Flutter 动态化热更新的思考与实践(二)----Dart 代码转换AST
Flutter 动态化热更新的思考与实践(三)---- 解析AST之Runtime
Flutter 动态化热更新的思考与实践(四)---- 解析AST之Widget
Flutter 动态化热更新的思考与实践(五)---- 调用AST动态化的代码
Widget Ast 数据的解析相较于Runtime就简单许多,是个静态解析的过程,只要将Ast数据节点映射到对应的Widget并组合就好,原理很简单,只是要做些体力活,因为需要解析各个Widget的属性 = =
1. Widget Ast 数据示例
我们先写一个简单的列表UI,然后对这个列表UI做一个动态化处理:
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
class ListViewDSL extends StatefulWidget {
@override
_ListViewDSLState createState() => _ListViewDSLState();
}
class _ListViewDSLState extends State<ListViewDSL> {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
backgroundColor: Colors.red,
title: Text(
'ListViewDSL',
style: TextStyle(fontSize: 20, color: Colors.white),
),
centerTitle: true,
),
body: ListView.builder(
itemBuilder: (context, index) {
return Container(
child: Text('Hellow world'),
color: Colors.red,
height: 45,
);
},
itemCount: 50,
padding: EdgeInsets.only(left: 16, right: 16),
),
);
}
}
根据前两篇文章内容,我们可以先看一下这段代码生成的Ast是什么样子(截取部分):

我们需要重点解析@override Widget build(BuildContext context)方法中的内容,对应Ast节点

中的数据。对Widget生成的Ast数据的分析,主要包括几个节点类型:
- ClassDeclaration
- MethodDeclaration
- BlockStatement
- ReturnStatement
- MethodInvocation
- ArgumentList
- NamedExpression
- FunctionExpression
- MemberExpression
等等,进一步分析发现,Widget的实例对应的Ast节点是MethodInvocation,Widget下各属性列表对应Ast节点是ArgumentList,属性列表中的参数对应的Ast节点是NamedExpression,如下图:
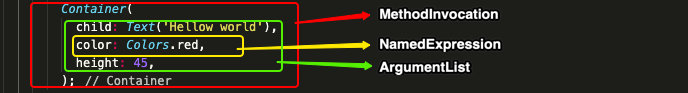
根据这三个主要节点基本就可以描述一个Widget,我们解析的思路就集中在这三种数据节点上,再看看里面都包含了什么东西。
2. 如何解析
我们把解析的步骤分两部分,一部分是对Widget本身的解析,一部分是对Widget中各属性参数的解析。
2.1 解析属性参数
属性的解析没什么高级技巧,因为在Flutter中禁用了dart的反射,所以我们只能一个一个枚举来解析,比如对color属性的解析,基本就将系统支持的color都枚举出来:
Color parseColor(Expression expression) {
if (expression.isPrefixedIdentifier &&
(expression.asPrefixedIdentifier).prefix == 'Colors') {
switch ((expression.asPrefixedIdentifier).identifier) {
case 'amber':
return Colors.amber;
case 'amberAccent':
return Colors.amberAccent;
case 'black':
return Colors.black;
case 'black12':
return Colors.black12;
case 'black26':
return Colors.black26;
case 'black38':
return Colors.black38;
case 'black45':
return Colors.black45;
case 'black54':
return Colors.black54;
case 'black87':
return Colors.black87;
case 'blue':
return Colors.blue;
case 'blueAccent':
return Colors.blueAccent;
case 'blueGrey':
return Colors.blueGrey;
case 'brown':
return Colors.brown;
case 'cyan':
return Colors.cyan;
case 'cyanAccent':
return Colors.cyanAccent;
case 'deepOrange':
return Colors.deepOrange;
case 'deepOrangeAccent':
return Colors.deepOrangeAccent;
case 'deepPurple':
