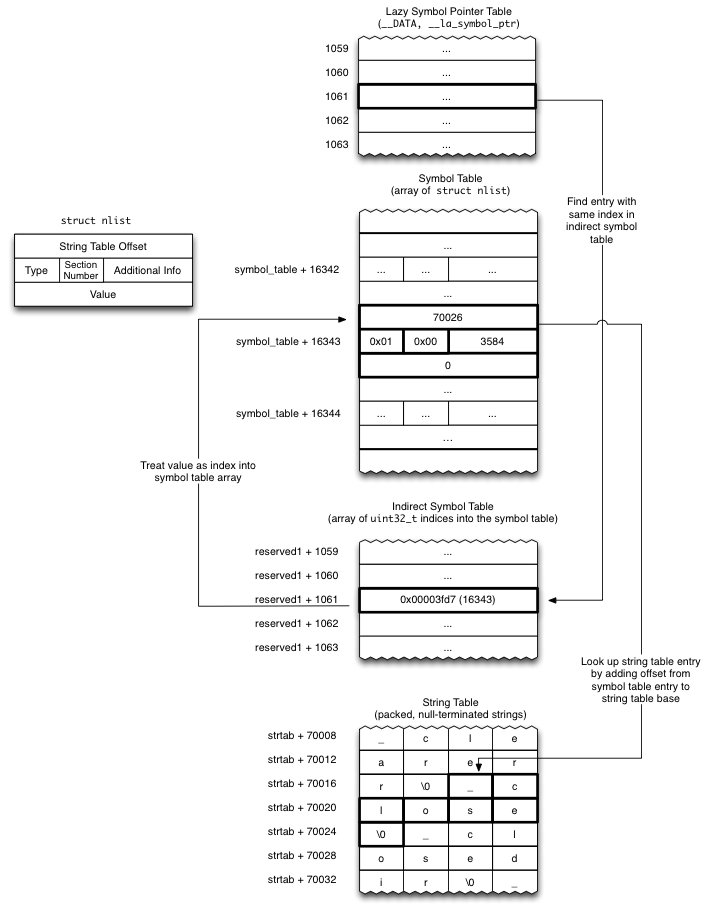
最后,用github上的lazy说明图总结下流程。
fishhook 首先通过遍历镜像的 load commans 段获取符号表、动态符号表和字符串表,接着遍历 Data 段,得到 LAZY_SYMBOL_POINTERS 和 NON_LAZY_SYMBOL_POINTERS,里面记录着镜像的符号段在动态符号表的位置( indirect_symtab+section->reserve1 )和所有符号对应的实现指针地址( section->addr ),再通过遍历动态符号取得每个符号和符号名进行比对,与传入的符号相同时则进行实现的替换。
fishhook也有其局限性,由于是依赖 Mach-O 的动态绑定机制实现的,所以只能Hook在外部共享库中的函数,对于编译时就已经确定的内部/自定义的 C 函数 fishhook 就无能为力了。