上一篇介绍了如何自定义starter
这一篇来揭开starter的神秘面纱。其实starter的原理就是Spring Boot自动装配的原理。 Auto-configuration
在SpringBoot官方文档的第四章“6. Using the @SpringBootApplication Annotation”一节中,对@SpringBootApplication与@EnableAutoConfiguration做出了解释:
A single @SpringBootApplication annotation can be used to enable those three features, that is:
@EnableAutoConfiguration: enable Spring Boot’s auto-configuration mechanism(启动SpringBoot的自动配置)
@ComponentScan: enable @Component scan on the package where the application is located (see the best practices)
@ConfigurationPropertiesScan: enable @ConfigurationProperties scan on the package where the application is located (see the best practices)
@Configuration: allow to register extra beans in the context or import additional configuration classes
理解 @EnableAutoConfiguration
从官网可以知道,@EnableAutoConfiguration是启动自动配置的关键。
直接查看源码,这里我的SpringBoot版本是2.2.6
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@AutoConfigurationPackage
@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)
public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration {
String ENABLED_OVERRIDE_PROPERTY = "spring.boot.enableautoconfiguration";
/**
* Exclude specific auto-configuration classes such that they will never be applied.
* @return the classes to exclude
*/
Class<?>[] exclude() default {};
/**
* Exclude specific auto-configuration class names such that they will never be
* applied.
* @return the class names to exclude
* @since 1.3.0
*/
String[] excludeName() default {};
}
这里可以看到该注解有两个属性,分别是exclude()与excludeName(),根据注解的意思可以知道,这里是提供两种方式来排除自动加载的类。除此之外SpringBoot还提供了一种外部化配置spring.autoconfigure.exclude来排除不想加载的类。
该注解如何排除排除组件下面会继续分析。
这里看到了@Import注解,该注解的意思是导入一个配置类。在org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassParser#processImports方法中实现,以后会专门写篇文章来讲解。其中AutoConfigurationImportSelector实现了DeferredImportSelector接口,而DeferredImportSelector又继承ImportSelector。所以关键逻辑在selectImports(AnnotationMetadata)方法中实现:
public class AutoConfigurationImportSelector implements DeferredImportSelector, BeanClassLoaderAware,
ResourceLoaderAware, BeanFactoryAware, EnvironmentAware, Ordered {
@Override
···
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
if (!isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) {
return NO_IMPORTS;
}
// 1 加载元信息
AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata = AutoConfigurationMetadataLoader
.loadMetadata(this.beanClassLoader);
// 2 核心代码,下面重点分析
AutoConfigurationEntry autoConfigurationEntry = getAutoConfigurationEntry(autoConfigurationMetadata,
annotationMetadata);
return StringUtils.toStringArray(autoConfigurationEntry.getConfigurations());
}
protected AutoConfigurationEntry getAutoConfigurationEntry(AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata,
AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
if (!isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) {
return EMPTY_ENTRY;
}
// 2.1 获取标注@EnableAutoConfiguration类的元信息
AnnotationAttributes attributes = getAttributes(annotationMetadata);
// 2.2
List<String> configurations = getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes);
// 2.3 放入LinkedHashSet去重
configurations = removeDuplicates(configurations);