return Colors.deepPurple;
case 'deepPurpleAccent':
return Colors.deepPurpleAccent;
case 'green':
return Colors.green;
case 'greenAccent':
return Colors.greenAccent;
case 'grey':
return Colors.grey;
case 'indigo':
return Colors.indigo;
case 'indigoAccent':
return Colors.indigoAccent;
case 'lightBlue':
return Colors.lightBlue;
case 'lightBlueAccent':
return Colors.lightBlueAccent;
case 'lightGreen':
return Colors.lightGreen;
case 'lightGreenAccent':
return Colors.lightGreenAccent;
case 'lime':
return Colors.lime;
case 'limeAccent':
return Colors.limeAccent;
case 'orange':
return Colors.orange;
case 'orangeAccent':
return Colors.orangeAccent;
case 'pink':
return Colors.pink;
case 'pinkAccent':
return Colors.pinkAccent;
case 'purple':
return Colors.purple;
case 'purpleAccent':
return Colors.purpleAccent;
case 'red':
return Colors.red;
case 'redAccent':
return Colors.redAccent;
case 'teal':
return Colors.teal;
case 'tealAccent':
return Colors.tealAccent;
case 'transparent':
return Colors.transparent;
case 'white':
return Colors.white;
case 'white10':
return Colors.white10;
case 'white12':
return Colors.white12;
case 'white24':
return Colors.white24;
case 'white30':
return Colors.white30;
case 'white38':
return Colors.white38;
case 'white54':
return Colors.white54;
case 'white60':
return Colors.white60;
case 'white70':
return Colors.white70;
case 'yellow':
return Colors.yellow;
case 'yellowAccent':
return Colors.yellowAccent;
}
} else if (expression.isPropertyAccess) {
var propertyExpression = expression.asPropertyAccess.expression;
switch (expression.asPropertyAccess.name) {
case 'shade50':
return (parseColor(propertyExpression) as MaterialColor).shade50;
case 'shade100':
return (parseColor(propertyExpression) as MaterialColor).shade100;
case 'shade200':
return (parseColor(propertyExpression) as MaterialColor).shade200;
case 'shade300':
return (parseColor(propertyExpression) as MaterialColor).shade300;
case 'shade400':
return (parseColor(propertyExpression) as MaterialColor).shade400;
case 'shade500':
return (parseColor(propertyExpression) as MaterialColor).shade500;
case 'shade600':
return (parseColor(propertyExpression) as MaterialColor).shade600;
case 'shade700':
return (parseColor(propertyExpression) as MaterialColor).shade700;
case 'shade800':
return (parseColor(propertyExpression) as MaterialColor).shade800;
case 'shade900':
return (parseColor(propertyExpression) as MaterialColor).shade900;
}
} else if (expression.isMethodInvocation) {