// 2.4 排除自动装配类
Set<String> exclusions = getExclusions(annotationMetadata, attributes);
// 2.5
checkExcludedClasses(configurations, exclusions);
// 2.6
configurations.removeAll(exclusions);
// 2.7
configurations = filter(configurations, autoConfigurationMetadata);
// 2.8
fireAutoConfigurationImportEvents(configurations, exclusions);
return new AutoConfigurationEntry(configurations, exclusions);
}
···
}
1.加载元信息
final class AutoConfigurationMetadataLoader {
protected static final String PATH = "META-INF/spring-autoconfigure-metadata.properties";
static AutoConfigurationMetadata loadMetadata(ClassLoader classLoader) {
return loadMetadata(classLoader, PATH);
}
static AutoConfigurationMetadata loadMetadata(ClassLoader classLoader, String path) {
try {
Enumeration<URL> urls = (classLoader != null) ? classLoader.getResources(path)
: ClassLoader.getSystemResources(path);
Properties properties = new Properties();
while (urls.hasMoreElements()) {
properties.putAll(PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(new UrlResource(urls.nextElement())));
}
return loadMetadata(properties);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load @ConditionalOnClass location [" + path + "]", ex);
}
}
···
}
AutoConfigurationMetadata是自动装配元信息接口,信息配置在META-INF/spring-autoconfigure-metadata.properties中。
2.1 获取标注@EnableAutoConfiguration类的元信息
protected AnnotationAttributes getAttributes(AnnotationMetadata metadata) {
String name = getAnnotationClass().getName();
AnnotationAttributes attributes = AnnotationAttributes.fromMap(metadata.getAnnotationAttributes(name, true));
Assert.notNull(attributes, () -> "No auto-configuration attributes found. Is " + metadata.getClassName()
+ " annotated with " + ClassUtils.getShortName(name) + "?");
return attributes;
}
protected Class<?> getAnnotationClass() {
return EnableAutoConfiguration.class;
}
2.2 读取META-INF/spring.factories下的资源
protected Class<?> getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass() {
return EnableAutoConfiguration.class;
}
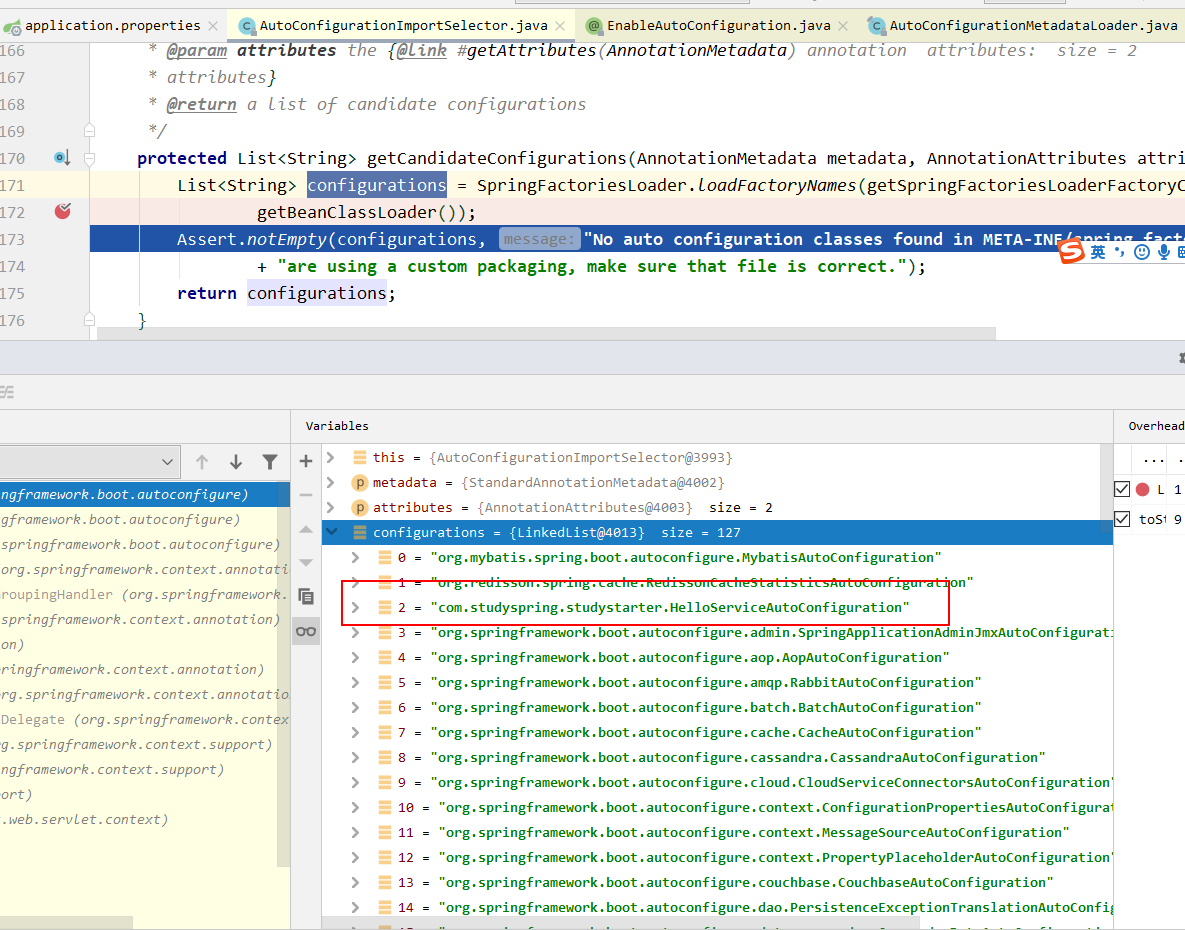
protected List<String> getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata, AnnotationAttributes attributes) {
List<String> configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(),
getBeanClassLoader());
Assert.notEmpty(configurations, "No auto configuration classes found in META-INF/spring.factories. If you "
+ "are using a custom packaging, make sure that file is correct.");
return configurations;
}
该方法实际执行的是SpringFactoriesLoader#loadFactoryNames(Class,ClassLoader)方法:
public static final String FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION = "META-INF/spring.factories";
public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryType, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
String factoryTypeName = factoryType.getName();
return loadSpringFactories(classLoader).getOrDefault(factoryTypeName, Collections.emptyList());
}
private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
MultiValueMap<String, String> result = cache.get(classLoader);
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
try {
Enumeration<URL> urls = (classLoader != null ?