var methodInvocation = expression.asMethodInvocation;
var calleeExpression = methodInvocation.callee;
if (calleeExpression.isMemberExpression) {
var callee = calleeExpression.asMemberExpression;
var masterColor = parseColor(callee.object);
num argumentValue = 255;
var argumentList = methodInvocation.argumentList;
if (argumentList != null && argumentList.length > 0) {
if (argumentList[0].isNumericLiteral) {
argumentValue = (argumentList[0] as NumericLiteral).value;
}
}
switch (callee.property) {
case 'withAlpha':
return masterColor.withAlpha(argumentValue);
case 'withBlue':
return masterColor.withBlue(argumentValue);
case 'withRed':
return masterColor.withRed(argumentValue);
case 'withGreen':
return masterColor.withGreen(argumentValue);
case 'withOpacity':
return masterColor.withOpacity(argumentValue);
}
} else if (calleeExpression.isIdentifier &&
(calleeExpression.asIdentifier).name == 'Color') {
num argumentValue = 255;
var argumentList = methodInvocation.argumentList;
if (argumentList != null && argumentList.length > 0) {
if (argumentList[0].isNumericLiteral) {
argumentValue = (argumentList[0] as NumericLiteral).value;
}
}
return Color(argumentValue);
}
}
return Colors.black;
}
纯体力活 ~ ~..其他属性的解析也同样如此,无需多言,但也没必要将框架内的所有属性都解析一遍,这个时候最好看一下公司项目中常用哪些基本属性,只处理常用的就好,在未来也可以继续拓展。
2.2 解析Widget
Widget部分的解析也同样是个笨方法,需要枚举框架中的Widget或自定义的Widget,不过为了方便以后拓展新的Widget,还是将这个结构用工厂模式设计了一下,如下图:
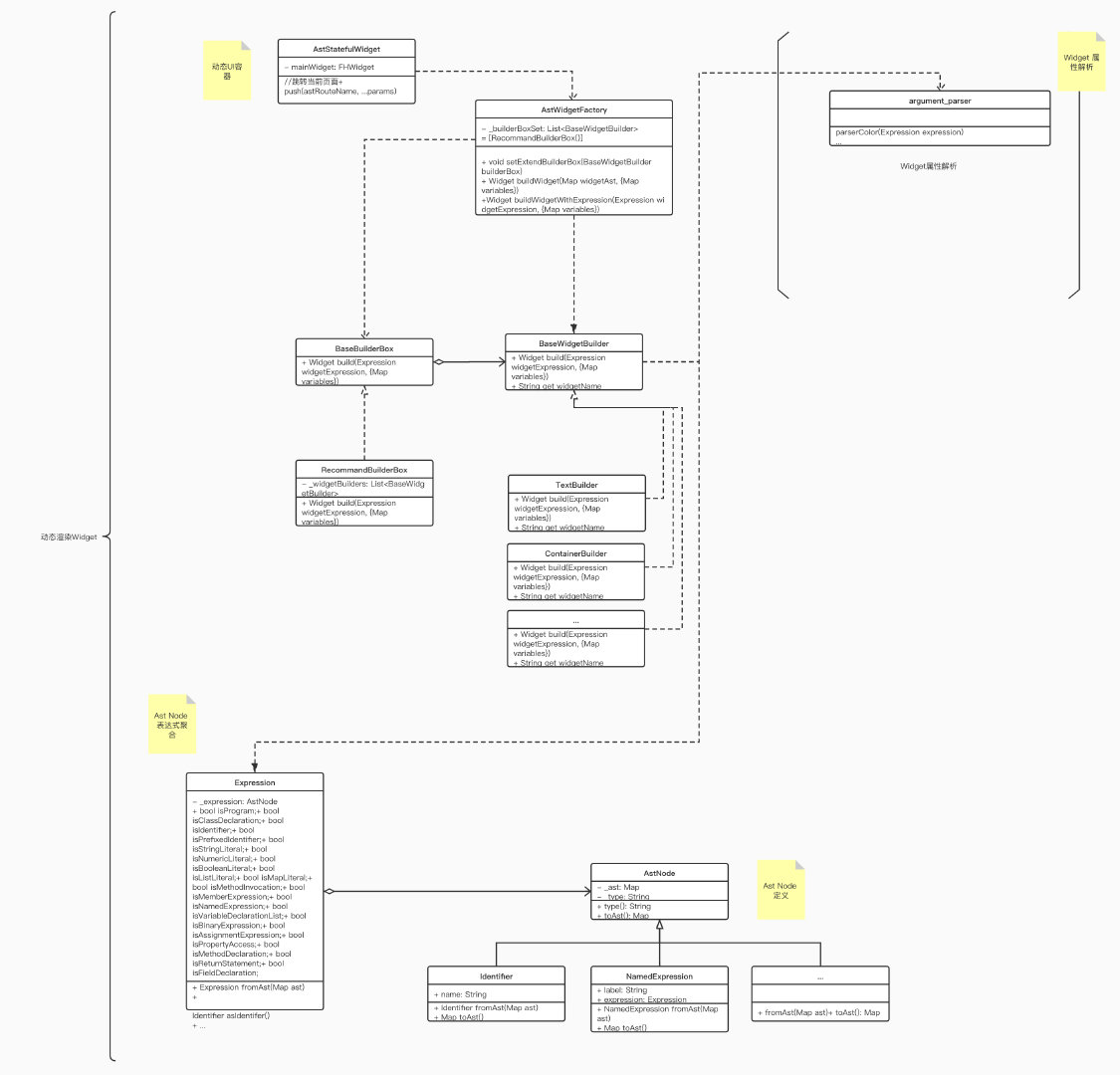
我们每需要解析新增的Widget时,需要继承BaseWidgetBuilder,然后Flutter框架自带的Widget放到RecommandBuilderBox中,自定义扩展的Widget 集合可以通过继承BaseBuilderBox实现,然后Widget的解析统一通过AstWidgetFactory来操作,将调用与实现解耦。比如对Container组件的解析:
class ContainerBuilder implements BaseWidgetBuilder {
@override
Widget build(Expression widgetExpression, {Map variables}) {
var argumentList = widgetExpression.asMethodInvocation.argumentList;
var color;
double width;
double height;
var alignment = Alignment.center;
var padding = EdgeInsets.zero;
var margin = EdgeInsets.zero;
var constraints;
var decoration;
var foregroundDecoration;
Widget child;
for (var arg in argumentList) {
if (arg.isNamedExpression) {
var expression = arg.asNamedExpression.expression;
switch (arg.asNamedExpression.label) {
case 'color':
color = parseColor(expression);
break;
case 'width':
width = parseBaseLiteral(expression)?.toDouble();
break;
case 'height':
height = parseBaseLiteral(expression)?.toDouble();
break;
case 'alignment':
alignment = parseAlignment(expression);
break;
case 'padding':
padding = parseEdgeInsets(expression);
break;
case 'margin':
margin = parseEdgeInsets(expression);