classLoader.getResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION) :
ClassLoader.getSystemResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION));
result = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>();
while (urls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = urls.nextElement();
UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(url);
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
for (Map.Entry<?, ?> entry : properties.entrySet()) {
String factoryTypeName = ((String) entry.getKey()).trim();
for (String factoryImplementationName : StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String) entry.getValue())) {
result.add(factoryTypeName, factoryImplementationName.trim());
}
}
}
cache.put(classLoader, result);
return result;
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load factories from location [" +
FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION + "]", ex);
}
}
SpringFactoriesLoader是Spring的工厂机制的加载器,loadFactoryNames(Class,ClassLoader)加载原理如下:SpringFactoriesLoader是Spring的工厂机制的加载器,loadFactoryNames(Class,ClassLoader)加载原理如下:
- 搜索ClassLoader下面所有的
META-INF/spring.factories资源。 - 将一个或者多个
META-INF/spring.factories资源内容作为Properties文件读取,合并为一个key为接口的全类名,Value是实现类全类名列表的Map,作为loadSpringFactories(classLoader)方法的返回值。 参考META-INF/spring.factories - 再从上一步返回的Map中查找并返回方法指定类名所映射的实现类全类名列表。
2.3 放入LinkedHashSet去重
protected final <T> List<T> removeDuplicates(List<T> list) {
return new ArrayList<>(new LinkedHashSet<>(list));
}
2.4 排除自动装配组件
protected Set<String> getExclusions(AnnotationMetadata metadata, AnnotationAttributes attributes) {
Set<String> excluded = new LinkedHashSet<>();
excluded.addAll(asList(attributes, "exclude"));
excluded.addAll(Arrays.asList(attributes.getStringArray("excludeName")));
excluded.addAll(getExcludeAutoConfigurationsProperty());
return excluded;
}
// 从外部化配置中找到spring.autoconfigure.exclude配置值
private List<String> getExcludeAutoConfigurationsProperty() {
if (getEnvironment() instanceof ConfigurableEnvironment) {
Binder binder = Binder.get(getEnvironment());
return binder.bind(PROPERTY_NAME_AUTOCONFIGURE_EXCLUDE, String[].class).map(Arrays::asList)
.orElse(Collections.emptyList());
}
String[] excludes = getEnvironment().getProperty(PROPERTY_NAME_AUTOCONFIGURE_EXCLUDE, String[].class);
return (excludes != null) ? Arrays.asList(excludes) : Collections.emptyList();
}
将标注@EnableAutoConfiguration配置类注解属性exclude和excludeName,以及spring.autoconfigure.exclude配置值累加到排除集合excluded。
2.5 检查排除类名集合是否合法
private void checkExcludedClasses(List<String> configurations, Set<String> exclusions) {
List<String> invalidExcludes = new ArrayList<>(exclusions.size());
for (String exclusion : exclusions) {
if (ClassUtils.isPresent(exclusion, getClass().getClassLoader()) && !configurations.contains(exclusion)) {
invalidExcludes.add(exclusion);
}
}
if (!invalidExcludes.isEmpty()) {
// 触发排除类非法异常
handleInvalidExcludes(invalidExcludes);
}
}
当排除类存在于当前的classLoader且不在自动候选名单configurations中时,handleInvalidExcludes(List)被执行,触发排除类非法异常
2.6 将排除类集exclusions合从候选名单configurations中移除
configurations.removeAll(exclusions);
2.7 配合autoConfigurationMetadata对象执行过滤操作
private List<String> filter(List<String> configurations, AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata) {
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
String[] candidates = StringUtils.toStringArray(configurations);
boolean[] skip = new boolean[candidates.length];
boolean skipped = false;
for (AutoConfigurationImportFilter filter : getAutoConfigurationImportFilters()) {
invokeAwareMethods(filter);
boolean[] match = filter.match(candidates, autoConfigurationMetadata);