break;
case 'constraints':
constraints = parseBoxConstraints(expression);
break;
case 'decoration':
decoration = parseBoxDecoration(expression);
break;
case 'foregroundDecoration':
foregroundDecoration = parseBoxDecoration(expression);
break;
case 'child':
child =
FHWidgetBuilderFactory.buildWidgetWithExpression(expression);
break;
}
}
}
return Container(
color: color,
width: width,
height: height,
alignment: alignment,
padding: padding,
margin: margin,
constraints: constraints,
decoration: decoration,
foregroundDecoration: foregroundDecoration,
child: child,
);
}
@override
String get widgetName => 'Container';
}
只要解析常用的属性就好,基本能满足大部分的需求。
2.3 渲染
解析完成后就可以通过调用setState让界面重新渲染我们解析后的Widget,这就需要提供一个父Widget,作为支持我们动态渲染的容器,我简单做了一个实现:
class AstStatefulWidget extends StatefulWidget {
final Map ast;
AstStatefulWidget(this.ast);
@override
_AstStatefulWidgetState createState() => _AstStatefulWidgetState();
}
class _AstStatefulWidgetState extends State<AstStatefulWidget> {
Widget _bodyWidget;
static const TAG = "AstStatefulWidgetState";
Future _parseRootAst(Map rootAst) async {
var rootExpression = Expression.fromAst(rootAst);
if (rootExpression.isProgram) {
var bodyList = rootExpression.asProgram.body;
if ((bodyList?.length ?? 0) == 2) {
var stateClass = bodyList[1].asClassDeclaration;
if (stateClass.superClause == 'State') {
var stateBodyList = stateClass.body;
for (var bodyNode in stateBodyList) {
if (bodyNode.isMethodDeclaration) {
switch (bodyNode.asMethodDeclaration.name) {
case 'build':
var buildBodyReturn = bodyNode.asMethodDeclaration.body.body;
if (buildBodyReturn.isNotEmpty &&
buildBodyReturn[0].isReturnStatement &&
buildBodyReturn[0].asReturnStatement.argument != null) {
setState(() {
_bodyWidget =
FHWidgetBuilderFactory.buildWidgetWithExpression(
buildBodyReturn[0].asReturnStatement.argument);
});
}
break;
case 'initState':
break;
case 'didUpdateWidget':
break;
case 'dispose':
break;
}
} else if (bodyNode.isFieldDeclaration) {
//TODO state field declaration
}
}
}
}
}
return Future.value();
}
@override
void initState() {
_parseRootAst(widget.ast);
super.initState();
}
@override
void dispose() {
super.dispose();
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Material(
color: Colors.white,
child: _bodyWidget == null
? Center(
child: SizedBox.fromSize(
size: Size.square(30), child: CircularProgressIndicator()),
)
: _bodyWidget,
);
}
}
这个AstStatefulWidget接收Ast数据作为参数,就可以渲染Ast中描述的UI。
3. 运行效果
整个Widget解析的原理还是比较简单的,完整的代码详见文末提供的Git地址,我们看看最后实现的效果:
完整代码Git 地址:DynamicFlutter