for (int i = 0; i < match.length; i++) {
if (!match[i]) {
skip[i] = true;
candidates[i] = null;
skipped = true;
}
}
}
if (!skipped) {
return configurations;
}
List<String> result = new ArrayList<>(candidates.length);
for (int i = 0; i < candidates.length; i++) {
if (!skip[i]) {
result.add(candidates[i]);
}
}
···
return new ArrayList<>(result);
}
protected List<AutoConfigurationImportFilter> getAutoConfigurationImportFilters() {
return SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactories(AutoConfigurationImportFilter.class, this.beanClassLoader);
}
其中AutoConfigurationImportFilter对象集合同样被SpringFactoriesLoader加载,所以在META-INF/spring.factories中查找AutoConfigurationImportFilter,发现有三处声明,即在org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-autoconfigure中:
# Auto Configuration Import Filters
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigurationImportFilter=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.OnBeanCondition,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.OnClassCondition,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.OnWebApplicationCondition
不过此处的SpringFactoriesLoader#loadFactories(Class,ClassLoader)方法与之前的loadFactoryNames(Class,ClassLoader)不同,前者调用了后者
public static <T> List<T> loadFactories(Class<T> factoryType, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
Assert.notNull(factoryType, "'factoryType' must not be null");
ClassLoader classLoaderToUse = classLoader;
if (classLoaderToUse == null) {
classLoaderToUse = SpringFactoriesLoader.class.getClassLoader();
}
List<String> factoryImplementationNames = loadFactoryNames(factoryType, classLoaderToUse);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Loaded [" + factoryType.getName() + "] names: " + factoryImplementationNames);
}
List<T> result = new ArrayList<>(factoryImplementationNames.size());
for (String factoryImplementationName : factoryImplementationNames) {
// instantiateFactory()实例化方法
result.add(instantiateFactory(factoryImplementationName, factoryType, classLoaderToUse));
}
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(result);
return result;
}
区别是前者获取工厂类名单factoriesName后,逐一进行实例化。换言之,AutoConfigurationImportSelector#filter(List<String>,AutoConfigurationMetadata)方法实际上是过滤META-INF/spring.factories资源中那些当前ClassLoader不存在的Class。
2.8 自动装配事件
private void fireAutoConfigurationImportEvents(List<String> configurations, Set<String> exclusions) {
List<AutoConfigurationImportListener> listeners = getAutoConfigurationImportListeners();
if (!listeners.isEmpty()) {
AutoConfigurationImportEvent event = new AutoConfigurationImportEvent(this, configurations, exclusions);
for (AutoConfigurationImportListener listener : listeners) {
invokeAwareMethods(listener);
listener.onAutoConfigurationImportEvent(event);
}
}
}
protected List<AutoConfigurationImportListener> getAutoConfigurationImportListeners() {
return SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactories(AutoConfigurationImportListener.class, this.beanClassLoader);
}
AutoConfigurationImportListener接口与传统的Spring ApplicationListener不同,ApplicationListener与Spring应用上下文紧密相关,监听ApplicationEvent。Spring事件下次单独写一篇文章。
而AutoConfigurationImportListener属于自定义监听器,仅监听AutoConfigurationImportEvent事件,其实例被SpringFactoriesLoader加载,其中ConditionEvaluationReportAutoConfigurationImportListener就是内建实现,用于记录自动装配的条件评估详情,
配置在META-INF/spring.factories资源中:
# Auto Configuration Import Listeners
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigurationImportListener=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionEvaluationReportAutoConfigurationImportListener
参考书籍:《Spring Boot编程思想》